MidtermReview2012
... 2. Which state of matter tends to occupy the largest amount of space? The smallest? In other words, which state of matter is the densest? Which is the least dense? ...
... 2. Which state of matter tends to occupy the largest amount of space? The smallest? In other words, which state of matter is the densest? Which is the least dense? ...
Strong Nuclear Interaction
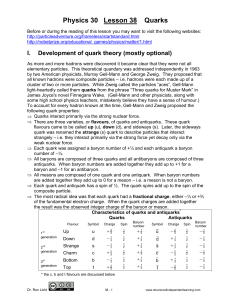
... The Strong Interaction bears the name for good reason: it’s about 100x as strong as the electromagnetic interaction that’s responsible for holding atoms together. Were quarks not confined into Strong Interaction neutral clumps, chemistry would be dominated by the Strong Nuclear Interaction. Chemical ...
... The Strong Interaction bears the name for good reason: it’s about 100x as strong as the electromagnetic interaction that’s responsible for holding atoms together. Were quarks not confined into Strong Interaction neutral clumps, chemistry would be dominated by the Strong Nuclear Interaction. Chemical ...
Final Exam - Seattle Central College
... • Law of Conservation of Energy - Know 6 forms of energy: heat, chemical, light, electrical, mechanical, and nuclear ...
... • Law of Conservation of Energy - Know 6 forms of energy: heat, chemical, light, electrical, mechanical, and nuclear ...
Chemistry 201 - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State University
... There are six significant figures in this measured quantity There are five significant figures in this measured quantity There are four significant figures in this measured quantity There are three significant figures in this measured quantity There are two significant figures in this measured quant ...
... There are six significant figures in this measured quantity There are five significant figures in this measured quantity There are four significant figures in this measured quantity There are three significant figures in this measured quantity There are two significant figures in this measured quant ...
Chapter 46
... Another quark was needed to account for some discrepancies between predictions of the model and experimental results A new quantum number, C, was assigned to the property of charm Charm would be conserved in strong and electromagnetic interactions, but not in weak interactions In 1974, a new meson, ...
... Another quark was needed to account for some discrepancies between predictions of the model and experimental results A new quantum number, C, was assigned to the property of charm Charm would be conserved in strong and electromagnetic interactions, but not in weak interactions In 1974, a new meson, ...
Isotope, radioactivity and half life worksheet Which type of ionizing
... of the food. Isotopes like cobalt-60 are used. Since ionizing radiation must travel a certain distance and penetrate the food completely, which type of radiation would be the most appropriate for this application? Explain your answer. ...
... of the food. Isotopes like cobalt-60 are used. Since ionizing radiation must travel a certain distance and penetrate the food completely, which type of radiation would be the most appropriate for this application? Explain your answer. ...
Sample Exercise 2.1 Illustrating the Size of an Atom
... (a) The number of protons (22) is the atomic number of the element. By referring to a periodic table or list of elements, we see that the element with atomic number 22 is titanium (Ti). The mass number of this isotope of titanium is 22 + 26 = 48 (the sum of the protons and neutrons). Because the ion ...
... (a) The number of protons (22) is the atomic number of the element. By referring to a periodic table or list of elements, we see that the element with atomic number 22 is titanium (Ti). The mass number of this isotope of titanium is 22 + 26 = 48 (the sum of the protons and neutrons). Because the ion ...
No Slide Title - FSU High Energy Physics
... electrons “multiplied” in several (6 to 14) stages by ionization and acceleration in high electric field between “dynodes”, with gain 104 to 1010 photocathode and dynodes made from material with low ionization energy; photocathodes: thin layer of semiconductor made e.g. from Sb (antimony) plus one ...
... electrons “multiplied” in several (6 to 14) stages by ionization and acceleration in high electric field between “dynodes”, with gain 104 to 1010 photocathode and dynodes made from material with low ionization energy; photocathodes: thin layer of semiconductor made e.g. from Sb (antimony) plus one ...
8th Grade Science: 1st Six Weeks At-A
... locations of protons and neutrons in the nucleus and electrons in the electron cloud. Ⓡ SCI.8.5B Identify that protons determine an element’s identity, and valence electrons determine its chemical properties including reactivity. Ⓡ SCI.8.5C Interpret the arrangement of the Periodic Table including g ...
... locations of protons and neutrons in the nucleus and electrons in the electron cloud. Ⓡ SCI.8.5B Identify that protons determine an element’s identity, and valence electrons determine its chemical properties including reactivity. Ⓡ SCI.8.5C Interpret the arrangement of the Periodic Table including g ...
Ch02-sample-and-practice-set-2
... (a) The number of protons (22) is the atomic number of the element. By referring to a periodic table or list of elements, we see that the element with atomic number 22 is titanium (Ti). The mass number of this isotope of titanium is 22 + 26 = 48 (the sum of the protons and neutrons). Because the ion ...
... (a) The number of protons (22) is the atomic number of the element. By referring to a periodic table or list of elements, we see that the element with atomic number 22 is titanium (Ti). The mass number of this isotope of titanium is 22 + 26 = 48 (the sum of the protons and neutrons). Because the ion ...
3 - Greene County ESC
... number of protons may or may not have the same mass. Thos with different masses (different numbers of neutrons) are called isotopes. 2. Illustrate that atoms with the same number of positively charged protons and negatively charged electrons are electrically neutral. 4. Show that when elements are l ...
... number of protons may or may not have the same mass. Thos with different masses (different numbers of neutrons) are called isotopes. 2. Illustrate that atoms with the same number of positively charged protons and negatively charged electrons are electrically neutral. 4. Show that when elements are l ...
Understanding Nothing - University of Southampton
... For massless particles these are different sorts of particles! (The weak nuclear force only acts on left-handed spinning particles!) Why do they get tied up into massive particles? The strong nuclear force is the answer for quarks…. ...
... For massless particles these are different sorts of particles! (The weak nuclear force only acts on left-handed spinning particles!) Why do they get tied up into massive particles? The strong nuclear force is the answer for quarks…. ...
Document
... the operatorial method of Tomonaga and Schwinger, making commonplace the use of Feynman diagrams for the description of fundamental interactions. A Feynman Diagram is a pictorial representation of a fundamental physical process that corresponds in a rigorous way to a mathematical expression. The pic ...
... the operatorial method of Tomonaga and Schwinger, making commonplace the use of Feynman diagrams for the description of fundamental interactions. A Feynman Diagram is a pictorial representation of a fundamental physical process that corresponds in a rigorous way to a mathematical expression. The pic ...
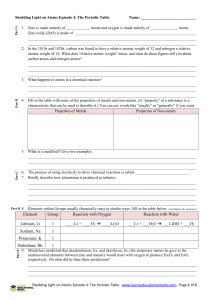
Element Group Reaction with Oxygen Reaction with Water Lithium
... Zinc oxide (ZnO) is made of ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 2. In the 1810s and 1820s, carbon w ...
... Zinc oxide (ZnO) is made of ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 2. In the 1810s and 1820s, carbon w ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.