Chapter 21 Nuclear Chemistry
... of the sample that is due to 14C is measured to be 11.6 disintegrations per second. The activity of a carbon sample of equal mass from fresh wood is 15.2 disintegrations per second. The half-life of 14C is 5715 yr. What is the age of the archeological sample? Nuclear Chemistry ...
... of the sample that is due to 14C is measured to be 11.6 disintegrations per second. The activity of a carbon sample of equal mass from fresh wood is 15.2 disintegrations per second. The half-life of 14C is 5715 yr. What is the age of the archeological sample? Nuclear Chemistry ...
LIST OF TOPICS COVERED DURING THIS COURSE
... The following should serve as a checklist for your notebook. The topics below include all topics that have been covered this semester and are testable on your final exam. These topics should be studied from a variety of source including inclass notes, homework questions, lab questions, assignments, ...
... The following should serve as a checklist for your notebook. The topics below include all topics that have been covered this semester and are testable on your final exam. These topics should be studied from a variety of source including inclass notes, homework questions, lab questions, assignments, ...
Name
... 4. In a high-energy collision between a cosmic-ray particle and a particle near the top of the earth’s atmosphere, 120 km above sea level, a pion is created. The pion has a total energy of 1.35 X 105 MeV and is traveling vertically downward. In the pion’s rest frame, the pion decays 35.0 ns after i ...
... 4. In a high-energy collision between a cosmic-ray particle and a particle near the top of the earth’s atmosphere, 120 km above sea level, a pion is created. The pion has a total energy of 1.35 X 105 MeV and is traveling vertically downward. In the pion’s rest frame, the pion decays 35.0 ns after i ...
1.1. Atomic structure
... simple substances, and we ought never to suppose them compounded until experiment and observation have proved them to be so. In sum, Lavoisier began the modern study of chemistry: he insisted on precise terminology and on precise measurement, and suggested as part of the agenda the classification of ...
... simple substances, and we ought never to suppose them compounded until experiment and observation have proved them to be so. In sum, Lavoisier began the modern study of chemistry: he insisted on precise terminology and on precise measurement, and suggested as part of the agenda the classification of ...
V. Chemical reactions
... b. How many electrons can be found in the first energy level of an atom? 2 c. How many electrons can be found in the second energy level of an atom? 8 d. How can the electron arrangement/configuration be determined for a neutral atom? Determine the number of electrons then arrange from level closest ...
... b. How many electrons can be found in the first energy level of an atom? 2 c. How many electrons can be found in the second energy level of an atom? 8 d. How can the electron arrangement/configuration be determined for a neutral atom? Determine the number of electrons then arrange from level closest ...
All That Matters - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... and the neutron. The proton and neutron are roughly the same size, and the electron is over 1,800 times smaller than either the proton or neutron. These particles were all discovered in the course of research into the nature of the atom, but none of the scientists who found them were actually lookin ...
... and the neutron. The proton and neutron are roughly the same size, and the electron is over 1,800 times smaller than either the proton or neutron. These particles were all discovered in the course of research into the nature of the atom, but none of the scientists who found them were actually lookin ...
Answer key
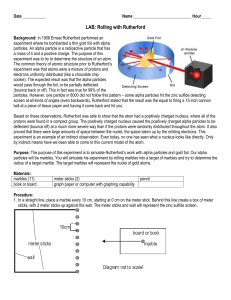
... Rutherford shot alpha particles at a sheet of gold foil. Most of the particles when straight through the foil while a few were deflected. This suggests that the atom is mostly empty space in addition to having a small central core that is positively charged. List the number of protons, neutrons, and ...
... Rutherford shot alpha particles at a sheet of gold foil. Most of the particles when straight through the foil while a few were deflected. This suggests that the atom is mostly empty space in addition to having a small central core that is positively charged. List the number of protons, neutrons, and ...
Chapter 4 – Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms
... o Different _________ __________ will have different numbers and arrangements of ______________. o The energy of the ___________ determines how the electrons are arranged within the energy level. o In order to describe orbitals and the energy of the electrons within them, scientists use ___________ ...
... o Different _________ __________ will have different numbers and arrangements of ______________. o The energy of the ___________ determines how the electrons are arranged within the energy level. o In order to describe orbitals and the energy of the electrons within them, scientists use ___________ ...
File
... Rutherford shot alpha particles at a sheet of gold foil. Most of the particles when straight through the foil while a few were deflected. This suggests that the atom is mostly empty space in addition to having a small central core that is positively charged. List the number of protons, neutrons, and ...
... Rutherford shot alpha particles at a sheet of gold foil. Most of the particles when straight through the foil while a few were deflected. This suggests that the atom is mostly empty space in addition to having a small central core that is positively charged. List the number of protons, neutrons, and ...
Chapter 21 Nuclear Chemistry
... of the sample that is due to 14C is measured to be 11.6 disintegrations per second. The activity of a carbon sample of equal mass from fresh wood is 15.2 disintegrations per second. The half-life of 14C is 5715 yr. What is the age of the archeological sample? Nuclear Chemistry ...
... of the sample that is due to 14C is measured to be 11.6 disintegrations per second. The activity of a carbon sample of equal mass from fresh wood is 15.2 disintegrations per second. The half-life of 14C is 5715 yr. What is the age of the archeological sample? Nuclear Chemistry ...
Chemistry Unit Test Study Guide (2012-2013)
... The pH of a substance can be determined using ____________________ paper Neutral substances have a pH of __________. An example of a common neutral substance is ____________. Acids- Name 3 properties (ex: feel, taste, uses, etc.): 1. _______________ 2. _______________ 3. _____________ a. pH range fo ...
... The pH of a substance can be determined using ____________________ paper Neutral substances have a pH of __________. An example of a common neutral substance is ____________. Acids- Name 3 properties (ex: feel, taste, uses, etc.): 1. _______________ 2. _______________ 3. _____________ a. pH range fo ...
Course Syllabus and Assignment 1
... There will be a weekly homework assignment, with homework collected on Monday of each week. The homework will be graded and returned the same week. Homework counts 30% towards the final grade. A midterm exam at a date suitable for the class will be given. It will also count 30% towards the final gr ...
... There will be a weekly homework assignment, with homework collected on Monday of each week. The homework will be graded and returned the same week. Homework counts 30% towards the final grade. A midterm exam at a date suitable for the class will be given. It will also count 30% towards the final gr ...
Chem 1411 Chapt2
... Radioactivity- Spontaneous emission of radiation, atomic and subatomic particles. X-Rays- High energy light(photons). Gamma Rays(γ)- Light with energy higher than x-rays Alpha Rays(α)- A stream of helium nuclei(24He+2) Beta Rays(β)- A stream of electrons emitted from the nucleus of an atom. Atomic s ...
... Radioactivity- Spontaneous emission of radiation, atomic and subatomic particles. X-Rays- High energy light(photons). Gamma Rays(γ)- Light with energy higher than x-rays Alpha Rays(α)- A stream of helium nuclei(24He+2) Beta Rays(β)- A stream of electrons emitted from the nucleus of an atom. Atomic s ...
Handout
... ball at a piece of tissue paper and having it come back and hit you. Based on these observations, Rutherford was able to show that the atom had a positively charged nucleus, where all of the protons were found in a compact group. The positively charged nucleus caused the positively charged alpha par ...
... ball at a piece of tissue paper and having it come back and hit you. Based on these observations, Rutherford was able to show that the atom had a positively charged nucleus, where all of the protons were found in a compact group. The positively charged nucleus caused the positively charged alpha par ...
acceleration: change in an object`s speed or direction (velocity) over
... earthquake: energy traveling as waves passing through Earth ecosystem: all the living populations in an area along with the nonliving parts of that environment electromagnet: a magnet made of a coil of wire wrapped around a magnetized core electromagnetic wave: form of energy that can travel through ...
... earthquake: energy traveling as waves passing through Earth ecosystem: all the living populations in an area along with the nonliving parts of that environment electromagnet: a magnet made of a coil of wire wrapped around a magnetized core electromagnetic wave: form of energy that can travel through ...
Potential Energy of a system of charges
... Size of nucleus must be smaller than this -- VERY compact compared to size of atom (~10-11 m) 110 fm is small by atomic standards, but not by nuclear standards ...
... Size of nucleus must be smaller than this -- VERY compact compared to size of atom (~10-11 m) 110 fm is small by atomic standards, but not by nuclear standards ...
Nuclear Energy
... • The products of nuclear fission reactions are radioactive, but the energy released from these reactions is less harmful to the environment than the use of fossil fuels. • The products are intensely radioactive and must be treated and/or stored. ...
... • The products of nuclear fission reactions are radioactive, but the energy released from these reactions is less harmful to the environment than the use of fossil fuels. • The products are intensely radioactive and must be treated and/or stored. ...
Matter
... – Collection of the combination same type of atom elements and/or – Cannot be compounds or decomposed both. • Compound • USUALLY – 2 or more different heterogeneous atoms chemically bonded together. ...
... – Collection of the combination same type of atom elements and/or – Cannot be compounds or decomposed both. • Compound • USUALLY – 2 or more different heterogeneous atoms chemically bonded together. ...
UIC Colloquium on CMS - University of Colorado Boulder
... are needed to make up normal matter, there are two other pairs for a total of 6. (Nobody knows why this is so.) This 3 family structure extends to particles like electrons. There are 2 particles like the electron plus a set of 3 neutrinos. ...
... are needed to make up normal matter, there are two other pairs for a total of 6. (Nobody knows why this is so.) This 3 family structure extends to particles like electrons. There are 2 particles like the electron plus a set of 3 neutrinos. ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.