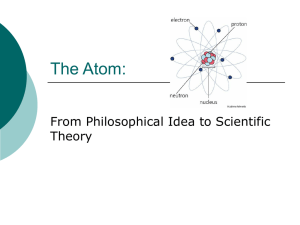
People asked the question – for thousands of years: What is matter
... Millikan determined the charge of an electron. He used an apparatus, as shown below, to produce tiny oil droplets. Very fine oil droplets were sprayed into a chamber and then were allowed to fall between two charged plates where they were then observed, visually. The air inside the chamber was expos ...
... Millikan determined the charge of an electron. He used an apparatus, as shown below, to produce tiny oil droplets. Very fine oil droplets were sprayed into a chamber and then were allowed to fall between two charged plates where they were then observed, visually. The air inside the chamber was expos ...
The Atom - Williamstown Independent Schools
... are composed of the same two elements then ratios of the masses of the second element combined with a certain mass of the first element is always a ratio of small whole numbers. ...
... are composed of the same two elements then ratios of the masses of the second element combined with a certain mass of the first element is always a ratio of small whole numbers. ...
Lecture 8a
... • A nuclear spin of I, when interacting with the electronic spin, perturbs the energy of the system in such a way that each electronic state is further split into 2I+1 sublevels, as further shown above • For n nuclei, there can be 2nI+1 resonances (lines) • Since the magneton is inversely related to ...
... • A nuclear spin of I, when interacting with the electronic spin, perturbs the energy of the system in such a way that each electronic state is further split into 2I+1 sublevels, as further shown above • For n nuclei, there can be 2nI+1 resonances (lines) • Since the magneton is inversely related to ...
SCSD Physical Science 9th - Shenandoah Community Schools
... That have measurable properties Mass (I,D,M) Electrical charge (I,D,M) o Each atom has a positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons (I, D, M) • Understand the composition and size of atomic nucleus (I,D,M) o Is composed of protons and neutrons (I,D,M) More massive than ele ...
... That have measurable properties Mass (I,D,M) Electrical charge (I,D,M) o Each atom has a positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons (I, D, M) • Understand the composition and size of atomic nucleus (I,D,M) o Is composed of protons and neutrons (I,D,M) More massive than ele ...
Announcements
... •Don’t forget about your project. Presentations will be Monday May 1 at 3:20pm. A written paper is also due at the same time. Exam 4 is after the presentations ...
... •Don’t forget about your project. Presentations will be Monday May 1 at 3:20pm. A written paper is also due at the same time. Exam 4 is after the presentations ...
Quantum mechanics is the theory that we use to describe the
... This includes all electric and magnetic forces which arise from the motion of charged particles, and also from stationary electric charges. This force is responsible for most of the phenomena we see around us, such as light, friction, and the structure of elements and molecules. This force can be bo ...
... This includes all electric and magnetic forces which arise from the motion of charged particles, and also from stationary electric charges. This force is responsible for most of the phenomena we see around us, such as light, friction, and the structure of elements and molecules. This force can be bo ...
Student Expectation
... Key Concept 2: Electrons are located outside of the nucleus and arranged by energy levels in the electron cloud. There are a certain number of electrons that each energy level can hold. Key Concept 3: Electrons located in the outermost shell of the electron cloud are called “valence electrons” and h ...
... Key Concept 2: Electrons are located outside of the nucleus and arranged by energy levels in the electron cloud. There are a certain number of electrons that each energy level can hold. Key Concept 3: Electrons located in the outermost shell of the electron cloud are called “valence electrons” and h ...
The format of this test is MULTIPLE CHOICE
... 2. All matter is made up of tiny particles called __atoms___. 3. When a solid becomes a liquid, _melting_____ occurs. 4. An _element_____ is made up of only one type of atom. 5. __freezing___ changes a liquid into a solid. 6. A mixture is made up of 2 or more substances that are physically combined ...
... 2. All matter is made up of tiny particles called __atoms___. 3. When a solid becomes a liquid, _melting_____ occurs. 4. An _element_____ is made up of only one type of atom. 5. __freezing___ changes a liquid into a solid. 6. A mixture is made up of 2 or more substances that are physically combined ...
The Periodic table and subatomic particles
... Taste bitter and feel slippery (*NOTE: do not taste or touch in the lab) Have a pH less than 7 React with active metals to produce H2(g) ...
... Taste bitter and feel slippery (*NOTE: do not taste or touch in the lab) Have a pH less than 7 React with active metals to produce H2(g) ...
The Nobel Prize in Physics 2004
... for calculating such strong interaction effects. The situation seemed to be even worse for higher energies; if the beta function is positive (the way the coupling constant changes with energy) the interaction will be even stronger and the calculations become increasingly absurd. The German theoretic ...
... for calculating such strong interaction effects. The situation seemed to be even worse for higher energies; if the beta function is positive (the way the coupling constant changes with energy) the interaction will be even stronger and the calculations become increasingly absurd. The German theoretic ...
File - Mr. Stewart`s Physical Science
... Explain that the law of definite proportions allows for predictions of reaction amounts. P.12.A.8 Students know most elements have two or more isotopes, some of which have practical applications. I/S. Know that isotopes of an element have different numbers of neutrons and the same number of prot ...
... Explain that the law of definite proportions allows for predictions of reaction amounts. P.12.A.8 Students know most elements have two or more isotopes, some of which have practical applications. I/S. Know that isotopes of an element have different numbers of neutrons and the same number of prot ...
I can
... different states of matter (e.g., gas dissolved in liquid). Items assessing periodic trends must be at the conceptual level. Items will not assess valence electrons or electron configurations. Items that assess mixtures and solutions may include components in different states of matter (e.g., ...
... different states of matter (e.g., gas dissolved in liquid). Items assessing periodic trends must be at the conceptual level. Items will not assess valence electrons or electron configurations. Items that assess mixtures and solutions may include components in different states of matter (e.g., ...
Characteristics of Waves
... There are 3 basic rules, named after the scientists that discovered them, that govern the filling of these orbitals with electrons… ...
... There are 3 basic rules, named after the scientists that discovered them, that govern the filling of these orbitals with electrons… ...
Early Atomic Models
... caused deflection of the beam. This was eventually accomplished by J.J. Thomson. The rays were believed to be streams of particles. Thomson named them electrons and changed the model of the atom. ...
... caused deflection of the beam. This was eventually accomplished by J.J. Thomson. The rays were believed to be streams of particles. Thomson named them electrons and changed the model of the atom. ...
Document
... (d) It emits energy while moving in orbits Solution An electron does not emit energy while moving in orbit. This is so because if it would have done that it would have eventually fallen into the nucleus and the atom would have collapsed. Hence, answer is (d). ...
... (d) It emits energy while moving in orbits Solution An electron does not emit energy while moving in orbit. This is so because if it would have done that it would have eventually fallen into the nucleus and the atom would have collapsed. Hence, answer is (d). ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.