Chapter 5 Notes: The Structure of Matter
... Shows the exact number of atoms of each element Subscripts (written below) = how many atoms of the element ...
... Shows the exact number of atoms of each element Subscripts (written below) = how many atoms of the element ...
1996 AP Physics B Free-Response
... flowing through it, but in which the current from the battery is as small as possible. b. Using all of these components, draw a circuit diagram in which each resistor has nonzero current flowing through it, but in which the current from the battery is as large as possible (without short circuiting t ...
... flowing through it, but in which the current from the battery is as small as possible. b. Using all of these components, draw a circuit diagram in which each resistor has nonzero current flowing through it, but in which the current from the battery is as large as possible (without short circuiting t ...
The Chemical Context of Life by Dr. Ty C.M. Hoffman
... represent energy levels. The columns are called groups. Elements within groups have similar properties to each other. In the abbreviated periodic table shown in the slide, energy levels are depicted as cir ...
... represent energy levels. The columns are called groups. Elements within groups have similar properties to each other. In the abbreviated periodic table shown in the slide, energy levels are depicted as cir ...
Introduction to the physics of light
... A continuum spectrum results when the gas pressures are higher, so that lines are broadened by collisions between the atoms until they are smeared into a continuum. An absorption spectrum occurs when light passes through a cold, dilute gas and atoms in the gas absorb at characteristic frequencies. W ...
... A continuum spectrum results when the gas pressures are higher, so that lines are broadened by collisions between the atoms until they are smeared into a continuum. An absorption spectrum occurs when light passes through a cold, dilute gas and atoms in the gas absorb at characteristic frequencies. W ...
MIDTERM EXAM – JANUARY, 2003
... 76. The alkali metals and alkaline earth metals occupy the ______________ block of the periodic table 77. The name of the group which contains fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine is 78. When they react chemically, the halogens (Group VII or 17) change in what way? Naming, Bonding and W ...
... 76. The alkali metals and alkaline earth metals occupy the ______________ block of the periodic table 77. The name of the group which contains fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine is 78. When they react chemically, the halogens (Group VII or 17) change in what way? Naming, Bonding and W ...
Particles and Waves booklet 1 Teacher (3.6MB Word)
... deflected (A and B). The large deflections at C and D suggest that the nucleus is also positively charged and has a large mass. When the neutron was discovered in 1932 it explained how isotopes could exist. The standard model ...
... deflected (A and B). The large deflections at C and D suggest that the nucleus is also positively charged and has a large mass. When the neutron was discovered in 1932 it explained how isotopes could exist. The standard model ...
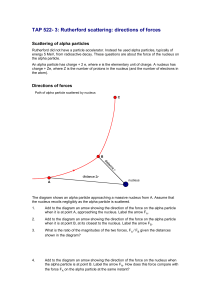
TAP 522- 3: Rutherford scattering: directions of forces
... TAP 522- 3: Rutherford scattering: directions of forces Scattering of alpha particles Rutherford did not have a particle accelerator. Instead he used alpha particles, typically of energy 5 MeV, from radioactive decay. These questions are about the force of the nucleus on the alpha particle. An alpha ...
... TAP 522- 3: Rutherford scattering: directions of forces Scattering of alpha particles Rutherford did not have a particle accelerator. Instead he used alpha particles, typically of energy 5 MeV, from radioactive decay. These questions are about the force of the nucleus on the alpha particle. An alpha ...
ionization energies
... notice patterns in the chemical properties of certain elements. • Consider the three metals Li, Na, and K • All 3 metals are soft • All 3 metals are less dense than water • All 3 metals have similar appearance and low melting points • The most interesting feature is that all 3 metals react with the ...
... notice patterns in the chemical properties of certain elements. • Consider the three metals Li, Na, and K • All 3 metals are soft • All 3 metals are less dense than water • All 3 metals have similar appearance and low melting points • The most interesting feature is that all 3 metals react with the ...
F. The Quantum Atom Theory - River Dell Regional School District
... size, mass, but differ from those of other elements*. 3. Atoms cannot be subdivided or destroyed*. ( supports law of conservation of mass) 4.Atoms combine in small whole number ratios to form compounds. (def comp,Mult prop) 5. Atoms combine, separate, or rearrange in chemical reactions. * Modified i ...
... size, mass, but differ from those of other elements*. 3. Atoms cannot be subdivided or destroyed*. ( supports law of conservation of mass) 4.Atoms combine in small whole number ratios to form compounds. (def comp,Mult prop) 5. Atoms combine, separate, or rearrange in chemical reactions. * Modified i ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.