DN241 - Fast Op Amps Operate Rail-to-Rail on 2.7V
... over series composite topologies is that it does not require onerous attention to compensation and does not reduce the effective bandwidth of the op amps. The tradeoff is that supply current increases, but the designer should remember that a 3VP-P signal requires ±30mA of peak current itself, so a 3 ...
... over series composite topologies is that it does not require onerous attention to compensation and does not reduce the effective bandwidth of the op amps. The tradeoff is that supply current increases, but the designer should remember that a 3VP-P signal requires ±30mA of peak current itself, so a 3 ...
two load line of vdb amplifier
... Class A operation of an amplifier means that the transistor operates in the active region at all times. Fig(a) shows Class A Amplifier. Output is not clipped. Collector current flows for 360° throughout the cycle. Some parameters useful in Class A Amplifiers are Power Gain Output Power, etc. With a ...
... Class A operation of an amplifier means that the transistor operates in the active region at all times. Fig(a) shows Class A Amplifier. Output is not clipped. Collector current flows for 360° throughout the cycle. Some parameters useful in Class A Amplifiers are Power Gain Output Power, etc. With a ...
Section I7: Summary
... Section I7: Summary In this section we’ve looked at how feedback is an important consideration for an effective system designer. It can be used to improve the stability of the system and to decrease the sensitivity of the system to changes in device and/or operational parameters. Topics that should ...
... Section I7: Summary In this section we’ve looked at how feedback is an important consideration for an effective system designer. It can be used to improve the stability of the system and to decrease the sensitivity of the system to changes in device and/or operational parameters. Topics that should ...
Lab 10 - ece.unm.edu
... The common collector amplifier as shown in Figure 10-1 is one of the most useful small-signal amplifier configurations. The same biasing scheme and frequency response approximation technique as used for the common emitter amplifier can also be used for the common collector amplifier. The only change ...
... The common collector amplifier as shown in Figure 10-1 is one of the most useful small-signal amplifier configurations. The same biasing scheme and frequency response approximation technique as used for the common emitter amplifier can also be used for the common collector amplifier. The only change ...
Multi-Transistor Circuits: Current Mirror and Differential Pair Phys 3610/6610 Lab 20 Student: TA:
... Gcm = Vout /Vin of the amplifier when both differential inputs are connected together (common) and are driven by Vin . Task 2: Ground one input and apply a 0 to < 25 mV square wave input signal at 1 kHz to the other input. Measure the circuit gain GG = Vout /Vin to get the common mode rejection rati ...
... Gcm = Vout /Vin of the amplifier when both differential inputs are connected together (common) and are driven by Vin . Task 2: Ground one input and apply a 0 to < 25 mV square wave input signal at 1 kHz to the other input. Measure the circuit gain GG = Vout /Vin to get the common mode rejection rati ...
LINEAR AND SWITCHING AMPLIFIER OVERVIEW
... called Class-A or Class-AB. In this type of amplifier, the output power transistors are always in a midconduction state to one degree or another, depending on sound loudness and speaker impedance. Mid-conduction refers to having both a voltage drop across and a finite current flowing through the tra ...
... called Class-A or Class-AB. In this type of amplifier, the output power transistors are always in a midconduction state to one degree or another, depending on sound loudness and speaker impedance. Mid-conduction refers to having both a voltage drop across and a finite current flowing through the tra ...
AW-120 DUAL MONO FTT BALANCED POWER AMPLIFIER
... The following technical data were measured on randomised test objects and are typical data. All measurements are made with the following equipment: Distortion analyser:Tektronix AA501 Oscilloscope: Tektronix 468 Oscillator: Tektronix SG505 Frequency counter: Rascal 9838 Phase meter: Hewlett Packard ...
... The following technical data were measured on randomised test objects and are typical data. All measurements are made with the following equipment: Distortion analyser:Tektronix AA501 Oscilloscope: Tektronix 468 Oscillator: Tektronix SG505 Frequency counter: Rascal 9838 Phase meter: Hewlett Packard ...
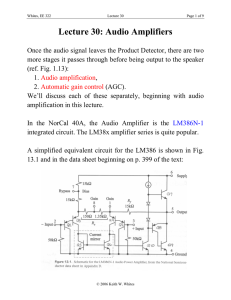
Lecture 30: Audio Amplifiers
... We’ll describe the operation of this circuit beginning near the input. (Note that Sedra and Smith, 5th edition, Sec. 14.8 has a nice description of a closely related circuit: the LM380 IC.) There are three stages of amplification in the LM386: 1. pnp common-emitter amplifiers (Q1 and Q2), 2. pnp dif ...
... We’ll describe the operation of this circuit beginning near the input. (Note that Sedra and Smith, 5th edition, Sec. 14.8 has a nice description of a closely related circuit: the LM380 IC.) There are three stages of amplification in the LM386: 1. pnp common-emitter amplifiers (Q1 and Q2), 2. pnp dif ...
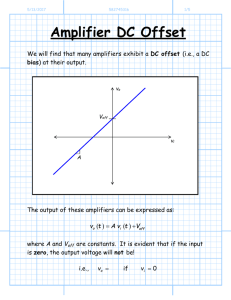
DC Offset
... Thus, the gain of this amplifier when in saturation is zero. A change in the input voltage will result in no change on the output—the output voltage will simply be vo L . Again, the transition into saturation is gradual for real amplifiers. In fact, we will find that many of the amplifiers studie ...
... Thus, the gain of this amplifier when in saturation is zero. A change in the input voltage will result in no change on the output—the output voltage will simply be vo L . Again, the transition into saturation is gradual for real amplifiers. In fact, we will find that many of the amplifiers studie ...
to print
... S60. The SE shares with the normal version the "single - ended structure, class A, only two amplification stages, no global feedback and regulated independent supplies for each channel. However, the Special Edition version offers some important differences: - The power output has been increased to 7 ...
... S60. The SE shares with the normal version the "single - ended structure, class A, only two amplification stages, no global feedback and regulated independent supplies for each channel. However, the Special Edition version offers some important differences: - The power output has been increased to 7 ...
Introducing the McIntosh MC275 Tube Power Amplifier
... Introducing the McIntosh MC275 Tube Power Amplifier ...
... Introducing the McIntosh MC275 Tube Power Amplifier ...
transistor
... small change in base current. This action results in voltage amplification because the load resistor placed in series with the collector reacts to this large changes in collector current which, in turn , results in large variation in the output voltage. ...
... small change in base current. This action results in voltage amplification because the load resistor placed in series with the collector reacts to this large changes in collector current which, in turn , results in large variation in the output voltage. ...
feedback current amplifier
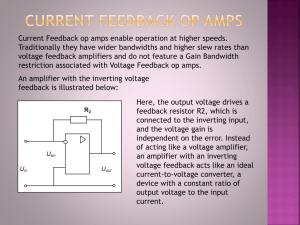
... Current Feedback op amps enable operation at higher speeds. Traditionally they have wider bandwidths and higher slew rates than voltage feedback amplifiers and do not feature a Gain Bandwidth restriction associated with Voltage Feedback op amps. An amplifier with the inverting voltage feedback is il ...
... Current Feedback op amps enable operation at higher speeds. Traditionally they have wider bandwidths and higher slew rates than voltage feedback amplifiers and do not feature a Gain Bandwidth restriction associated with Voltage Feedback op amps. An amplifier with the inverting voltage feedback is il ...
EUA2510 2.7W Boosted Class-D Audio Power Amplifier
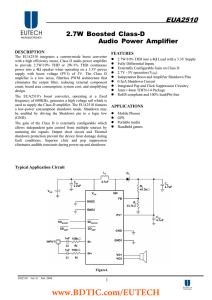
... 2.7W Boosted Class-D Audio Power Amplifier DESCRIPTION The EUA2510 integrates a current-mode boost converter with a high efficiency mono, Class D audio power amplifier to provide 2.7W/10% THD or 2W/1% THD continuous power into a 4Ω speaker when operating on a 3.3V power supply with boost voltage (PV ...
... 2.7W Boosted Class-D Audio Power Amplifier DESCRIPTION The EUA2510 integrates a current-mode boost converter with a high efficiency mono, Class D audio power amplifier to provide 2.7W/10% THD or 2W/1% THD continuous power into a 4Ω speaker when operating on a 3.3V power supply with boost voltage (PV ...
70 Watt AM Shortwave Transmitter Circuit
... The published diagrams of Station QRP are for educational purposes only. These are offered for the furtherance of one's knowledge regarding radio frequency design and principles ...
... The published diagrams of Station QRP are for educational purposes only. These are offered for the furtherance of one's knowledge regarding radio frequency design and principles ...
Amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that increases the power of a signal.It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude. In this sense, an amplifier modulates the output of the power supply to make the output signal stronger than the input signal. An amplifier is effectively the opposite of an attenuator: while an amplifier provides gain, an attenuator provides loss.An amplifier can either be a separate piece of equipment or an electrical circuit within another device. The ability to amplify is fundamental to modern electronics, and amplifiers are extremely widely used in almost all electronic equipment. The types of amplifiers can be categorized in different ways. One is by the frequency of the electronic signal being amplified; audio amplifiers amplify signals in the audio (sound) range of less than 20 kHz, RF amplifiers amplify frequencies in the radio frequency range between 20 kHz and 300 GHz. Another is which quantity, voltage or current is being amplified; amplifiers can be divided into voltage amplifiers, current amplifiers, transconductance amplifiers, and transresistance amplifiers. A further distinction is whether the output is a linear or nonlinear representation of the input. Amplifiers can also be categorized by their physical placement in the signal chain.The first practical electronic device that amplified was the Audion (triode) vacuum tube, invented in 1906 by Lee De Forest, which led to the first amplifiers. The terms ""amplifier"" and ""amplification"" (from the Latin amplificare, 'to enlarge or expand') were first used for this new capability around 1915 when triodes became widespread. For the next 50 years, vacuum tubes were the only devices that could amplify. All amplifiers used them until the 1960s, when transistors appeared. Most amplifiers today use transistors, though tube amplifiers are still produced.