Data Sheet (current)
... Low Power CMOS Dual Operational Amplifier General Description The LPC662 CMOS Dual operational amplifier is ideal for operation from a single supply. It features a wide range of operating voltage from +5V to +15V, rail-to-rail output swing in addition to an input common-mode range that includes grou ...
... Low Power CMOS Dual Operational Amplifier General Description The LPC662 CMOS Dual operational amplifier is ideal for operation from a single supply. It features a wide range of operating voltage from +5V to +15V, rail-to-rail output swing in addition to an input common-mode range that includes grou ...
Chapter 5 Low-Noise Design Methodology
... be added, the bias current of the input transistor can be increased or a transistor with a larger fT can be selected. The noise can be recalculated to see if it is still within specifications. This iterating process ensures obtaining satisfactory noise performance and prevents locking in on a high-n ...
... be added, the bias current of the input transistor can be increased or a transistor with a larger fT can be selected. The noise can be recalculated to see if it is still within specifications. This iterating process ensures obtaining satisfactory noise performance and prevents locking in on a high-n ...
Written - Rose
... Calculate v o . The circuit has two operational amplifiers. For the first op amp, the inverting terminal is connected to ground through a 400Ω resistor and a feedback resistor is connected between the inverting terminal and the output node. The output voltage of the first op amp becomes one of the i ...
... Calculate v o . The circuit has two operational amplifiers. For the first op amp, the inverting terminal is connected to ground through a 400Ω resistor and a feedback resistor is connected between the inverting terminal and the output node. The output voltage of the first op amp becomes one of the i ...
Frequency response I
... Mark the break frequencies and represent them on the frequency axis the critical values for changes Make bode plot for each of the first order term For each first order term, keep the DC to the break frequency constant equal to the gain at DC After the break frequency, the gain magnitude sta ...
... Mark the break frequencies and represent them on the frequency axis the critical values for changes Make bode plot for each of the first order term For each first order term, keep the DC to the break frequency constant equal to the gain at DC After the break frequency, the gain magnitude sta ...
10W, Dual Output Power Supply
... The power supply is designed around the ON Semiconductor NCP1014 monolithic current mode controller with integrated Mosfet in a discontinuous mode (DCM) flyback converter topology. The design includes a pi-network differential mode input EMI filter and resistive turn-on inrush current limiting. The ...
... The power supply is designed around the ON Semiconductor NCP1014 monolithic current mode controller with integrated Mosfet in a discontinuous mode (DCM) flyback converter topology. The design includes a pi-network differential mode input EMI filter and resistive turn-on inrush current limiting. The ...
tvr-c3 - KevinChant.com
... accurate comparison of the unknown frequency can be made with the known one, Turn the time base control to "OFF" position, inject the oscillator frequency to either "Horiz. Amp" or "Horiz, Plate" terminal. The unknown signal can be applied to a suitable "VERTICAL" input, adjustment of the oscillator ...
... accurate comparison of the unknown frequency can be made with the known one, Turn the time base control to "OFF" position, inject the oscillator frequency to either "Horiz. Amp" or "Horiz, Plate" terminal. The unknown signal can be applied to a suitable "VERTICAL" input, adjustment of the oscillator ...
IPSERIES sm.qxd
... 75°C), and HIGH > 167°F (75°C). Built-in protection circuitry shall monitor voltage and current levels to minimize potential damage from overloads, and disable output during shorts, DC offset, or excessive operating temperatures over 167°F (110° C) via a relay for each channel. The relay shall also ...
... 75°C), and HIGH > 167°F (75°C). Built-in protection circuitry shall monitor voltage and current levels to minimize potential damage from overloads, and disable output during shorts, DC offset, or excessive operating temperatures over 167°F (110° C) via a relay for each channel. The relay shall also ...
Ch 16: Electric Circuits: Advanced Topics
... For example, if the base voltage is more than 0.8 V above the collector voltage, then current can freely flow from the emitter to the collector, as if it were just a wire. If the base voltage is less than 0.8 V above the collector voltage, then current does not flow from the emitter to the collector ...
... For example, if the base voltage is more than 0.8 V above the collector voltage, then current can freely flow from the emitter to the collector, as if it were just a wire. If the base voltage is less than 0.8 V above the collector voltage, then current does not flow from the emitter to the collector ...
TDA2040 - Tinkersphere
... Obviously, active crossovers can only be used if a power amplifier is provided for each drive unit. This makes it particularly interesting and economically sound to use monolithic power amplifiers. In some applications, complex filters are not really necessary and simple RC low-pass and high-pass ne ...
... Obviously, active crossovers can only be used if a power amplifier is provided for each drive unit. This makes it particularly interesting and economically sound to use monolithic power amplifiers. In some applications, complex filters are not really necessary and simple RC low-pass and high-pass ne ...
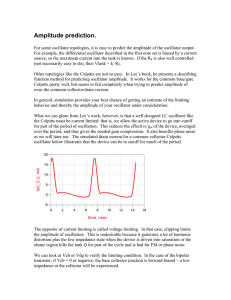
Oscillator Notes 2
... The bias current of the amplifier is directly related to the output voltage swing and RL. If the supply voltage is fixed, then you can reduce current to save power. 1. Increase RL. This may be practical in situations where the frequency is relatively low and interconnection lengths short. This is qu ...
... The bias current of the amplifier is directly related to the output voltage swing and RL. If the supply voltage is fixed, then you can reduce current to save power. 1. Increase RL. This may be practical in situations where the frequency is relatively low and interconnection lengths short. This is qu ...
Amplifier - Bodzio Software
... Please note, that R1 may need to be split into a fixed resistor + a trimpot, to get exact attenuation value. Also, instead of R2 we may use the input impedance of the amplifier (typically within 10-20kohm), so this would simplify the design, if the input capacitance is also low. All relays are low-c ...
... Please note, that R1 may need to be split into a fixed resistor + a trimpot, to get exact attenuation value. Also, instead of R2 we may use the input impedance of the amplifier (typically within 10-20kohm), so this would simplify the design, if the input capacitance is also low. All relays are low-c ...
GOLDMUND MIMESIS 28 POWER AMPLIFIER
... Then switch the power on if the short-circuit has been detected and removed. To avoid the fuses to blow, avoid to short-circuit the output terminals accidentally. Always switch OFF the amp before trying any manipulation of the speaker cables. There is no risk to leave the speaker terminals unconnect ...
... Then switch the power on if the short-circuit has been detected and removed. To avoid the fuses to blow, avoid to short-circuit the output terminals accidentally. Always switch OFF the amp before trying any manipulation of the speaker cables. There is no risk to leave the speaker terminals unconnect ...
eautioll Warllillg - technicalaudio.com
... 1. To make a recording, a suitable input must be connected to the recording amplifier. This may be done by use of anyone, or all, of the bridging or microphone inputs. The microphone inputs normally are shipped for use with 30-50 ohm microphones. However, the input transformer is provided with a tap ...
... 1. To make a recording, a suitable input must be connected to the recording amplifier. This may be done by use of anyone, or all, of the bridging or microphone inputs. The microphone inputs normally are shipped for use with 30-50 ohm microphones. However, the input transformer is provided with a tap ...
Krell Audio Components KCT
... the connecting cable in that its impedance will alter or distort the signal voltage operating the amplifier. In contrast, CAST transfers current rather than voltage from a high impedance source to a low impedance load. In doing so, a cable's effect is minimized, if not totally eliminated, as its imp ...
... the connecting cable in that its impedance will alter or distort the signal voltage operating the amplifier. In contrast, CAST transfers current rather than voltage from a high impedance source to a low impedance load. In doing so, a cable's effect is minimized, if not totally eliminated, as its imp ...
May 2001 LT1815: 220MHz, 1500V/µs Amplifier Saves Space and Power
... offer lower distortion for a given supply current than many other op amps. When desired, the user can dynamically switch between full speed, shutdown and one or more low power modes using various combinations of open-drain logic, as shown in Figure 6. For example, a communication system employing th ...
... offer lower distortion for a given supply current than many other op amps. When desired, the user can dynamically switch between full speed, shutdown and one or more low power modes using various combinations of open-drain logic, as shown in Figure 6. For example, a communication system employing th ...
Amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that increases the power of a signal.It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude. In this sense, an amplifier modulates the output of the power supply to make the output signal stronger than the input signal. An amplifier is effectively the opposite of an attenuator: while an amplifier provides gain, an attenuator provides loss.An amplifier can either be a separate piece of equipment or an electrical circuit within another device. The ability to amplify is fundamental to modern electronics, and amplifiers are extremely widely used in almost all electronic equipment. The types of amplifiers can be categorized in different ways. One is by the frequency of the electronic signal being amplified; audio amplifiers amplify signals in the audio (sound) range of less than 20 kHz, RF amplifiers amplify frequencies in the radio frequency range between 20 kHz and 300 GHz. Another is which quantity, voltage or current is being amplified; amplifiers can be divided into voltage amplifiers, current amplifiers, transconductance amplifiers, and transresistance amplifiers. A further distinction is whether the output is a linear or nonlinear representation of the input. Amplifiers can also be categorized by their physical placement in the signal chain.The first practical electronic device that amplified was the Audion (triode) vacuum tube, invented in 1906 by Lee De Forest, which led to the first amplifiers. The terms ""amplifier"" and ""amplification"" (from the Latin amplificare, 'to enlarge or expand') were first used for this new capability around 1915 when triodes became widespread. For the next 50 years, vacuum tubes were the only devices that could amplify. All amplifiers used them until the 1960s, when transistors appeared. Most amplifiers today use transistors, though tube amplifiers are still produced.