37.0-42.0 GHz GaAs MMIC Power Amplifier Features Chip Device Layout
... mounting surface should be clean and flat. If using conductive epoxy, recommended epoxies are Tanaka TS3332LD, Die Mat DM6030HK or DM6030HK-Pt cured in a nitrogen atmosphere per manufacturer's cure schedule. Apply epoxy sparingly to avoid getting any on to the top surface of the die. An epoxy fillet ...
... mounting surface should be clean and flat. If using conductive epoxy, recommended epoxies are Tanaka TS3332LD, Die Mat DM6030HK or DM6030HK-Pt cured in a nitrogen atmosphere per manufacturer's cure schedule. Apply epoxy sparingly to avoid getting any on to the top surface of the die. An epoxy fillet ...
ZNBG3115
... To minimise board space the ZNBG3115/3116 is offered in a QSOP16 package. To reduce the pin count Drain 1 and Drain 2 have been internally connected. This is possible because only one of the two bias stages can biased at one time.The QSOP16 offers a 40% reduction in size over the QSOP20 version. Cap ...
... To minimise board space the ZNBG3115/3116 is offered in a QSOP16 package. To reduce the pin count Drain 1 and Drain 2 have been internally connected. This is possible because only one of the two bias stages can biased at one time.The QSOP16 offers a 40% reduction in size over the QSOP20 version. Cap ...
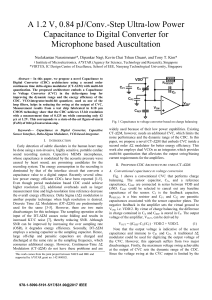
A 1.2 V, 0.84 pJ/Conv.-Step Ultra-low Power Capacitance to Digital
... increase the swing at the output of the CVC. Thus, choosing an optimal value of CF enhances the energy efficiency of the proposed CDC architecture. C. Proposed CDC architecture using second order CT-ΔΣM with multi-bit quantization The proposed architecture showing CVC embedded in a second order ΔΣ l ...
... increase the swing at the output of the CVC. Thus, choosing an optimal value of CF enhances the energy efficiency of the proposed CDC architecture. C. Proposed CDC architecture using second order CT-ΔΣM with multi-bit quantization The proposed architecture showing CVC embedded in a second order ΔΣ l ...
Cntfet Technology Based Precision Full
... conventional rectifiers like full-wave rectifier[10][11] the minimum applied voltage should be above the Knee voltage of the semiconductor material being used (which is 0.7 V for silicon and 0.3v for germanium). This is a significant advantage of this circuit. ...
... conventional rectifiers like full-wave rectifier[10][11] the minimum applied voltage should be above the Knee voltage of the semiconductor material being used (which is 0.7 V for silicon and 0.3v for germanium). This is a significant advantage of this circuit. ...
ÿþM u l t i c h i p m o d u l e s o l u t i o n s M M I C P
... The packaged HPA is also attached to the carrier by mean of reflow soldering, specifically onto an array of via-holes, placed under the exposed pad. This array is designed in order to minimize the parasitic inductance to ground of the mounted packaged IC, when using microstrip launching. Indeed, thi ...
... The packaged HPA is also attached to the carrier by mean of reflow soldering, specifically onto an array of via-holes, placed under the exposed pad. This array is designed in order to minimize the parasitic inductance to ground of the mounted packaged IC, when using microstrip launching. Indeed, thi ...
FEATURES DESCRIPTION D
... RAIL-TO-RAIL OUTPUT A class AB output stage with common-source transistors is used to achieve rail-to-rail output. For high-impedance loads (> 200Ω), the output voltage swing is typically 100mV from the supply rails. With 10Ω loads, a useful output swing can be achieved while maintaining high open-l ...
... RAIL-TO-RAIL OUTPUT A class AB output stage with common-source transistors is used to achieve rail-to-rail output. For high-impedance loads (> 200Ω), the output voltage swing is typically 100mV from the supply rails. With 10Ω loads, a useful output swing can be achieved while maintaining high open-l ...
An Integrated Bridgeless PWM Based Power Converter for Power
... voltage. Compared to the previous approaches (single-stage design and two-stage design [10]), the proposed approach increase the power efficiency and reduce component counts by lowering conduction losses and by eliminating the full-bridge diode rectifier in the single-stage PFC ac-dc converters. Mor ...
... voltage. Compared to the previous approaches (single-stage design and two-stage design [10]), the proposed approach increase the power efficiency and reduce component counts by lowering conduction losses and by eliminating the full-bridge diode rectifier in the single-stage PFC ac-dc converters. Mor ...
ADP3336 High Accuracy Ultralow IQ , 500 mA anyCAP® Adjustable
... The ADP3336 is a member of the ADP333x family of precision low dropout anyCAP voltage regulators. The ADP3336 operates with an input voltage range of 2.6 V to 12 V and delivers a continuous load current up to 500 mA. The ADP3336 stands out from conventional LDOs with the lowest thermal resistance of ...
... The ADP3336 is a member of the ADP333x family of precision low dropout anyCAP voltage regulators. The ADP3336 operates with an input voltage range of 2.6 V to 12 V and delivers a continuous load current up to 500 mA. The ADP3336 stands out from conventional LDOs with the lowest thermal resistance of ...
AD8055
... Gain flatness 0.1 dB to 40 MHz 0.01% differential gain error 0.02° differential phase error Drives 4 video loads (37.5 V) with 0.02% differential Gain and 0.1° differential phase Low power, ±5 V supplies 5 mA typ/amplifier power supply current High output drive current: over 60 mA ...
... Gain flatness 0.1 dB to 40 MHz 0.01% differential gain error 0.02° differential phase error Drives 4 video loads (37.5 V) with 0.02% differential Gain and 0.1° differential phase Low power, ±5 V supplies 5 mA typ/amplifier power supply current High output drive current: over 60 mA ...
BiCMOS PFC/PWM Combination Controller
... current-mode control. The dc-to-dc converter uses peak current-mode control to perform the step-down power conversion. The PFC stage is leading-edge modulated while the second stage is trailing-edge synchronized to allow for minimum overlap between the boost and PWM switches. This reduces ripple cur ...
... current-mode control. The dc-to-dc converter uses peak current-mode control to perform the step-down power conversion. The PFC stage is leading-edge modulated while the second stage is trailing-edge synchronized to allow for minimum overlap between the boost and PWM switches. This reduces ripple cur ...
KSA114 2 PNP Epitaxial Silicon Transistor Absolute Maximum Ratings
... 2. A critical component is any component of a life support device or system whose failure to perform can be reasonably expected to cause the failure of the life support device or system, or to affect its safety or effectiveness. ...
... 2. A critical component is any component of a life support device or system whose failure to perform can be reasonably expected to cause the failure of the life support device or system, or to affect its safety or effectiveness. ...
Chapter 12 - UNT College of Engineering
... DAC Performance Specifications – 4 • Relative accuracy is the deviation of the actual from the ideal output voltage as a fraction of the full-scale voltage. • Settling time is the time required for the outputs to switch and settle within ½ LSB when the input switches form all 0s to all 1s. ...
... DAC Performance Specifications – 4 • Relative accuracy is the deviation of the actual from the ideal output voltage as a fraction of the full-scale voltage. • Settling time is the time required for the outputs to switch and settle within ½ LSB when the input switches form all 0s to all 1s. ...
Homework #1 SOLUTIONS
... (c) Now write down the expression for this new circuit’s output with respect to the current input for AC signals (Hint: in the expression from part (a), substitute the parallel combination Rx k C for the resistor Rx that you chose). We have already seen the simple case, if we do not consider the ful ...
... (c) Now write down the expression for this new circuit’s output with respect to the current input for AC signals (Hint: in the expression from part (a), substitute the parallel combination Rx k C for the resistor Rx that you chose). We have already seen the simple case, if we do not consider the ful ...
Customer Specific Device from ON Semiconductor 1.7 MHz, 1 A
... device also has a built−in 1.7 MHz (nominal) oscillator which reduces component size by allowing a small inductor and capacitors. Automatic switching PWM/PFM mode offers improved system efficiency. Additional features include integrated soft−start, cycle−by−cycle current limiting and thermal shutdow ...
... device also has a built−in 1.7 MHz (nominal) oscillator which reduces component size by allowing a small inductor and capacitors. Automatic switching PWM/PFM mode offers improved system efficiency. Additional features include integrated soft−start, cycle−by−cycle current limiting and thermal shutdow ...
MAX5302 Low-Power, 12-Bit Voltage-Output DAC with Serial Interface __________________General Description
... bits (C2, C1, C0), followed by the 12+1 data bits D11...D0, S0 (Figure 4). Set the sub-bit (S0) to zero. The 3-bit control code determines the register to be updated and the configuration when exiting shutdown. Figures 5 and 6 show the serial-interface timing requirements. The chip-select (CS) pin m ...
... bits (C2, C1, C0), followed by the 12+1 data bits D11...D0, S0 (Figure 4). Set the sub-bit (S0) to zero. The 3-bit control code determines the register to be updated and the configuration when exiting shutdown. Figures 5 and 6 show the serial-interface timing requirements. The chip-select (CS) pin m ...
Advanced Monolithic Systems
... is providing the power for the control circuitry and supplies the drive current to the NPN output transistor. This allows the NPN to be driven into saturation; thereby reducing the dropout voltage by a VBE compared to conventional designs. For the control voltage the current requirement is small, eq ...
... is providing the power for the control circuitry and supplies the drive current to the NPN output transistor. This allows the NPN to be driven into saturation; thereby reducing the dropout voltage by a VBE compared to conventional designs. For the control voltage the current requirement is small, eq ...
SSM2167 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... The VCA is a low distortion, variable gain amplifier whose gain is set by the side-chain control circuitry. An external blocking capacitor (C2) must be used between the buffer output and the VCA input. The 1 kΩ impedance between amplifiers determines the value of this capacitor, which is typically b ...
... The VCA is a low distortion, variable gain amplifier whose gain is set by the side-chain control circuitry. An external blocking capacitor (C2) must be used between the buffer output and the VCA input. The 1 kΩ impedance between amplifiers determines the value of this capacitor, which is typically b ...
TL082-Q1 JFET-INPUT OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER FEATURES
... and other changes to its products and services at any time and to discontinue any product or service without notice. Customers should obtain the latest relevant information before placing orders and should verify that such information is current and complete. All products are sold subject to TI’s te ...
... and other changes to its products and services at any time and to discontinue any product or service without notice. Customers should obtain the latest relevant information before placing orders and should verify that such information is current and complete. All products are sold subject to TI’s te ...
Amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that increases the power of a signal.It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude. In this sense, an amplifier modulates the output of the power supply to make the output signal stronger than the input signal. An amplifier is effectively the opposite of an attenuator: while an amplifier provides gain, an attenuator provides loss.An amplifier can either be a separate piece of equipment or an electrical circuit within another device. The ability to amplify is fundamental to modern electronics, and amplifiers are extremely widely used in almost all electronic equipment. The types of amplifiers can be categorized in different ways. One is by the frequency of the electronic signal being amplified; audio amplifiers amplify signals in the audio (sound) range of less than 20 kHz, RF amplifiers amplify frequencies in the radio frequency range between 20 kHz and 300 GHz. Another is which quantity, voltage or current is being amplified; amplifiers can be divided into voltage amplifiers, current amplifiers, transconductance amplifiers, and transresistance amplifiers. A further distinction is whether the output is a linear or nonlinear representation of the input. Amplifiers can also be categorized by their physical placement in the signal chain.The first practical electronic device that amplified was the Audion (triode) vacuum tube, invented in 1906 by Lee De Forest, which led to the first amplifiers. The terms ""amplifier"" and ""amplification"" (from the Latin amplificare, 'to enlarge or expand') were first used for this new capability around 1915 when triodes became widespread. For the next 50 years, vacuum tubes were the only devices that could amplify. All amplifiers used them until the 1960s, when transistors appeared. Most amplifiers today use transistors, though tube amplifiers are still produced.