Sub-Saharan Africa - Lazard Asset Management
... economy in favor of the private sector. The latest wave of structural reforms took place under the stand by agreement reached with IMF in 2010 and concluded successfully in May 2012.20 Still, much progress needs to be made, particularly to improve business conditions in order to attract more private ...
... economy in favor of the private sector. The latest wave of structural reforms took place under the stand by agreement reached with IMF in 2010 and concluded successfully in May 2012.20 Still, much progress needs to be made, particularly to improve business conditions in order to attract more private ...
Uncertainty, Capital Flows, and Maturity Mismatch
... This Version: February 2015. First Version: November 2012 Abstract Output growth in emerging markets is significantly more volatile than in advanced economies, due in large part to fluctuations in total factor productivity (TFP). This paper shows that where maturity mismatch is widespread, as in eme ...
... This Version: February 2015. First Version: November 2012 Abstract Output growth in emerging markets is significantly more volatile than in advanced economies, due in large part to fluctuations in total factor productivity (TFP). This paper shows that where maturity mismatch is widespread, as in eme ...
January 2015 - Public Documents Profile Viewer
... Third-party content—The World Bank does not necessarily own each component of the content contained within the work. The World Bank therefore does not warrant that the use of any third-party-owned individual component or part contained in the work will not infringe on the rights of those third parti ...
... Third-party content—The World Bank does not necessarily own each component of the content contained within the work. The World Bank therefore does not warrant that the use of any third-party-owned individual component or part contained in the work will not infringe on the rights of those third parti ...
CEEC – Transition and Enlargement
... increase in money supply moves LM to LM‘, interst rates declines initially to B, spending expands and economy moves to C capital flows out until interest rate is back to international level A ...
... increase in money supply moves LM to LM‘, interst rates declines initially to B, spending expands and economy moves to C capital flows out until interest rate is back to international level A ...
Why Are There MNEs?
... a subsidiary in a foreign country. Most FDI involves acquiring existing facilities. An obvious question is "How much FDI confers management control?" Countries have different standards on this issue. The U.S. standard is ten percent or more purchased by one foreign entity (note this means that a U.S ...
... a subsidiary in a foreign country. Most FDI involves acquiring existing facilities. An obvious question is "How much FDI confers management control?" Countries have different standards on this issue. The U.S. standard is ten percent or more purchased by one foreign entity (note this means that a U.S ...
$doc.title
... weaker bargaining position represented by the borrowing country, or if conditions rather meet some minimum necessary to repaying debts and restoring financial balance, as few studies have been effecte ...
... weaker bargaining position represented by the borrowing country, or if conditions rather meet some minimum necessary to repaying debts and restoring financial balance, as few studies have been effecte ...
Economics AQA AS Unit 1 WORKBOOK ANSWERS
... Analysis of reasons why inequality is inevitable (up to 3 marks for one point or more). Points include: A free market economy incentivises entrepreneurship and profit is the reward; owners of firms receive profits; private ownership of factors of production and owners receive factor payments from th ...
... Analysis of reasons why inequality is inevitable (up to 3 marks for one point or more). Points include: A free market economy incentivises entrepreneurship and profit is the reward; owners of firms receive profits; private ownership of factors of production and owners receive factor payments from th ...
Impacts of External Shocks on Nations` Policy Responses and
... = Changes in External Shocks – Changes in Policy Responses + Error Term These three components were not only statistically relevant to economic performance but also theoretically meaningful to be employed to explore transmission mechanisms of world business cycle by using this external shock account ...
... = Changes in External Shocks – Changes in Policy Responses + Error Term These three components were not only statistically relevant to economic performance but also theoretically meaningful to be employed to explore transmission mechanisms of world business cycle by using this external shock account ...
German-Central European Supply Chain--Cluster Report
... competitiveness in knowledge-intensive sectors. As unit labor cost differentials with Germany narrow, the CE4 countries may struggle to sustain their current role in the supply chain. In order to remain part of the GCESC—or branch out into more specialized export production activities, as some count ...
... competitiveness in knowledge-intensive sectors. As unit labor cost differentials with Germany narrow, the CE4 countries may struggle to sustain their current role in the supply chain. In order to remain part of the GCESC—or branch out into more specialized export production activities, as some count ...
The Optimal Level of International Reserves For Emerging Market
... capital ‡ow volatility, the danger of which was learned the hard way in the international …nancial crises of the 1990s (Aizenman and Marion, 2003; Stiglitz, 2006).1 Against this backdrop, there has been surprisingly little work trying to quantify the level of reserves that can be justi…ed as an insu ...
... capital ‡ow volatility, the danger of which was learned the hard way in the international …nancial crises of the 1990s (Aizenman and Marion, 2003; Stiglitz, 2006).1 Against this backdrop, there has been surprisingly little work trying to quantify the level of reserves that can be justi…ed as an insu ...
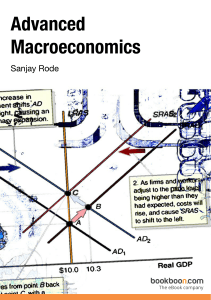
Advanced Macroeconomics - Juridica – Kolegji Evropian
... interest rates and the balance of payments. This book attempts to explain the domestic and international factors responsible for creating the equilibrium of the balance of payments, interest rates and inflation. It is hoped that this book’s contents will help students to think, analyze and apply wha ...
... interest rates and the balance of payments. This book attempts to explain the domestic and international factors responsible for creating the equilibrium of the balance of payments, interest rates and inflation. It is hoped that this book’s contents will help students to think, analyze and apply wha ...
The EBE Book of Economic Questions for HSC Students
... Reduced demand for exports of the trading partners Reduced levels of capital inflow from high income economy to its trading partner ...
... Reduced demand for exports of the trading partners Reduced levels of capital inflow from high income economy to its trading partner ...
III Select Credit Fund Ltd. October 2010
... Investing in securities and other financial products entails certain risks, including the possible loss of the entire principal amount invested. Certain investments in particular, including those involving structured products, futures, options and other derivatives, are complex, may entail substanti ...
... Investing in securities and other financial products entails certain risks, including the possible loss of the entire principal amount invested. Certain investments in particular, including those involving structured products, futures, options and other derivatives, are complex, may entail substanti ...
Capital Imports Composition, Complementarities, and the Skill
... best knowledge, we are the …rst to empirically document that some types of capital are more complementary to unskilled workers. Acemoglu (2002) suggests an explanation for why this is the case: An increase in the supply of skilled labor in industrial economies, which occurred during the same period ...
... best knowledge, we are the …rst to empirically document that some types of capital are more complementary to unskilled workers. Acemoglu (2002) suggests an explanation for why this is the case: An increase in the supply of skilled labor in industrial economies, which occurred during the same period ...
Présentation sur fond blanc
... agree it shall not be copied, reproduced, or distributed to a third party without our prior written approval. The information contained in this document is not intended for all categories of customers. Your attention is drawn to the fact that units or shares in these UCITS may not be purchased if th ...
... agree it shall not be copied, reproduced, or distributed to a third party without our prior written approval. The information contained in this document is not intended for all categories of customers. Your attention is drawn to the fact that units or shares in these UCITS may not be purchased if th ...
Official PDF , 258 pages
... pattern followed by the share of manufacturing in total employment as a result of the process of structural change generated by increases in per capita income. The author finds that, worldwide, this relationship has become more adverse in recent decades, thereby generating a widespread process of “d ...
... pattern followed by the share of manufacturing in total employment as a result of the process of structural change generated by increases in per capita income. The author finds that, worldwide, this relationship has become more adverse in recent decades, thereby generating a widespread process of “d ...
Antigua and Barbuda: Staff Report for the 2012 Article IV
... 3½ percent of GDP in 2013 and beyond, consistent with an overall fiscal surplus of 0.6–0.8 percent of GDP. This would lead to a decline in the ratio of debt-to-GDP from close to 100 percent in 2012 in this scenario, to 76 percent in 2016. The current account deficit is expected to widen with increas ...
... 3½ percent of GDP in 2013 and beyond, consistent with an overall fiscal surplus of 0.6–0.8 percent of GDP. This would lead to a decline in the ratio of debt-to-GDP from close to 100 percent in 2012 in this scenario, to 76 percent in 2016. The current account deficit is expected to widen with increas ...
The Optimal Level of International Reserves For Emerging Market
... The recent buildup in international reserves in emerging market countries has revived old debates about the appropriate amount of reserves for an open economy. It has been argued that many emerging market countries accumulated reserves as a form of self-insurance against capital ‡ow volatility, the ...
... The recent buildup in international reserves in emerging market countries has revived old debates about the appropriate amount of reserves for an open economy. It has been argued that many emerging market countries accumulated reserves as a form of self-insurance against capital ‡ow volatility, the ...
Financial facts - Great West Life
... Participating policyowners’ premiums go into a separate account called the participating account. Great-West Life manages this account, investing its assets in a diversified portfolio of bonds, mortgages and equities, including real estate. This frees policyowners from the details of hands-on manage ...
... Participating policyowners’ premiums go into a separate account called the participating account. Great-West Life manages this account, investing its assets in a diversified portfolio of bonds, mortgages and equities, including real estate. This frees policyowners from the details of hands-on manage ...
The Production Account and GDP
... financial and economic markets. It is important to mention here that while the SNA is an internationally agreed system for measuring and monitoring economic transactions and economic growth, there are some countries that have used a slightly different system, in particular the former Communist count ...
... financial and economic markets. It is important to mention here that while the SNA is an internationally agreed system for measuring and monitoring economic transactions and economic growth, there are some countries that have used a slightly different system, in particular the former Communist count ...
world economy research institute transition countries
... data, and retained in the current report, is the use of weighted averages of some indicators (e.g. GNI per capita, GDP growth rates, percentage changes of export and import volumes), calculated for the distinguished subgroups and the group of transition economies as a whole, in order to facilitate i ...
... data, and retained in the current report, is the use of weighted averages of some indicators (e.g. GNI per capita, GDP growth rates, percentage changes of export and import volumes), calculated for the distinguished subgroups and the group of transition economies as a whole, in order to facilitate i ...
From Recession to Recovery: How Soon and How
... Recessions are distinctly shallower, briefer, and less frequent than expansions. In a typical recession, GDP falls by about 2¾ percent (Table 1).7 In contrast, during an expansion, GDP tends to rise by almost 20 percent. This illustrates mainly the importance of trend growth; the higher the long-run ...
... Recessions are distinctly shallower, briefer, and less frequent than expansions. In a typical recession, GDP falls by about 2¾ percent (Table 1).7 In contrast, during an expansion, GDP tends to rise by almost 20 percent. This illustrates mainly the importance of trend growth; the higher the long-run ...
From Recession to Recovery
... Recessions are distinctly shallower, briefer, and less frequent than expansions. In a typical recession, GDP falls by about 2¾ percent (Table 1).7 In contrast, during an expansion, GDP tends to rise by almost 20 percent. This illustrates mainly the importance of trend growth; the higher the long-run ...
... Recessions are distinctly shallower, briefer, and less frequent than expansions. In a typical recession, GDP falls by about 2¾ percent (Table 1).7 In contrast, during an expansion, GDP tends to rise by almost 20 percent. This illustrates mainly the importance of trend growth; the higher the long-run ...
Open Access
... foreign markets. A contradicting theory is that causes for growth can come firstly within the country itself and later on, after satisfying the home market, the country can start exporting. The purpose of this dissertation is twofold. The first task is to examine the nexus between international trad ...
... foreign markets. A contradicting theory is that causes for growth can come firstly within the country itself and later on, after satisfying the home market, the country can start exporting. The purpose of this dissertation is twofold. The first task is to examine the nexus between international trad ...
LCCARL082_en.pdf
... The monetary stance was for the most part conservative. In the face of growing actual and expected external imbalances, the central banks of the region put in place measures to rein in import demand growth and avoid an unwarranted reduction in foreign exchange reserves. These measures also responded ...
... The monetary stance was for the most part conservative. In the face of growing actual and expected external imbalances, the central banks of the region put in place measures to rein in import demand growth and avoid an unwarranted reduction in foreign exchange reserves. These measures also responded ...