External sector management in South Asia(27.11.14)
... The most important and common feature of external sector management in South Asia is their deliberate effort towards greater integration with the world economy. Such integration is popularly known as globalization .Joseph Stiglitz, a Nobel laureate economist, defines globalization as "closer integra ...
... The most important and common feature of external sector management in South Asia is their deliberate effort towards greater integration with the world economy. Such integration is popularly known as globalization .Joseph Stiglitz, a Nobel laureate economist, defines globalization as "closer integra ...
Chile_en.pdf
... currency appreciation resumed —a pattern that had been interrupted, in late 2008, by the sharp exchange rate rises that accompanied the onset of the crisis. In response, the monetary authority has limited itself thus far to issuing statements, but has not ruled out the possibility of taking measures ...
... currency appreciation resumed —a pattern that had been interrupted, in late 2008, by the sharp exchange rate rises that accompanied the onset of the crisis. In response, the monetary authority has limited itself thus far to issuing statements, but has not ruled out the possibility of taking measures ...
ECONOMICS
... Demand Reasons Size of population impacts demand Population’s income levels effect demand Increase in the wealth Preferences and tastes Difference in consumptions patterns ...
... Demand Reasons Size of population impacts demand Population’s income levels effect demand Increase in the wealth Preferences and tastes Difference in consumptions patterns ...
Unemployment since 2000 GDP growth Inflation since 1920 UK
... inflation rate of 2% per annum, and the Monetary Policy Committee of the Bank of England has responsibility for meeting the target. The main instrument for achieving this has been the interest rate, but the financial crisis of the late 2000s and the subsequent recession required a new approach. ...
... inflation rate of 2% per annum, and the Monetary Policy Committee of the Bank of England has responsibility for meeting the target. The main instrument for achieving this has been the interest rate, but the financial crisis of the late 2000s and the subsequent recession required a new approach. ...
Colombia_en.pdf
... lowest point in almost 50 years. Up to October, year-onyear inflation stood at 2.7% (2.0% from December 2008 to October 2009) following a reduction in international prices for food and fuels, a slight increase in demand, the appreciation in the peso and a downward trend in costs. The El Niño phenome ...
... lowest point in almost 50 years. Up to October, year-onyear inflation stood at 2.7% (2.0% from December 2008 to October 2009) following a reduction in international prices for food and fuels, a slight increase in demand, the appreciation in the peso and a downward trend in costs. The El Niño phenome ...
Monetary Policy - Economics of Agricultural Development
... Exchange rates in developing countries often set by government and “pegged” to currency of a major developed country ...
... Exchange rates in developing countries often set by government and “pegged” to currency of a major developed country ...
Econ 114 Mock Midterm 3
... 3. The natural rate of unemployment is the rate of unemployment that is natural to any economy and can never change. 4. Liquidity refers to the ease with which an asset flows through the bank. 5. The money multiplier is the amount of reserves that the banking system generates with each dollar of mon ...
... 3. The natural rate of unemployment is the rate of unemployment that is natural to any economy and can never change. 4. Liquidity refers to the ease with which an asset flows through the bank. 5. The money multiplier is the amount of reserves that the banking system generates with each dollar of mon ...
Uruguay_en.pdf
... The weakening of Uruguay’s currency enabled a partial correction in the imbalance of relative prices with other countries, and helped restore competitiveness. In recent months, economic policy has sought to strike a balance between controlling inflation and alleviating the deterioration in prices re ...
... The weakening of Uruguay’s currency enabled a partial correction in the imbalance of relative prices with other countries, and helped restore competitiveness. In recent months, economic policy has sought to strike a balance between controlling inflation and alleviating the deterioration in prices re ...
3.2.1.1 The Objectives of Government Economic Policy
... During periods of economic growth, consumers have high levels of spending. In the UK, consumers have a high marginal propensity to import, so there is likely to be more spending on imports. This leads to a worsening of the current account deficit. However, export-led growth, such as that of China an ...
... During periods of economic growth, consumers have high levels of spending. In the UK, consumers have a high marginal propensity to import, so there is likely to be more spending on imports. This leads to a worsening of the current account deficit. However, export-led growth, such as that of China an ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES G7 CURRENT ACCOUNT IMBALANCES: SUSTAINABILITY AND ADJUSTMENT
... consumption-driven current account deficits involve significantly larger depreciations than deficits financing investment, and (iii) there is little evidence that deficits in economies that run persistent deficits, have large net foreign debt positions, experience greater short-term capital flows, o ...
... consumption-driven current account deficits involve significantly larger depreciations than deficits financing investment, and (iii) there is little evidence that deficits in economies that run persistent deficits, have large net foreign debt positions, experience greater short-term capital flows, o ...
Honduras_en.pdf
... attributable mainly to a decline in traditional exports, mostly coffee, which fell by 45.3%, affected by both the coffee-leaf rust and a year-on-year decrease of 30.7% in the price of coffee. The central bank forecasts a current-account deficit of 8.1% of GDP for 2013. Despite sluggish global growth ...
... attributable mainly to a decline in traditional exports, mostly coffee, which fell by 45.3%, affected by both the coffee-leaf rust and a year-on-year decrease of 30.7% in the price of coffee. The central bank forecasts a current-account deficit of 8.1% of GDP for 2013. Despite sluggish global growth ...
BRAZIL`S 1998-1999 CURRENCY CRISIS
... year, the central bank used a net of $7.5 billion in reserves to defend the real’s crawling peg. Furthermore, it was clear from the current account deficit, stalled GDP growth, and soaring public debt that the country had economic problems. During this time, the East Asian financial crisis showed th ...
... year, the central bank used a net of $7.5 billion in reserves to defend the real’s crawling peg. Furthermore, it was clear from the current account deficit, stalled GDP growth, and soaring public debt that the country had economic problems. During this time, the East Asian financial crisis showed th ...
producer surplus
... Not determined which country gains more. Division depends on How much price changes. Comments (page 28) that the evaluation of gains uses the “onedollar, one-vote metric.” Importantly, this ignores distributional issues. This is a static story. No Full Employment. Limits of free trade price, from gr ...
... Not determined which country gains more. Division depends on How much price changes. Comments (page 28) that the evaluation of gains uses the “onedollar, one-vote metric.” Importantly, this ignores distributional issues. This is a static story. No Full Employment. Limits of free trade price, from gr ...
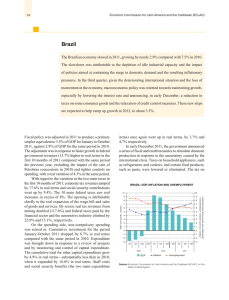
Brazil_en.pdf
... US$ 25.4 billion. The wider trade surplus helped to offset the strong deflationary pressure of services in the Brazilian ...
... US$ 25.4 billion. The wider trade surplus helped to offset the strong deflationary pressure of services in the Brazilian ...
ECCU_en.pdf
... growth has been registered for all countries with the exception of Antigua and Barbuda. This growth was mainly fuelled by an increase in tourism activity (4.7%) and other services such as electricity and water (2.1%) and public administration and social services (5.2%). Construction, which accounts ...
... growth has been registered for all countries with the exception of Antigua and Barbuda. This growth was mainly fuelled by an increase in tourism activity (4.7%) and other services such as electricity and water (2.1%) and public administration and social services (5.2%). Construction, which accounts ...
Colombia_en.pdf
... private investment, which had been an engine of growth in previous years, continues to expand, albeit at much lower rates. Business and household confidence indicators trended downward over the course of the year, turning frankly negative in the second semester. Inflation has been a concern for the ...
... private investment, which had been an engine of growth in previous years, continues to expand, albeit at much lower rates. Business and household confidence indicators trended downward over the course of the year, turning frankly negative in the second semester. Inflation has been a concern for the ...
Khon Kaen University International College
... • Global business means dealing with consumers, strategic partners, distributors, and competitors ...
... • Global business means dealing with consumers, strategic partners, distributors, and competitors ...
Presentation, Powerpoint 2.4Mb - The Cambridge Trust for New
... • Capital flows have been volatile in LA, with predominance of portfolio capitals and FDI. Since mid-2009 there is a quick recovery of capital inflows. • There was a quick and deep contagious of the international financial crisis in LA, but recovery was also quick. Previous policy of reduction of ex ...
... • Capital flows have been volatile in LA, with predominance of portfolio capitals and FDI. Since mid-2009 there is a quick recovery of capital inflows. • There was a quick and deep contagious of the international financial crisis in LA, but recovery was also quick. Previous policy of reduction of ex ...
Is Fiscal Profligacy the Cause of the Crisis? Prabhat Patnaik
... has been so ruthlessly practiced in India that tariff rates on imported goods are invariably kept far below even the “tariff bounds” that are allowed to the country by the WTO rules themselves. The result has been both a widening of the current account deficit and a crisis of manufacturing. It is no ...
... has been so ruthlessly practiced in India that tariff rates on imported goods are invariably kept far below even the “tariff bounds” that are allowed to the country by the WTO rules themselves. The result has been both a widening of the current account deficit and a crisis of manufacturing. It is no ...
WHATDUNIT? The Great Depression Mystery
... -->lay offs -->less spending -->lower confidence -->less investment -->less machinery purchased -->higher unemployment • Until surpluses are used up ...
... -->lay offs -->less spending -->lower confidence -->less investment -->less machinery purchased -->higher unemployment • Until surpluses are used up ...