* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download producer surplus
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
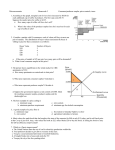
Chapter 2 Basic theory Using Supply and Demand. Producer and Consumer Surplus Link to syllabus Local link to syllabus Description of first paper World Exports, 2005. p. 20 Exports Plus Imports/GDP p. 21 Chapter 2. Basic theory, using Supply and Demand Producer and Consumer Surplus. Basic supply and demand curves for exports, imports. World Exports, 2009. p. 20 Volume of World Trade and Output. P. 23 Exports Plus Imports/GDP p. 21 Trade is more important for some countries than others. Someplace in this chapter he notes that half of world trade is among DCs. Volume of World Trade and Output. P. 21 Defines (page 19) consumer surplus: the increase in the economic well being for consumers who are able to buy the product at a market price lower than the maximum they are willing to pay. Defines (page 23) producer surplus: the increase in the economic wellbeing of producers who are able to sell the product at a market price higher than the lowest price at which they would have produced. Figure 2.2 page 22 The market for bikes Total domestic supply and demand. Producer surplus is h Consumer surplus is c Figure 2.2 page 24. Producer and consumer surplus (national market for bikes) Producer surplus is h, consumer is c Engaging in production and exchange results in a total increase in welfare of c +h 2 Figure 2.3 Page 23 Effects of trade on production, consumption and price Figure 2.3 page 25. Effects of trade on production, consumption, etc., using supply and demand. Sx is rest of world’s supply of exports. Dm is U.S. demand for imports Doesn’t seem to use the terms excess supply and excess demand. Comments: Distributional effects. No inclusion of effects that would result from the assumption of full employment. Magnitude of effects depends on slopes of curves. Can do effect on world prices, exports, production etc. of change in population, or change in technology. Import substitution Figure 2.4 page 25 Effects of trade on well-being of producers, consumers, nation Figure 2.4 page 28. Effects of trade on wellbeing of producers, consumers, nation. US consumer surplus increases, producer’s decreases, net effect =b+d RoW: consumer lose, producers gain, net effect is n. World impact is the sum of both. Arbitrage: buying something in one market, selling it in another to profit from the price difference. Mentions elasticity frequently. Price elasticity of demand: % change in quantity demanded from a 1% change in price. Doesn’t really use it. No good reason for splitting U.S. impact into b+d, but only “n” for R.o.W. In principle, “b+d+n” can be measured. Not determined which country gains more. Division depends on How much price changes. Comments (page 28) that the evaluation of gains uses the “onedollar, one-vote metric.” Importantly, this ignores distributional issues. This is a static story. No Full Employment. Limits of free trade price, from graph. Relate to what determines comp. advantage/direction of trade.