Lecture 36 - Lipid Metabolism 2
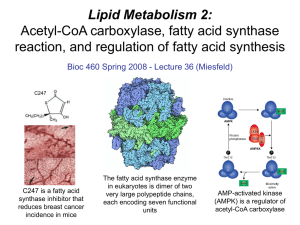
... Acetyl CoA carboxylase - catalyzes the commitment step in fatty acid synthesis using a biotin-mediated reaction mechanism that carboxylates acetyl-CoA to form the C3 compound malonyl-CoA.. Fatty acid synthase - this large multi-functional enzyme is responsible for catalyzing a series of reactions th ...
... Acetyl CoA carboxylase - catalyzes the commitment step in fatty acid synthesis using a biotin-mediated reaction mechanism that carboxylates acetyl-CoA to form the C3 compound malonyl-CoA.. Fatty acid synthase - this large multi-functional enzyme is responsible for catalyzing a series of reactions th ...
Practice Test for BIO 311C
... D) The O2 released during photosynthesis comes from water. E) RuBP is produced during cyclic electron flow in the light reactions of photosynthesis. 76) The oxygen consumed during cellular respiration is involved directly in which process or event? A) the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA B) the c ...
... D) The O2 released during photosynthesis comes from water. E) RuBP is produced during cyclic electron flow in the light reactions of photosynthesis. 76) The oxygen consumed during cellular respiration is involved directly in which process or event? A) the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA B) the c ...
Regulation of Glycogen Metabolism
... When epinephrine binds to the α−adrenergic receptor, Calcium ions are released into the cytosol increasing the concentration of Ca2+. This reinforces the cells’ response to cAMP. The Five Principles of Hormonal Signal Transduction 1. The specificity of action in tissues is conferred by the receptor. ...
... When epinephrine binds to the α−adrenergic receptor, Calcium ions are released into the cytosol increasing the concentration of Ca2+. This reinforces the cells’ response to cAMP. The Five Principles of Hormonal Signal Transduction 1. The specificity of action in tissues is conferred by the receptor. ...
testosterone
... each of the following types of organic compounds: carbohydrates: monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides lipids: triglycerides, phospholipids, steroids nucleic acids: DNA, RNA, ATP proteins: amino acid, peptide bond, levels of structure, glycoprotein, lipoprotein ...
... each of the following types of organic compounds: carbohydrates: monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides lipids: triglycerides, phospholipids, steroids nucleic acids: DNA, RNA, ATP proteins: amino acid, peptide bond, levels of structure, glycoprotein, lipoprotein ...
chapter_5_Mod_2009
... – Those molecules feedback and bind to an enzyme early in the sequence’. – They inhibit that enzyme, and stop the sequence. – This decreases the amount of end-product made. This functions to keep levels of the end-product within a certain range. ...
... – Those molecules feedback and bind to an enzyme early in the sequence’. – They inhibit that enzyme, and stop the sequence. – This decreases the amount of end-product made. This functions to keep levels of the end-product within a certain range. ...
Metabolic Pathways
... • Metabolic pathways are controlled by the presence or absence of particular enzymes in the metabolic pathway and through the regulation of the rate of reaction of key enzymes within the pathway. • Regulation can be controlled by intra- and extracellular signal molecules. • Induced fit and the role ...
... • Metabolic pathways are controlled by the presence or absence of particular enzymes in the metabolic pathway and through the regulation of the rate of reaction of key enzymes within the pathway. • Regulation can be controlled by intra- and extracellular signal molecules. • Induced fit and the role ...
Bax - Hypromatrix
... Bax (for Bcl-associated X protein) belongs to the Bcl-2 protein family. Bcl-2 family members form hetero- or homodimers and act as anti- or pro-apoptotic regulators that are involved in a wide variety of cellular activities. Bax has extensive amino acid homology with Bcl-2 and both homodimerizes and ...
... Bax (for Bcl-associated X protein) belongs to the Bcl-2 protein family. Bcl-2 family members form hetero- or homodimers and act as anti- or pro-apoptotic regulators that are involved in a wide variety of cellular activities. Bax has extensive amino acid homology with Bcl-2 and both homodimerizes and ...
Lecture: Fatty Acids Synthesis Recall the physiological role of
... Recall triglyceride degradation in adipose tissue by hormone sensitive lipase, and identify the hormone that regulates the hormone sensitive lipase. o During fasting, adipose TG broken down (lipolysis) o Lipases cleave FAs from TG: hormone sensitive lipase starts process Signaled by decreasing ins ...
... Recall triglyceride degradation in adipose tissue by hormone sensitive lipase, and identify the hormone that regulates the hormone sensitive lipase. o During fasting, adipose TG broken down (lipolysis) o Lipases cleave FAs from TG: hormone sensitive lipase starts process Signaled by decreasing ins ...
1. Substrate level phosphorylation A) is part
... group with the methyl carbon labeled with 14C is used in the last reaction cycle. All other reactions before and after use unlabeled acetate. Which carbon is labeled in the resulting product molecule? As you know, fatty acids are numbered with the carboxyl group being number 1. A) carbon number 2 B) ...
... group with the methyl carbon labeled with 14C is used in the last reaction cycle. All other reactions before and after use unlabeled acetate. Which carbon is labeled in the resulting product molecule? As you know, fatty acids are numbered with the carboxyl group being number 1. A) carbon number 2 B) ...
Milk Composition
... Do we need to alter protein content in milk? -decrease milk protein content - thought to be negatively related to dietary lipid content only true if fermentation is negatively affected by lipid. - increase milk protein content - rumen bypass or protected amino acids 10% efficiency with maximum incre ...
... Do we need to alter protein content in milk? -decrease milk protein content - thought to be negatively related to dietary lipid content only true if fermentation is negatively affected by lipid. - increase milk protein content - rumen bypass or protected amino acids 10% efficiency with maximum incre ...
Water soluble Vit. Vit C: (Ascorbic Acid)
... ,,vegetable diet lack this vit.. Alcoholism is an important precipitating factor for niacin deficiency . ...
... ,,vegetable diet lack this vit.. Alcoholism is an important precipitating factor for niacin deficiency . ...
AMPK and mTOR: Antagonist ATP Sensors
... AMP Activated Protein Kinase (AMPK) AMP Activated Protein Kinase (AMPK) is a metabolic-stress-sensing protein kinase; meaning it functions as a cellular fuel gauge. This enzyme serves to maintain cellular energy homeostasis, specifically during times of stress caused by exercise or nutrient intake ( ...
... AMP Activated Protein Kinase (AMPK) AMP Activated Protein Kinase (AMPK) is a metabolic-stress-sensing protein kinase; meaning it functions as a cellular fuel gauge. This enzyme serves to maintain cellular energy homeostasis, specifically during times of stress caused by exercise or nutrient intake ( ...
Small G-protein
... Rab-GTPases - small GTP binding proteins on vesicles. Related to the oncogene product Ras. Act as tethering factors that mediate initial interaction between membrane Bind to Rab effectors on target membrane. Over 30 diferent Rab proteins specific to different membranes. Another protein (guanine-nuc. ...
... Rab-GTPases - small GTP binding proteins on vesicles. Related to the oncogene product Ras. Act as tethering factors that mediate initial interaction between membrane Bind to Rab effectors on target membrane. Over 30 diferent Rab proteins specific to different membranes. Another protein (guanine-nuc. ...
rapid determination of total lipids in mosquitoes
... a much more efficient and widely used analytical lipid solvenr. The disadvantage is that the methanol in combination with tissul water also extracts non-lipid material such as glycerol, sugars, amino acids and some peptidis. This requires re-extraction with water to remove this non-lipid material or ...
... a much more efficient and widely used analytical lipid solvenr. The disadvantage is that the methanol in combination with tissul water also extracts non-lipid material such as glycerol, sugars, amino acids and some peptidis. This requires re-extraction with water to remove this non-lipid material or ...
SSG1-1
... The expressions of Gene in the SSG1-1 cells were increased upper twofold more than in the WT cells ...
... The expressions of Gene in the SSG1-1 cells were increased upper twofold more than in the WT cells ...
red blood cell (rbc) membrane and enzyme disorders
... fully compensated hemolytic anemia diagnosed later in life ...
... fully compensated hemolytic anemia diagnosed later in life ...
Thiol regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and innate immunity
... http://ngrams.googlelabs.com). Both inflammatory cytokines, particularly IL (interleukin)-1 and TNF (tumour necrosis factor), and oxidative stress have been implicated in so many diseases that it would be difficult to find one where neither has been involved. Both are interpreted with an ‘axis-of-ev ...
... http://ngrams.googlelabs.com). Both inflammatory cytokines, particularly IL (interleukin)-1 and TNF (tumour necrosis factor), and oxidative stress have been implicated in so many diseases that it would be difficult to find one where neither has been involved. Both are interpreted with an ‘axis-of-ev ...
fae04be7f127386
... For proteins synthesized on the rough endoplasmic reticulum, additional sorting signals such as sugars and phosphate groups can be added by enzymes that modify the chemical structure of the protein. ...
... For proteins synthesized on the rough endoplasmic reticulum, additional sorting signals such as sugars and phosphate groups can be added by enzymes that modify the chemical structure of the protein. ...
lec27_2013 - Andrew.cmu.edu
... i) the substrate is used to name the enzyme, Keep in mind that many enzymatic reactions run in both directions in metabolism, consequently the “product” may be used to name the enzyme. ii) the nature of the chemical reaction. iii) most names end in “-ase” Enzymes Involved in Group Transfer Reactions ...
... i) the substrate is used to name the enzyme, Keep in mind that many enzymatic reactions run in both directions in metabolism, consequently the “product” may be used to name the enzyme. ii) the nature of the chemical reaction. iii) most names end in “-ase” Enzymes Involved in Group Transfer Reactions ...
G5. Strategies for Stabilization of Enzymes in Organic
... Other methods for modifying enzymes have not yet been able to achieve same popularity than previously mentioned methods. The basics of propanol-rinsed enzyme preparation (PREP) are based on reactions with dry n-propanol. The goal is to achieve low-water media by rinsing enzymes with n-propanol. Apar ...
... Other methods for modifying enzymes have not yet been able to achieve same popularity than previously mentioned methods. The basics of propanol-rinsed enzyme preparation (PREP) are based on reactions with dry n-propanol. The goal is to achieve low-water media by rinsing enzymes with n-propanol. Apar ...
Lipid Metabolizması - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... Fatty Acid Synthesis • Fatty acids are built from 2-C units derived from acetyl-CoA • Acetate units are activated for transfer to growing FA chain by conversion to malonylCoA • Decarboxylation of malonyl-CoA and reducing power of NADPH drive chain growth • Chain grows to 16-carbons (eight acetylCoA ...
... Fatty Acid Synthesis • Fatty acids are built from 2-C units derived from acetyl-CoA • Acetate units are activated for transfer to growing FA chain by conversion to malonylCoA • Decarboxylation of malonyl-CoA and reducing power of NADPH drive chain growth • Chain grows to 16-carbons (eight acetylCoA ...
Chapter 16 (Part 3)
... Fatty Acid Synthesis • Fatty acids are built from 2-C units derived from acetyl-CoA • Acetate units are activated for transfer to growing FA chain by conversion to malonylCoA • Decarboxylation of malonyl-CoA and reducing power of NADPH drive chain growth • Chain grows to 16-carbons (eight acetylCoA ...
... Fatty Acid Synthesis • Fatty acids are built from 2-C units derived from acetyl-CoA • Acetate units are activated for transfer to growing FA chain by conversion to malonylCoA • Decarboxylation of malonyl-CoA and reducing power of NADPH drive chain growth • Chain grows to 16-carbons (eight acetylCoA ...
Biochem. of anesthetics
... • More lipophilic = greater sequestration in the myelin and cell membrane; serves as depot for slow release of anesthetic = slower onset, but prolonged action Fraction unbound • Increase in molecular weight correlates to increase in plasma & tissue proteins binding • High protein binding slow upta ...
... • More lipophilic = greater sequestration in the myelin and cell membrane; serves as depot for slow release of anesthetic = slower onset, but prolonged action Fraction unbound • Increase in molecular weight correlates to increase in plasma & tissue proteins binding • High protein binding slow upta ...
Efficient Uniform Isotope Labeling of Proteins Expressed in
... Uniform isotope labeling is a key tool for NMR studies on recombinant proteins and their interaction with ligands of pharmaceutical interest. For this purpose, most recombinant proteins have been expressed in labeled form using E. coli. However, such expression is restricted to proteins of a noncomp ...
... Uniform isotope labeling is a key tool for NMR studies on recombinant proteins and their interaction with ligands of pharmaceutical interest. For this purpose, most recombinant proteins have been expressed in labeled form using E. coli. However, such expression is restricted to proteins of a noncomp ...
Lipid signaling

Lipid signaling, broadly defined, refers to any biological signaling event involving a lipid messenger that binds a protein target, such as a receptor, kinase or phosphatase, which in turn mediate the effects of these lipids on specific cellular responses. Lipid signaling is thought to be qualitatively different from other classical signaling paradigms (such as monoamine neurotransmission) because lipids can freely diffuse through membranes (see osmosis.) One consequence of this is that lipid messengers cannot be stored in vesicles prior to release and so are often biosynthesized ""on demand"" at their intended site of action. As such, many lipid signaling molecules cannot circulate freely in solution but, rather, exist bound to special carrier proteins in serum.























