Unit 2
... 7. To use an approximate guideline for the buffer capacity (± 1 pH unit change) of a buffer system. 8. To calculate pH changes in buffer systems from the addition of strong acid or strong base. Reading Assignments: ...
... 7. To use an approximate guideline for the buffer capacity (± 1 pH unit change) of a buffer system. 8. To calculate pH changes in buffer systems from the addition of strong acid or strong base. Reading Assignments: ...
Aim: What is fermentation?
... sugars can occur by fermentation. •Glycolysis can generate ATP from glucose by substratelevel phosphorylation as long as there is a supply of NAD+ to accept electrons. ...
... sugars can occur by fermentation. •Glycolysis can generate ATP from glucose by substratelevel phosphorylation as long as there is a supply of NAD+ to accept electrons. ...
Chapter 25
... • Organic molecules that exist in minute quantities in food – Essential vitamins must be obtained by diet ...
... • Organic molecules that exist in minute quantities in food – Essential vitamins must be obtained by diet ...
acids and bases - Althea`s Academy
... A variation of the colorimetric method which is more practical includes strips of paper impregnated with an indicator ◦ Merely dipping the paper in the unknown sol’n produces a color on the paper which can be compared with charts supplied by the manufacture ◦ This is of value to diabetic patients fo ...
... A variation of the colorimetric method which is more practical includes strips of paper impregnated with an indicator ◦ Merely dipping the paper in the unknown sol’n produces a color on the paper which can be compared with charts supplied by the manufacture ◦ This is of value to diabetic patients fo ...
Macromolecules practice worksheet key
... 5. Why are the chemical shapes of lipids different between saturated and unsaturated fats? Saturated fats have the maximum amount of hydrogens bound to the carbons of the F.A. chains, therefore, they lack double bonds and can pack tightly forming solids at room temp. and unsaturated fats have less ...
... 5. Why are the chemical shapes of lipids different between saturated and unsaturated fats? Saturated fats have the maximum amount of hydrogens bound to the carbons of the F.A. chains, therefore, they lack double bonds and can pack tightly forming solids at room temp. and unsaturated fats have less ...
26.9 Purines ond pyrimidines ,,,,,f sr`-c
... Organisms need to synthesizepurine and pyrimidine basesfor incorporation into the nucleic acids RNA and DNA. Moreover, nucleosides such as adenosine are found as part of ATB cyclic AMf; CoA (coenzymeA), NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide), and FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide). The atoms that c ...
... Organisms need to synthesizepurine and pyrimidine basesfor incorporation into the nucleic acids RNA and DNA. Moreover, nucleosides such as adenosine are found as part of ATB cyclic AMf; CoA (coenzymeA), NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide), and FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide). The atoms that c ...
mRNA Codon/Amino Acid Chart
... mRNA Codon/Amino Acid Chart Teacher Directions Explain to students that they are to: • Transcribe the DNA into mRNA codons by writing the complementary bases. • Find a codon’s first base in the first column of the chart; stay in this row. • Find the second base in the middle of the chart, stay in t ...
... mRNA Codon/Amino Acid Chart Teacher Directions Explain to students that they are to: • Transcribe the DNA into mRNA codons by writing the complementary bases. • Find a codon’s first base in the first column of the chart; stay in this row. • Find the second base in the middle of the chart, stay in t ...
Cellular Respiration Concept Questions
... 3. Cells that are more active have a higher number of mitochondria. Why would this be? 4. Cellular respiration uses glucose, a high energy molecule and produces CO2 and water, low energy molecules. a) Is it spontaneous? b) Is it exergonic? c) What happens to the energy released from glucose? 5. Why ...
... 3. Cells that are more active have a higher number of mitochondria. Why would this be? 4. Cellular respiration uses glucose, a high energy molecule and produces CO2 and water, low energy molecules. a) Is it spontaneous? b) Is it exergonic? c) What happens to the energy released from glucose? 5. Why ...
MEDICINAL CHEMISTRY-III
... enzymes (hydrolytic enzymes proteases…..). Anti-inflammatory drugs may act by interfering with one or more of these processes:-antibody production or antigen-antibody complex. -interference with the formation and release of chemical mediator of inflammation. -stabilization of liposomal membranes. ...
... enzymes (hydrolytic enzymes proteases…..). Anti-inflammatory drugs may act by interfering with one or more of these processes:-antibody production or antigen-antibody complex. -interference with the formation and release of chemical mediator of inflammation. -stabilization of liposomal membranes. ...
Microbial Metabolism
... What happens in anaerobic respiration? • Final electron acceptor is not oxygen – Various amounts of ATP produced – Slower and less ATP than aerobic respiration – Uses some parts of Krebs cycle – Thus slower growth for anaerobes than aerobes ...
... What happens in anaerobic respiration? • Final electron acceptor is not oxygen – Various amounts of ATP produced – Slower and less ATP than aerobic respiration – Uses some parts of Krebs cycle – Thus slower growth for anaerobes than aerobes ...
INTRODUCTORY BIOCHEMISTRY BI 28 Second Midterm
... CH2OPO3H218. [2] Gluconeogenesis shares some, but not all, enzymes with the glycolytic pathway. It would appear to be more efficient if both pathways used all of the same enzymes since the pathways are essentially the reverse of each other. Why don’t both pathways use all of the same enzymes? A) The ...
... CH2OPO3H218. [2] Gluconeogenesis shares some, but not all, enzymes with the glycolytic pathway. It would appear to be more efficient if both pathways used all of the same enzymes since the pathways are essentially the reverse of each other. Why don’t both pathways use all of the same enzymes? A) The ...
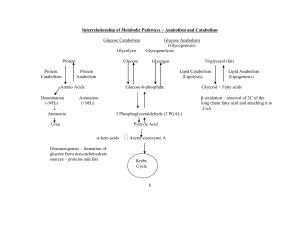
Overview of Energy and Metabolism
... BMR in influence by age, gender, physical condition, body weight, and genes. ...
... BMR in influence by age, gender, physical condition, body weight, and genes. ...
Name Date Ch 7 – Cellular Respiration and Fermentation (Biology
... Concept 7.5 Fermentation and anaerobic respiration enable cells to produce ATP without the use of oxygen. 23. What conditions force the cell to go into the fermentation process? At what point in the three processes of cellular respiration does this happen? ...
... Concept 7.5 Fermentation and anaerobic respiration enable cells to produce ATP without the use of oxygen. 23. What conditions force the cell to go into the fermentation process? At what point in the three processes of cellular respiration does this happen? ...
Naming Acids and Bases ppt
... Rules for Naming Acids that Do Not Contain Oxygen in the Anion: • Since all these acids have the same cation, H+, we don't need to name the cation. • The acid name comes from the root name of the anion name. • The prefix hydro- and the suffix -ic are then added to the root name of the anion. So, HC ...
... Rules for Naming Acids that Do Not Contain Oxygen in the Anion: • Since all these acids have the same cation, H+, we don't need to name the cation. • The acid name comes from the root name of the anion name. • The prefix hydro- and the suffix -ic are then added to the root name of the anion. So, HC ...
GLOBAL WARMING - Agronomy Courses
... – Absorbed through wall of the rumen in ruminants or large intestine of ruminants and nonruminants – Metabolized by the animal for energy • Main source of energy for ruminants – Provide 70% of the energy in ruminants – Production of different VFAs and methane vary with diet • Dietary factors that in ...
... – Absorbed through wall of the rumen in ruminants or large intestine of ruminants and nonruminants – Metabolized by the animal for energy • Main source of energy for ruminants – Provide 70% of the energy in ruminants – Production of different VFAs and methane vary with diet • Dietary factors that in ...
POULTRY BREEDING
... - achieve and maintain anaerobic conditions, - exclude aerobic microbes, - develop lactic acid bacteria. ...
... - achieve and maintain anaerobic conditions, - exclude aerobic microbes, - develop lactic acid bacteria. ...
Biological Molecules wHelp Sheet
... 23. Metabolism is the collective term used to describe all the chemical reactions taking place inside living organisms. Why is water so important for metabolic reactions? ...
... 23. Metabolism is the collective term used to describe all the chemical reactions taking place inside living organisms. Why is water so important for metabolic reactions? ...
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives 1. Background and Properties
... • Amides: The name of the related acid is used first and the oic acid or ic acid suffix is replaced by amide (only for 1º-amides). e.g. CH3CONH2 is ethanamide (or acetamide). 2º & 3º-amides have alkyl substituents on the nitrogen atom. These are designated by "N-alkyl" term(s) at the beginning of th ...
... • Amides: The name of the related acid is used first and the oic acid or ic acid suffix is replaced by amide (only for 1º-amides). e.g. CH3CONH2 is ethanamide (or acetamide). 2º & 3º-amides have alkyl substituents on the nitrogen atom. These are designated by "N-alkyl" term(s) at the beginning of th ...
25.4 ATP yield
... phate bonds required to activate the fatty acid as two AIP molecules. We can do this because hydrolysis of one molecule of AIP to AMP and 2P; is equivalent to the hydrolysis of 2AIP to 2ADP andzPi. Table 25.1 shows that for every molecule of palmitic acid completely oxidized to carbon dioxide and wa ...
... phate bonds required to activate the fatty acid as two AIP molecules. We can do this because hydrolysis of one molecule of AIP to AMP and 2P; is equivalent to the hydrolysis of 2AIP to 2ADP andzPi. Table 25.1 shows that for every molecule of palmitic acid completely oxidized to carbon dioxide and wa ...
Ch. 5 "The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
... Carbohydrates: Fuel and Building Material A. Sugars, the smallest carbohydrates, serve as fuel and carbon sources. B. Polysaccharides, the polymers of sugars, have storage and structural roles. ...
... Carbohydrates: Fuel and Building Material A. Sugars, the smallest carbohydrates, serve as fuel and carbon sources. B. Polysaccharides, the polymers of sugars, have storage and structural roles. ...
Chemistry 2000 Lecture 20: Organic bases
... already talked about, the only significant group of organic bases are compounds containing nitrogen atoms, mainly amines, although some others (e.g. imines, compounds that contain a carbon-nitrogen double bond) can also be reasonably strong bases. ...
... already talked about, the only significant group of organic bases are compounds containing nitrogen atoms, mainly amines, although some others (e.g. imines, compounds that contain a carbon-nitrogen double bond) can also be reasonably strong bases. ...
Butyric acid
Butyric acid (from Greek βούτῡρον, meaning ""butter""), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, abbreviated BTA, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in milk, especially goat, sheep and buffalo milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). It has an unpleasant smell and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). It can be detected by mammals with good scent detection abilities (such as dogs) at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million.Butyric acid is present in, and is the main distinctive smell of, human vomit.Butyric acid was first observed (in impure form) in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. The name of butyric acid comes from the Latin word for butter, butyrum (or buturum), the substance in which butyric acid was first found.