Amino Acids
... Isoelectric point: at neutral pH, alanine exists as the dipolar form II, net charge is zero. Isoelectric point (pI) is the pH at which aa is electrically neutral. For aa that has only two dissociable hydrogens, pI = (pK1 + pK2)/2, i.e., (2.3 + 9.1)/2 = 5.7. pI corresponds to pH at which structure II ...
... Isoelectric point: at neutral pH, alanine exists as the dipolar form II, net charge is zero. Isoelectric point (pI) is the pH at which aa is electrically neutral. For aa that has only two dissociable hydrogens, pI = (pK1 + pK2)/2, i.e., (2.3 + 9.1)/2 = 5.7. pI corresponds to pH at which structure II ...
Slide 1
... Gastric lipase -----acid stable • These enzymes are most effective for short and medium chain fatty acids • Milk, egg yolk and fats containing short chain fatty acids are suitable substrates for its action • Play important role in lipid digestion in neonates ...
... Gastric lipase -----acid stable • These enzymes are most effective for short and medium chain fatty acids • Milk, egg yolk and fats containing short chain fatty acids are suitable substrates for its action • Play important role in lipid digestion in neonates ...
Lecture 27
... Friday: Ketogenic vs. glucogenic (or both) amino acids-what common metabolites do this amino acids go towards? ...
... Friday: Ketogenic vs. glucogenic (or both) amino acids-what common metabolites do this amino acids go towards? ...
Chapter 7
... V. Biosynthesis and Storage (Figure 8.20). *Tissues differ in their preferred source of fuel. The brain, nervous system, and red blood cells rely primarily on glucose, while other tissues use a mix of glucose, fatty acids, and ketone bodies as fuel sources. A. Making carbohydrate (glucose). *When ca ...
... V. Biosynthesis and Storage (Figure 8.20). *Tissues differ in their preferred source of fuel. The brain, nervous system, and red blood cells rely primarily on glucose, while other tissues use a mix of glucose, fatty acids, and ketone bodies as fuel sources. A. Making carbohydrate (glucose). *When ca ...
0 - Microbiology
... of reaction to 16 hr. to confirm the presence of the two transaminases of much lower activity which had isoleucine and valine as substrates. In some preparations there seemed to be some evidence of slight alanine, ornithine, threonine and arginine transaminase activities but the results were variabl ...
... of reaction to 16 hr. to confirm the presence of the two transaminases of much lower activity which had isoleucine and valine as substrates. In some preparations there seemed to be some evidence of slight alanine, ornithine, threonine and arginine transaminase activities but the results were variabl ...
Condensation Polymerisation
... of glucose molecules. A condensation polymer is a polymer formed by the removal of atoms from adjacent monomer molecules to allow them to join together. Small molecules are produced as well as the polymer molecule and the process is known as condensation polymerisation. Formation of starch from gluc ...
... of glucose molecules. A condensation polymer is a polymer formed by the removal of atoms from adjacent monomer molecules to allow them to join together. Small molecules are produced as well as the polymer molecule and the process is known as condensation polymerisation. Formation of starch from gluc ...
Oxidation Oxidation of aldoses forms acids as end products . CHO
... of 300 to 400 glucose units . Amylose is soluble in water and is less viscous than starch . Amylopectin This polysaccharide possesses the same basic chain as amylose but they are larger molecules . They have molecular weight as high as 2,00,000 or more m corresponding to 1000 to 1300 glucose units G ...
... of 300 to 400 glucose units . Amylose is soluble in water and is less viscous than starch . Amylopectin This polysaccharide possesses the same basic chain as amylose but they are larger molecules . They have molecular weight as high as 2,00,000 or more m corresponding to 1000 to 1300 glucose units G ...
Test 2
... Stimulation of liver by the hormone glucagon results in several metabolic changes that lead to the increase in glucose synthesis and excretion by liver. One of these changes involves inhibition of glycolysis and stimulation of gluconeogenesis (i.e. the conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate to glucose). ...
... Stimulation of liver by the hormone glucagon results in several metabolic changes that lead to the increase in glucose synthesis and excretion by liver. One of these changes involves inhibition of glycolysis and stimulation of gluconeogenesis (i.e. the conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate to glucose). ...
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
... Once the Acetic Acid enters the Matrix it combines with Coenzyme A to form a new molecule called Acetyl-CoA. The Acetyl-CoA then enters the Krebs Cycle. ...
... Once the Acetic Acid enters the Matrix it combines with Coenzyme A to form a new molecule called Acetyl-CoA. The Acetyl-CoA then enters the Krebs Cycle. ...
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
... Once the Acetic Acid enters the Matrix it combines with Coenzyme A to form a new molecule called Acetyl-CoA. The Acetyl-CoA then enters the Krebs Cycle. ...
... Once the Acetic Acid enters the Matrix it combines with Coenzyme A to form a new molecule called Acetyl-CoA. The Acetyl-CoA then enters the Krebs Cycle. ...
appendix a
... Figure 1.6 – Schematic process of MS tune with IntelliStartTM. Figure 1.7 – Chromatograms of PGE2, Kit and IC. Figure 1.8 – Chromatograms of12S-HETE, Kit and IC. Figure 1.9 – Calibration line of PA results processed by TargetLynxTM program. Figure 1.10 – Representative peak of PA (2μM). ...
... Figure 1.6 – Schematic process of MS tune with IntelliStartTM. Figure 1.7 – Chromatograms of PGE2, Kit and IC. Figure 1.8 – Chromatograms of12S-HETE, Kit and IC. Figure 1.9 – Calibration line of PA results processed by TargetLynxTM program. Figure 1.10 – Representative peak of PA (2μM). ...
Lecture notes Chapter 27-28
... (ADP) and fiboflavin. Riboflavin, also known as vitamin B2, consists of ribitol, a sugar alcohol, and flavin. As a coenzyme, two nitrogen atoms in the flavin part of the FAD coenzyme accept the hydrogen, which reduces the FAD to FADH2. FAD typically participates in oxidation reactions that produce a ...
... (ADP) and fiboflavin. Riboflavin, also known as vitamin B2, consists of ribitol, a sugar alcohol, and flavin. As a coenzyme, two nitrogen atoms in the flavin part of the FAD coenzyme accept the hydrogen, which reduces the FAD to FADH2. FAD typically participates in oxidation reactions that produce a ...
O 2
... only used in cell that produces it only short term energy storage carbohydrates & fats are long term energy storage Whoa! Pass me the glucose & oxygen! ...
... only used in cell that produces it only short term energy storage carbohydrates & fats are long term energy storage Whoa! Pass me the glucose & oxygen! ...
Sulfuric Acid
... produced as a by-product are the manufacture of chlorofluorohydrocarbons, manufacture of aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons, production of high surface area silica, and the manufacture of phosphoric acid and esters of phosphoric acid. 5. Hydrogen Chloride Produced from Incineration of Waste Organics ...
... produced as a by-product are the manufacture of chlorofluorohydrocarbons, manufacture of aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons, production of high surface area silica, and the manufacture of phosphoric acid and esters of phosphoric acid. 5. Hydrogen Chloride Produced from Incineration of Waste Organics ...
Review #3 Chapters 9 – 10
... b. The Calvin cycle uses ATP and NADPH to convert CO2 to sugar c. Photosystem I contains P700 chlorophyll a molecules at the reaction center; photosystem II contains P680 molecules d. In chemiosmosis, electron transport chains pump protons (H+) across a membrane from a region of high H+ concentratio ...
... b. The Calvin cycle uses ATP and NADPH to convert CO2 to sugar c. Photosystem I contains P700 chlorophyll a molecules at the reaction center; photosystem II contains P680 molecules d. In chemiosmosis, electron transport chains pump protons (H+) across a membrane from a region of high H+ concentratio ...
Quality Components of Feeds
... and wetter silages normally have a lower pH, meaning more acid has been produced during the fermentation process. Drier silages require less acid to achieve stable conditions. Typical pasture silage should be pH< 4.5. Silages with a pH of less than 3.8 can cause decreases in feed intake and possible ...
... and wetter silages normally have a lower pH, meaning more acid has been produced during the fermentation process. Drier silages require less acid to achieve stable conditions. Typical pasture silage should be pH< 4.5. Silages with a pH of less than 3.8 can cause decreases in feed intake and possible ...
Amino Acid composition of vegetables and fruits from
... Fruits and vegetables constitute staple foodstuffs in most Asian countries including the Philippines. Although they are thought to be good sources of vitamins, minerals and fibre, their importance in providing a balanced diet of protein is usually overlooked. Ample research effort has however shown ...
... Fruits and vegetables constitute staple foodstuffs in most Asian countries including the Philippines. Although they are thought to be good sources of vitamins, minerals and fibre, their importance in providing a balanced diet of protein is usually overlooked. Ample research effort has however shown ...
Chapter 5, part A
... • Removing is Dephosphorylation - releasing energy – ATP is generated by the phosphorylation of ...
... • Removing is Dephosphorylation - releasing energy – ATP is generated by the phosphorylation of ...
Safety Data Sheet - Fisher Scientific
... Appropriate Engineering controls: Emergency eye wash fountains and safety showers should be available in the immediate vicinity of use/handling.Provide exhaust ventilation or other engineering controls to keep the airborne concentrations of vapor or mists below the applicable workplace exposure limi ...
... Appropriate Engineering controls: Emergency eye wash fountains and safety showers should be available in the immediate vicinity of use/handling.Provide exhaust ventilation or other engineering controls to keep the airborne concentrations of vapor or mists below the applicable workplace exposure limi ...
146/18 = 8.1 ATP/carbon Atom. For Lauric acid
... The globins are hydrolyzed to free amino acids that are recycled and the iron is removed from the porphyrin ring and saved in the iron-storage protein, ferritin, for later use. 28.42 Functional groups in biliverdin that are from oxidation: two carbon atoms at the top are oxidized from hydrocarbons t ...
... The globins are hydrolyzed to free amino acids that are recycled and the iron is removed from the porphyrin ring and saved in the iron-storage protein, ferritin, for later use. 28.42 Functional groups in biliverdin that are from oxidation: two carbon atoms at the top are oxidized from hydrocarbons t ...
Cellular Respiration
... cells to support energy needs - Maximum energy production Anaerobic metabolism – When the demand for oxygen outstrips the body’s ability to deliver it – Low energy production ...
... cells to support energy needs - Maximum energy production Anaerobic metabolism – When the demand for oxygen outstrips the body’s ability to deliver it – Low energy production ...
Basic Minerals™ A Comprehensive Mineral/Trace Element Formula
... • Manganese is essential for antioxidant systems in the body, bone growth, fat metabolism, and protein, nucleic acid, and cartilage synthesis. • Chromium is required for normal blood sugar and lipid metabolism; it is an integral component of glucose tolerance factor (GTF). • Molybdenum is involved i ...
... • Manganese is essential for antioxidant systems in the body, bone growth, fat metabolism, and protein, nucleic acid, and cartilage synthesis. • Chromium is required for normal blood sugar and lipid metabolism; it is an integral component of glucose tolerance factor (GTF). • Molybdenum is involved i ...
bottom-up-methodology
... ASN[CCO-CYTOSOL] # cysteine and methionine require sulfur handling; if it is not clear # how to start from SULFATE, try starting from HS (hydrogen sulfide) instead # sulfur bearing amino acids can generally be saved for last # requires serine, acetyl-CoA, and hydrogen sulfide CYS[CCO-CYTOSOL] # glut ...
... ASN[CCO-CYTOSOL] # cysteine and methionine require sulfur handling; if it is not clear # how to start from SULFATE, try starting from HS (hydrogen sulfide) instead # sulfur bearing amino acids can generally be saved for last # requires serine, acetyl-CoA, and hydrogen sulfide CYS[CCO-CYTOSOL] # glut ...
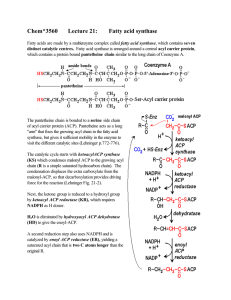
Chem*3560 Lecture 21: Fatty acid synthase
... protein of mass 8.8 kDa. Six additional catalytic subunits are arranged around the central ACP (Lehninger p. 777 and Figs. 21-5 to 21-7; however these figures should be regarded as schematic rather than realistic). The pantetheine arm is anchored into ACP, but is long enough to allow covalently boun ...
... protein of mass 8.8 kDa. Six additional catalytic subunits are arranged around the central ACP (Lehninger p. 777 and Figs. 21-5 to 21-7; however these figures should be regarded as schematic rather than realistic). The pantetheine arm is anchored into ACP, but is long enough to allow covalently boun ...
Butyric acid
Butyric acid (from Greek βούτῡρον, meaning ""butter""), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, abbreviated BTA, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in milk, especially goat, sheep and buffalo milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). It has an unpleasant smell and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). It can be detected by mammals with good scent detection abilities (such as dogs) at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million.Butyric acid is present in, and is the main distinctive smell of, human vomit.Butyric acid was first observed (in impure form) in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. The name of butyric acid comes from the Latin word for butter, butyrum (or buturum), the substance in which butyric acid was first found.