Biology 123 SI-Dr. Raut`s Class Session 10
... 1. How does the pyruvate that gets produced by glycolysis get to the citric acid cycle? What is this step called? Draw it out. First of all, pyruvate is in the cytoplasm and needs to be moved into the mitochondria. Since pyruvate has a negative charge, the mitochondria’s membrane does not want to le ...
... 1. How does the pyruvate that gets produced by glycolysis get to the citric acid cycle? What is this step called? Draw it out. First of all, pyruvate is in the cytoplasm and needs to be moved into the mitochondria. Since pyruvate has a negative charge, the mitochondria’s membrane does not want to le ...
pertemuan 11 (respirasi, glikolisis, siklus krebs) [โหมดความเข้ากันได้]
... involves energy capture through incorporation of carbon into small sugars, which are reduced by energy from photosynthetic electron transport. The citric acid cycle involves energy release through loss of carbon from small organic acids which are oxidized, producing electrons to be used in mitochond ...
... involves energy capture through incorporation of carbon into small sugars, which are reduced by energy from photosynthetic electron transport. The citric acid cycle involves energy release through loss of carbon from small organic acids which are oxidized, producing electrons to be used in mitochond ...
Mitochondrial Respiration
... involves energy capture through incorporation of carbon into small sugars, which are reduced by energy from photosynthetic electron transport. The citric acid cycle involves energy release through loss of carbon from small organic acids which are oxidized, producing electrons to be used in mitochond ...
... involves energy capture through incorporation of carbon into small sugars, which are reduced by energy from photosynthetic electron transport. The citric acid cycle involves energy release through loss of carbon from small organic acids which are oxidized, producing electrons to be used in mitochond ...
OCHeM.com ©1999 Thomas Poon Amino Acids, Peptides, and
... Be able to predict the structure of any amino acid based on its pKa values and the pH of the surrounding solution. The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation can be used to determine the major form of an amino acid at any pH. In general, if the pKa < pH a protic functional group will be “more acidic than th ...
... Be able to predict the structure of any amino acid based on its pKa values and the pH of the surrounding solution. The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation can be used to determine the major form of an amino acid at any pH. In general, if the pKa < pH a protic functional group will be “more acidic than th ...
lecture_22 - WordPress.com
... Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase: an enzyme similar to succinate dehydrogenase ...
... Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase: an enzyme similar to succinate dehydrogenase ...
dynasty® xt pro 14/10
... promote a healthy skin and hair coat. DHA plays a role in the anti-inflammatory process, is a structural component of nerve cells and a key component of heart tissue. Quality Protein with Guaranteed Lysine, Methionine and Threonine - Guaranteed lysine, methionine and threonine levels help ensure qua ...
... promote a healthy skin and hair coat. DHA plays a role in the anti-inflammatory process, is a structural component of nerve cells and a key component of heart tissue. Quality Protein with Guaranteed Lysine, Methionine and Threonine - Guaranteed lysine, methionine and threonine levels help ensure qua ...
Fatty acid productivity of Scenedesmus obliquus under nitrogen
... C18:1 was the most predominant composition, accounting for 52.8% and 66% of the total fatty acids in the mixotrophic and heterotrophic cultures, respectively. The highest unsaturated fatty acid content was obtained in mixotrophic culture ...
... C18:1 was the most predominant composition, accounting for 52.8% and 66% of the total fatty acids in the mixotrophic and heterotrophic cultures, respectively. The highest unsaturated fatty acid content was obtained in mixotrophic culture ...
Slide 1 - Elsevier
... FIGURE 36-1: A depolarizing stimulus at the presynaptic terminal triggers glutamate release. Glutamate binds to the NMDA receptor and, as a consequence, an influx of calcium ions occurs in the postsynaptic neuron. During certain pathological scenarios such as stroke, extrasynaptic NMDA receptors ar ...
... FIGURE 36-1: A depolarizing stimulus at the presynaptic terminal triggers glutamate release. Glutamate binds to the NMDA receptor and, as a consequence, an influx of calcium ions occurs in the postsynaptic neuron. During certain pathological scenarios such as stroke, extrasynaptic NMDA receptors ar ...
Nucleic acid chemistry - Beilstein
... were significantly more reactive than phosphordiesters or -triesters. Finally, this approach using phosphoramidites as nucleoside building blocks was significantly further developed in 1981 by Beaucage and Caruthers [4]. Since then, oligonucleotides of up to 50-mers in length have become available b ...
... were significantly more reactive than phosphordiesters or -triesters. Finally, this approach using phosphoramidites as nucleoside building blocks was significantly further developed in 1981 by Beaucage and Caruthers [4]. Since then, oligonucleotides of up to 50-mers in length have become available b ...
...the story of making proteins continued… After transcription occurs
... then joined together this is called a ________________________________. Both tRNA’s shift down a seat and the next tRNA comes into the ribosome with it’s matching anticodon and amino acid. This third amino acid gets bonded to the other two a chain is starting to form! This keeps continuing unti ...
... then joined together this is called a ________________________________. Both tRNA’s shift down a seat and the next tRNA comes into the ribosome with it’s matching anticodon and amino acid. This third amino acid gets bonded to the other two a chain is starting to form! This keeps continuing unti ...
Bios 302 FINAL FOR 1999.
... 11. (20 pts) Illustrate the possible fates of glucose 6-P in the liver and what functions these fates support. Illustrate how fructose 2,6-bisphosphate and cAMP are involved in regulating these pathways. (Note that only fates of G-6P are requested, not synthesis of G-6-P. You may simply name the pat ...
... 11. (20 pts) Illustrate the possible fates of glucose 6-P in the liver and what functions these fates support. Illustrate how fructose 2,6-bisphosphate and cAMP are involved in regulating these pathways. (Note that only fates of G-6P are requested, not synthesis of G-6-P. You may simply name the pat ...
Enzymatic Production of D-Amino Acids
... synthesis of Fluvalinate® and D-cycloserine®, respectively, which are further used as agrochemicals and pharmaceuticals (6). Industrial fermentation of microorganisms has been used to produce amino acids for world markets in animal nutrition and food additives for more than 30 yr. The ability to pro ...
... synthesis of Fluvalinate® and D-cycloserine®, respectively, which are further used as agrochemicals and pharmaceuticals (6). Industrial fermentation of microorganisms has been used to produce amino acids for world markets in animal nutrition and food additives for more than 30 yr. The ability to pro ...
Cellular Respiration
... different pathway. The combined process of this pathway and glycolysis is called fermentation. Fermentation releases energy from food molecules by producing ATP in the absence of oxygen. ...
... different pathway. The combined process of this pathway and glycolysis is called fermentation. Fermentation releases energy from food molecules by producing ATP in the absence of oxygen. ...
Artificial Insemination In Swine
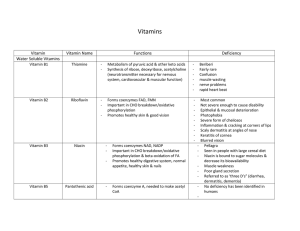
... 6. Folic Acid (B9) – helps make proteins from amino acids. 7. Biotin (B7) deficiency: dermatitis and loss of hair (same as pantothenic acid) 8. Vitamin B12 (cyanacobalamin is most common synthetic form) Found in animal products and manufactured by bacteria. Associated with appetite, anemia, and hat ...
... 6. Folic Acid (B9) – helps make proteins from amino acids. 7. Biotin (B7) deficiency: dermatitis and loss of hair (same as pantothenic acid) 8. Vitamin B12 (cyanacobalamin is most common synthetic form) Found in animal products and manufactured by bacteria. Associated with appetite, anemia, and hat ...
Anaerobic Respiration
... respiration when oxygen is present, but when oxygen is in short supply, they use anaerobic respiration instead. Certain bacteria can only use anaerobic respiration. In fact, they may not be able to survive at all in the presence of oxygen. ...
... respiration when oxygen is present, but when oxygen is in short supply, they use anaerobic respiration instead. Certain bacteria can only use anaerobic respiration. In fact, they may not be able to survive at all in the presence of oxygen. ...
幻灯片 1
... A small protein called colipase(辅脂酶) helps bind the water-soluble lipase to the lipid substrates. Colipase also activates lipase by holding it in a conformation with an open active site. The initial products of fat hydrolysis are free fatty acids and monoacylglycerols. These molecules are transporte ...
... A small protein called colipase(辅脂酶) helps bind the water-soluble lipase to the lipid substrates. Colipase also activates lipase by holding it in a conformation with an open active site. The initial products of fat hydrolysis are free fatty acids and monoacylglycerols. These molecules are transporte ...
Zdroje volných radikál* ROS
... Biochemistry of aging – Free radicals and antioxidants Petr Tůma and Eva Samcová ...
... Biochemistry of aging – Free radicals and antioxidants Petr Tůma and Eva Samcová ...
WHAT ARE NEURAL TUBE DEFECTS (NTDs)?
... monoglutamates for absorption [4] Monoglutamate is readily absorbed from the gut via energy-dependent, carrier-mediated mechanisms, involving membrane-associated folate-binding proteins [4] ...
... monoglutamates for absorption [4] Monoglutamate is readily absorbed from the gut via energy-dependent, carrier-mediated mechanisms, involving membrane-associated folate-binding proteins [4] ...
Respiratory chain is the most productive pathway to make ATP
... cofactor, acetyl coenzyme A. The catabolism of molecules from all three major foodscarbohydrate, protein and lipids-produces acetyl coenzyme A. Acetyl coenzyme A or acetyl CoA, is the fuel for citric acid cycle. Fatty acids are major source of acetyl CoA. A series of reactions called -oxidation pat ...
... cofactor, acetyl coenzyme A. The catabolism of molecules from all three major foodscarbohydrate, protein and lipids-produces acetyl coenzyme A. Acetyl coenzyme A or acetyl CoA, is the fuel for citric acid cycle. Fatty acids are major source of acetyl CoA. A series of reactions called -oxidation pat ...
1 - SMIC Nutrition Science
... Answer (key points): Anabolism tends to take place in the cytoplasm, whereas catabolism takes place primarily in mitochondria. This separation or compartmentalization is important, because it enables both anabolic and catabolic pathways to function simultaneously. Catabolic pathways that break down ...
... Answer (key points): Anabolism tends to take place in the cytoplasm, whereas catabolism takes place primarily in mitochondria. This separation or compartmentalization is important, because it enables both anabolic and catabolic pathways to function simultaneously. Catabolic pathways that break down ...
Cellular Respiration:
... FERMENTATION: This is another name for anaerobic respiration. ATPs are generated via glycolysis, and pyruvate is converted to either lactic acid (lactate) or ethyl alcohol (ethanol). Most significantly, the NADH is oxidized back to NAD+ so that glycolysis can continue to operate. Fermentation has b ...
... FERMENTATION: This is another name for anaerobic respiration. ATPs are generated via glycolysis, and pyruvate is converted to either lactic acid (lactate) or ethyl alcohol (ethanol). Most significantly, the NADH is oxidized back to NAD+ so that glycolysis can continue to operate. Fermentation has b ...
Butyric acid
Butyric acid (from Greek βούτῡρον, meaning ""butter""), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, abbreviated BTA, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in milk, especially goat, sheep and buffalo milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). It has an unpleasant smell and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). It can be detected by mammals with good scent detection abilities (such as dogs) at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million.Butyric acid is present in, and is the main distinctive smell of, human vomit.Butyric acid was first observed (in impure form) in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. The name of butyric acid comes from the Latin word for butter, butyrum (or buturum), the substance in which butyric acid was first found.

![pertemuan 11 (respirasi, glikolisis, siklus krebs) [โหมดความเข้ากันได้]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007851334_1-0a64bc276968ef728f82fe301bed0dd5-300x300.png)