Second test - rci.rutgers.edu
... B. both form a Schiff base with substrate C. both use an aldose as a group donor D. both use a ketose as a group donor ...
... B. both form a Schiff base with substrate C. both use an aldose as a group donor D. both use a ketose as a group donor ...
Photochemical smog, ozone and eutrophication notes
... 2. In the atmosphere, NO can combine with O2 in the presence of sunlight to form a brownish-yellow, noxious gas called nitrogen dioxide (NO2). This is photochemical smog. NO + O2 NO2 3. Nitrogen dioxide can mix with water vapor in the atmosphere to form nitric acid (HNO3), a component of acid rain ...
... 2. In the atmosphere, NO can combine with O2 in the presence of sunlight to form a brownish-yellow, noxious gas called nitrogen dioxide (NO2). This is photochemical smog. NO + O2 NO2 3. Nitrogen dioxide can mix with water vapor in the atmosphere to form nitric acid (HNO3), a component of acid rain ...
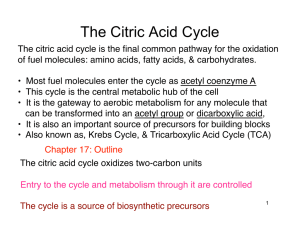
The Citric Acid Cycle
... The Citric Acid Cycle The citric acid cycle is the final common pathway for the oxidation of fuel molecules: amino acids, fatty acids, & carbohydrates. • Most fuel molecules enter the cycle as acetyl coenzyme A • This cycle is the central metabolic hub of the cell • It is the gateway to aerobic ...
... The Citric Acid Cycle The citric acid cycle is the final common pathway for the oxidation of fuel molecules: amino acids, fatty acids, & carbohydrates. • Most fuel molecules enter the cycle as acetyl coenzyme A • This cycle is the central metabolic hub of the cell • It is the gateway to aerobic ...
Slides
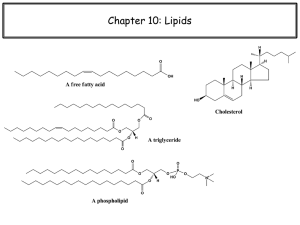
... • The main biological functions of lipids include energy storage, as structural components of cell membranes, and as important signaling molecules. • Lipids may be broadly defined as hydrophobic or amphiphilic small molecules; the amphiphilic nature of some lipids allows them to form structures such ...
... • The main biological functions of lipids include energy storage, as structural components of cell membranes, and as important signaling molecules. • Lipids may be broadly defined as hydrophobic or amphiphilic small molecules; the amphiphilic nature of some lipids allows them to form structures such ...
File
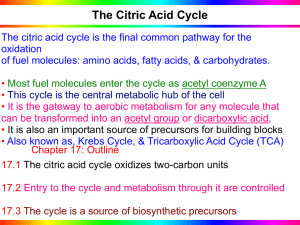
... The Citric Acid Cycle The citric acid cycle is the final common pathway for the oxidation of fuel molecules: amino acids, fatty acids, & carbohydrates. • Most fuel molecules enter the cycle as acetyl coenzyme A • This cycle is the central metabolic hub of the cell • It is the gateway to aerobic meta ...
... The Citric Acid Cycle The citric acid cycle is the final common pathway for the oxidation of fuel molecules: amino acids, fatty acids, & carbohydrates. • Most fuel molecules enter the cycle as acetyl coenzyme A • This cycle is the central metabolic hub of the cell • It is the gateway to aerobic meta ...
From: From one amino acid to another: tRNA
... From: From one amino acid to another: tRNA-dependent amino acid biosynthesis Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36(6):1813-1825. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn015 Nucleic Acids Res | © 2008 The Author(s)This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ...
... From: From one amino acid to another: tRNA-dependent amino acid biosynthesis Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36(6):1813-1825. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn015 Nucleic Acids Res | © 2008 The Author(s)This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ...
Carbonyl group is a functional group of (Aldehyde, Ketone)
... compounds of human body, here is some of them:①-Monosaccharides: Monosaccharide's are carbohydrates which can not be hydrolyzed to small molecules, contain carbons with functional aldehyde or keto group are present in nature. Aldohexose is glucose, Fructose is ketohexose respectively. Glucose is pre ...
... compounds of human body, here is some of them:①-Monosaccharides: Monosaccharide's are carbohydrates which can not be hydrolyzed to small molecules, contain carbons with functional aldehyde or keto group are present in nature. Aldohexose is glucose, Fructose is ketohexose respectively. Glucose is pre ...
Lipid Biosynthesis
... B) Rearrangement. C) Reduction. D) Dehydration. 3. Which of the following is the regulated step of fatty acid synthesis in eukaryotes? A) Carboxylation of acetyl CoA. B) Transportation of mitochondrial acetyl CoA into the cytosol. C) Assembly of the fatty acid chain. D) All of the above. ...
... B) Rearrangement. C) Reduction. D) Dehydration. 3. Which of the following is the regulated step of fatty acid synthesis in eukaryotes? A) Carboxylation of acetyl CoA. B) Transportation of mitochondrial acetyl CoA into the cytosol. C) Assembly of the fatty acid chain. D) All of the above. ...
Acidification of Urine
... • Amino acids are utilized in the liver for gluconeogenesis, leaving NH4+ and HCO3– as products from their amino and carboxyl groups. • NH4+ is incorporated into urea and the protons that are formed are buffered intracellularly by HCO3–, so little NH4+ and HCO3– escape into the ...
... • Amino acids are utilized in the liver for gluconeogenesis, leaving NH4+ and HCO3– as products from their amino and carboxyl groups. • NH4+ is incorporated into urea and the protons that are formed are buffered intracellularly by HCO3–, so little NH4+ and HCO3– escape into the ...
lipid
... The nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)aspirin, ibuprofen, and meclofenamate, for example— were shown to inhibit the enzyme prostaglandin H2 synthase (also called cyclooxygenase or COX1), which catalyzes an early step in the pathway from arachidonate to prostaglandins . Leukotrienes : first ...
... The nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)aspirin, ibuprofen, and meclofenamate, for example— were shown to inhibit the enzyme prostaglandin H2 synthase (also called cyclooxygenase or COX1), which catalyzes an early step in the pathway from arachidonate to prostaglandins . Leukotrienes : first ...
Buffer systems
... Chemical buffers are able to react immediately (within milliseconds). Chemical buffers are the first line of defense for the body for fluctuations in pH. ...
... Chemical buffers are able to react immediately (within milliseconds). Chemical buffers are the first line of defense for the body for fluctuations in pH. ...
lect3
... Fatty acids as a fuel Fatty acids are the preferred fuel for most tissues Fatty acids can only be metabolised aerobically Red blood cells can’t use fatty acids as they don’t have mitochondria Neurons can’t use fatty acids as they are unable to cross the blood brain barrier ...
... Fatty acids as a fuel Fatty acids are the preferred fuel for most tissues Fatty acids can only be metabolised aerobically Red blood cells can’t use fatty acids as they don’t have mitochondria Neurons can’t use fatty acids as they are unable to cross the blood brain barrier ...
The Chemical and Physical Basis of Life
... A. Acids - substances that dissociate in water to release H+ and anions. Acids are H+ or proton donors. B. Bases - substances that dissociate in water to release OH- and cations. Bases are H+ or proton acceptors. C. Salts - substances that dissociate in water into cations and anions which are not H+ ...
... A. Acids - substances that dissociate in water to release H+ and anions. Acids are H+ or proton donors. B. Bases - substances that dissociate in water to release OH- and cations. Bases are H+ or proton acceptors. C. Salts - substances that dissociate in water into cations and anions which are not H+ ...
Medical Biochemistry and Molecular Basis of Medical
... blood urea nitrogen (BUN) level following an overnight fast. After an overnight fast, a patient went to the doctor’s office to have a fasting blood test. Most of the parameters (HDL, VLDL, heme iron, etc) came back normal, but you both noticed the BUN level was slightly elevated. Your partner says t ...
... blood urea nitrogen (BUN) level following an overnight fast. After an overnight fast, a patient went to the doctor’s office to have a fasting blood test. Most of the parameters (HDL, VLDL, heme iron, etc) came back normal, but you both noticed the BUN level was slightly elevated. Your partner says t ...
Electron Carriers
... Also generates organic acids which can be converted to glucose or enter Krebs cycle to be oxidized for energy ...
... Also generates organic acids which can be converted to glucose or enter Krebs cycle to be oxidized for energy ...
The amino acids
... Di-peptide Amino acids bind, to form a protein. Upon binding, two protons from the NH3 and one oxygen from the carboxyl join to form a water. So the peptide bond has at the one side a C=O and at the other side an N-H. Only the ends of the chain are NH3 or carboxylic. ...
... Di-peptide Amino acids bind, to form a protein. Upon binding, two protons from the NH3 and one oxygen from the carboxyl join to form a water. So the peptide bond has at the one side a C=O and at the other side an N-H. Only the ends of the chain are NH3 or carboxylic. ...
Megaloblastic Anemias
... A complex organometallic vitamin with cobalt atom situated in the middle of a corrin ring. It cannot be synthesized in the human body & must be taken in diet (only animal products) Daily req = 2.5 mg In stomach it is released from diet, then binds R protein (glycoprotein found in saliva, milk, gastr ...
... A complex organometallic vitamin with cobalt atom situated in the middle of a corrin ring. It cannot be synthesized in the human body & must be taken in diet (only animal products) Daily req = 2.5 mg In stomach it is released from diet, then binds R protein (glycoprotein found in saliva, milk, gastr ...
Citric Acid Cycle
... However, in this reaction, CoA forms a thioester linkage to the new 4-carbon group, yielding succinyl CoA. Important Note: This reaction and its associated enzyme is very similar to the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (that converted pyruvate into acetyl CoA.) ...
... However, in this reaction, CoA forms a thioester linkage to the new 4-carbon group, yielding succinyl CoA. Important Note: This reaction and its associated enzyme is very similar to the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (that converted pyruvate into acetyl CoA.) ...
Chemistry of Cells: Biochemistry
... permission from the publisher. ESSENTIALS IN BIOLOGY WITH PHYSIOLOGY 2nd edition, by Campbell and Reece, 2007. These images have been produced from the originals by permission of the publisher. These illustrations may not be reproduced in any format for any purpose without express written permission ...
... permission from the publisher. ESSENTIALS IN BIOLOGY WITH PHYSIOLOGY 2nd edition, by Campbell and Reece, 2007. These images have been produced from the originals by permission of the publisher. These illustrations may not be reproduced in any format for any purpose without express written permission ...
VEN124 Section III
... • Nitrogen: most often limiting • Amino acids – Can be degraded as N source via transamination – Can be interconverted with related amino acids – Can be used as that amino acid ...
... • Nitrogen: most often limiting • Amino acids – Can be degraded as N source via transamination – Can be interconverted with related amino acids – Can be used as that amino acid ...
LIPIDS
... phosphate yields sphingomyelin while the addition of sugars yields cerebrosides and globosides. Those glycolipids that contain sialic acid are known as gangliosides. ...
... phosphate yields sphingomyelin while the addition of sugars yields cerebrosides and globosides. Those glycolipids that contain sialic acid are known as gangliosides. ...
Biosynthesis of Plant-derived flavor compounds
... compounds behind complex wine aromas such as guava, passionfruit or grapefruit — but when thiols go wrong, they can make a wine taste "funky." ...
... compounds behind complex wine aromas such as guava, passionfruit or grapefruit — but when thiols go wrong, they can make a wine taste "funky." ...
Hepoxilin

Hepoxilins (HxA3 and HxB3) are nonclassic eicosanoid hormones involved in inflammation.