Lecture 9: Citric Acid Cycle/Fatty Acid Catabolism
... label was released as CO2. Always the left carboxyl group is instead released as CO2, i.e., that from oxaloacetate. This was interpreted as proof that citrate is not in the cycle at all the labels would have been scrambled, and half of the CO2 would have been 14C. Prochiral Citrate. In a two-minute ...
... label was released as CO2. Always the left carboxyl group is instead released as CO2, i.e., that from oxaloacetate. This was interpreted as proof that citrate is not in the cycle at all the labels would have been scrambled, and half of the CO2 would have been 14C. Prochiral Citrate. In a two-minute ...
Amino acid and protein
... Ninhydrin is a chemical used to detect free amino acid and proteins Amino acids(NH2) also react with ninhydrin at pH=4. The reduction product obtained from ninhydrin then reacts with NH3 and excess ninhydrin to yield a blue colored substance. This reaction provides an extremely sensitive test ...
... Ninhydrin is a chemical used to detect free amino acid and proteins Amino acids(NH2) also react with ninhydrin at pH=4. The reduction product obtained from ninhydrin then reacts with NH3 and excess ninhydrin to yield a blue colored substance. This reaction provides an extremely sensitive test ...
Amino Acid Exporter: A Tool for the Next
... due to a lack of knowledge about the amino acids efflux systems. Significant improvements in microbial amino acid fermentation have been achieved by the strategies described above, but the productivity comes near to a limit. Thus, identification and characterization of the amino acid exporters appea ...
... due to a lack of knowledge about the amino acids efflux systems. Significant improvements in microbial amino acid fermentation have been achieved by the strategies described above, but the productivity comes near to a limit. Thus, identification and characterization of the amino acid exporters appea ...
HONORS BIOLOGY CHAPTERy 6 STUDY GUIDE
... Occurs where in cell? Starting molecule(s) Ending molecule(s) Purpose: ...
... Occurs where in cell? Starting molecule(s) Ending molecule(s) Purpose: ...
Amino acid and protein
... Ninhydrin is a chemical used to detect free amino acid and proteins Amino acids(NH2) also react with ninhydrin at pH=4. The reduction product obtained from ninhydrin then reacts with NH3 and excess ninhydrin to yield a blue colored substance. This reaction provides an extremely sensitive test ...
... Ninhydrin is a chemical used to detect free amino acid and proteins Amino acids(NH2) also react with ninhydrin at pH=4. The reduction product obtained from ninhydrin then reacts with NH3 and excess ninhydrin to yield a blue colored substance. This reaction provides an extremely sensitive test ...
Nucleic Acid metabolism De Novo Synthesis of Purine
... pathways, NAD and NADP formation. The enzyme is heavily controlled by a variety of compounds (di- and tri-phosphates, 2,3-DPG), presumably to try to match the synthesis of PRPP to a need for the products in which it ultimately appears ...
... pathways, NAD and NADP formation. The enzyme is heavily controlled by a variety of compounds (di- and tri-phosphates, 2,3-DPG), presumably to try to match the synthesis of PRPP to a need for the products in which it ultimately appears ...
The Initiation of Translation
... • Degenerate code: Amino acid may be specified by more than one codon. • Synonymous codons: codons that specify the same amino acid. • Isoaccepting tRNAs: different tRNAs that accept the same amino acid but have different ...
... • Degenerate code: Amino acid may be specified by more than one codon. • Synonymous codons: codons that specify the same amino acid. • Isoaccepting tRNAs: different tRNAs that accept the same amino acid but have different ...
Study Guide
... 1.Why are the fermentation pathways referred to as “anaerobic” pathways? _____ _______________________________________________________________ 2. What are the energy-containing products of glycolysis? __________________ _______________________________________________________________ 3. Of what impor ...
... 1.Why are the fermentation pathways referred to as “anaerobic” pathways? _____ _______________________________________________________________ 2. What are the energy-containing products of glycolysis? __________________ _______________________________________________________________ 3. Of what impor ...
LIPID OF BIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE
... sheath and cell membrane of RBCs. They act as cell membrane receptors for hormones and external stimuli also they provide recognition properties. ...
... sheath and cell membrane of RBCs. They act as cell membrane receptors for hormones and external stimuli also they provide recognition properties. ...
Note 17 - South Tuen Mun Government Secondary School
... (1) the change of _____________________ into acetyl-CoA (2-C) [this is not a part of the Krebs cycle] The products are NADH, acetyl-CoA, CO2 (carbon dioxide). ...
... (1) the change of _____________________ into acetyl-CoA (2-C) [this is not a part of the Krebs cycle] The products are NADH, acetyl-CoA, CO2 (carbon dioxide). ...
INHER TED D SEASES OF AM NO AC D METABOL SM pw
... • Such inhibition optimizes the transport of L-Dopa across the blood-brain barrier. • Within the brain AADC can convert LDopa to Dopamine • AADC also catalyzes the conversion of 50H tryptophan to serotonin • Inborn error affecting AADC activity results in brain deficiency of both dopamine and serot ...
... • Such inhibition optimizes the transport of L-Dopa across the blood-brain barrier. • Within the brain AADC can convert LDopa to Dopamine • AADC also catalyzes the conversion of 50H tryptophan to serotonin • Inborn error affecting AADC activity results in brain deficiency of both dopamine and serot ...
activity description – cladogram cytochrome oxidase c
... MOLECULAR BIOLOGY AND PHYLOGENY BACKGROUND: You have just completed an activity in which you made a cladogram showing the evolutionary relationships between seven organisms. The data used to draw that cladogram was based on shared characteristics that were inherited from their ancestors. Biochemical ...
... MOLECULAR BIOLOGY AND PHYLOGENY BACKGROUND: You have just completed an activity in which you made a cladogram showing the evolutionary relationships between seven organisms. The data used to draw that cladogram was based on shared characteristics that were inherited from their ancestors. Biochemical ...
Cellular Respiration
... The body will store only a fraction of the 33 grams, while breaking down the rest. The sugar will be broken down to ultimately form CO2 by aerobic respiration. The H atoms found in the sucrose molecules will unite with O gas to produce H2O. Most of the water produced will be eliminated by breathing ...
... The body will store only a fraction of the 33 grams, while breaking down the rest. The sugar will be broken down to ultimately form CO2 by aerobic respiration. The H atoms found in the sucrose molecules will unite with O gas to produce H2O. Most of the water produced will be eliminated by breathing ...
Phenyllactic Acid: A Potential Antimicrobial Compound in Lactic acid
... ά-ketoglutarate. The phenylalanine is first transaminated to phenylpyruvic acid (PPA) and PPA is further reduced to PhLA [28,29,30]. The transamination reaction is mediated by aromatic amino acid transferase (AAT) which has broad substrate specificity including leucine, tyrosine and methionine [31]. ...
... ά-ketoglutarate. The phenylalanine is first transaminated to phenylpyruvic acid (PPA) and PPA is further reduced to PhLA [28,29,30]. The transamination reaction is mediated by aromatic amino acid transferase (AAT) which has broad substrate specificity including leucine, tyrosine and methionine [31]. ...
Metabolism - Websupport1
... Citric acid will go through number of steps and will become back a 4 carbon molecule . The TCA cycle will begin with formation of citric acid and end with formation of oxaloacetic acid. The TCA cycle will run twice for one molecule of glucose, because one molecule of glucose produces two pyruvic aci ...
... Citric acid will go through number of steps and will become back a 4 carbon molecule . The TCA cycle will begin with formation of citric acid and end with formation of oxaloacetic acid. The TCA cycle will run twice for one molecule of glucose, because one molecule of glucose produces two pyruvic aci ...
Homework #1 BCHS 3304
... solution. Explain what may have happened if the absorbance measurement is lower than you predict. 7. What is the molar concentration of pure bromine. The density of bromine is 3.10 g/cm3. 8. Study exercises in FOB p 38 1, 3, 4, and 7. 9. Problems in FOB p 38 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, and 10. 10. Study Guide pr ...
... solution. Explain what may have happened if the absorbance measurement is lower than you predict. 7. What is the molar concentration of pure bromine. The density of bromine is 3.10 g/cm3. 8. Study exercises in FOB p 38 1, 3, 4, and 7. 9. Problems in FOB p 38 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, and 10. 10. Study Guide pr ...
List of Precursor Chemicals - Ministry of Health Jamaica
... Narcotic - A substance used to induce drowsiness sleep stupor or insensibility. These substances include Cocaine, Codeine, Pethidine, Morphine and Fentanyl which are used to relieve moderate or severe pain or in anaesthesia and are regulated under the Dangerous Drugs Act and Regulations of 1948. ...
... Narcotic - A substance used to induce drowsiness sleep stupor or insensibility. These substances include Cocaine, Codeine, Pethidine, Morphine and Fentanyl which are used to relieve moderate or severe pain or in anaesthesia and are regulated under the Dangerous Drugs Act and Regulations of 1948. ...
NUTRACEUTICALS: Let Food be Your Medicine
... active ingredients can be increased • Diet rich in nutraceuticals along with regular exercise, stress reduction and maintenance of healthy body weight will maximise health and reduce disease risk ...
... active ingredients can be increased • Diet rich in nutraceuticals along with regular exercise, stress reduction and maintenance of healthy body weight will maximise health and reduce disease risk ...
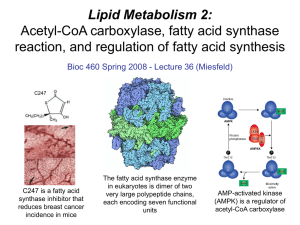
Lecture 36 - Lipid Metabolism 2
... coenzyme in redox reactions, and the building block is malonyl-CoA. • Acetyl-CoA carboxylase is the key regulated enzyme in fatty acid synthesis and is responsible for generating malonyl-CoA in a carboxylation reaction using acetyl-CoA. • The fatty acid synthase protein complex consists of six enzym ...
... coenzyme in redox reactions, and the building block is malonyl-CoA. • Acetyl-CoA carboxylase is the key regulated enzyme in fatty acid synthesis and is responsible for generating malonyl-CoA in a carboxylation reaction using acetyl-CoA. • The fatty acid synthase protein complex consists of six enzym ...
Read the following text! TEXT A Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline
... olefins or alkenes which contain one or more double bonds, i.e. di-olefins (dienes) or poly-olefins alkynes, which have one or more triple bonds. Formaldehyde is an organic compound with the formula CH2O. It is a simple derivative of a hydrocarbon, hence its systematic name is methanal. The comm ...
... olefins or alkenes which contain one or more double bonds, i.e. di-olefins (dienes) or poly-olefins alkynes, which have one or more triple bonds. Formaldehyde is an organic compound with the formula CH2O. It is a simple derivative of a hydrocarbon, hence its systematic name is methanal. The comm ...
Homework 3-1 Reading Notes Campbell`s Chapter 9
... it needs. If there is a glut of certain amino acid, for example, the anabolic pathway that synthesizes the amino acid from an intermediate in the citric acid cycle is switched off. The most common mechanism for this control is __________________ ______________________. The _______ _______________ of ...
... it needs. If there is a glut of certain amino acid, for example, the anabolic pathway that synthesizes the amino acid from an intermediate in the citric acid cycle is switched off. The most common mechanism for this control is __________________ ______________________. The _______ _______________ of ...
1 - Medical Mastermind Community
... Signal recognition particles binds to the signal codons of mRNA's encoding membrane or secreted proteins. Docking of ribosomes to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane involves a GTP/GDP cycle. Specialized proteins catalyze folding of the nascent polypeptide chains. Chain elongation and translocation o ...
... Signal recognition particles binds to the signal codons of mRNA's encoding membrane or secreted proteins. Docking of ribosomes to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane involves a GTP/GDP cycle. Specialized proteins catalyze folding of the nascent polypeptide chains. Chain elongation and translocation o ...
Product Datasheet
... Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) is a lipid signalling molecule formed by the hydrolysis of lysophosphatidyl choline by lysophospholipase D, also known as autotaxin (ATX). LPA signals through four different G protein-coupled receptors, LPA1/EDG-2, LPA2/EDG-4, LPA3/EDG-7, and LPA4/GPR23. Activation of per ...
... Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) is a lipid signalling molecule formed by the hydrolysis of lysophosphatidyl choline by lysophospholipase D, also known as autotaxin (ATX). LPA signals through four different G protein-coupled receptors, LPA1/EDG-2, LPA2/EDG-4, LPA3/EDG-7, and LPA4/GPR23. Activation of per ...
Problem: Many chronic inflammatory diseases including CKD are
... common in CKD and stimulates muscle protein wasting which may further enhance chronic inflammation. In vivo, this muscle wasting by acidosis also requires the presence of glucocorticoid (GC). Metabolic acidosis is thought to act by inhibiting the pH-sensitive System A amino acid transporter protein ...
... common in CKD and stimulates muscle protein wasting which may further enhance chronic inflammation. In vivo, this muscle wasting by acidosis also requires the presence of glucocorticoid (GC). Metabolic acidosis is thought to act by inhibiting the pH-sensitive System A amino acid transporter protein ...
Hepoxilin

Hepoxilins (HxA3 and HxB3) are nonclassic eicosanoid hormones involved in inflammation.