NME2.28: fat and carbohydrate metabolism in the
... o Pyruvate is converted to acetyl-CoA by pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) o Acetyl-CoA enters the first part of the TCA cycle (see NME 2.31) o Acetyl-CoA with oxaloacetate is converted to citrate o Citrate is exported from the mitochondria Citrate is re-converted to acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate in the cy ...
... o Pyruvate is converted to acetyl-CoA by pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) o Acetyl-CoA enters the first part of the TCA cycle (see NME 2.31) o Acetyl-CoA with oxaloacetate is converted to citrate o Citrate is exported from the mitochondria Citrate is re-converted to acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate in the cy ...
Composition of Muscle
... KINDS OF TRIGLYCERIDES • If the same kind of fatty acid occupies all three positions on the glycerol molecule, the result is a simple triglyceride. • If more than one kind of fatty acid is attached to glycerol, the result is a mixed triglyceride. • What determines what kinds of triglycerides an an ...
... KINDS OF TRIGLYCERIDES • If the same kind of fatty acid occupies all three positions on the glycerol molecule, the result is a simple triglyceride. • If more than one kind of fatty acid is attached to glycerol, the result is a mixed triglyceride. • What determines what kinds of triglycerides an an ...
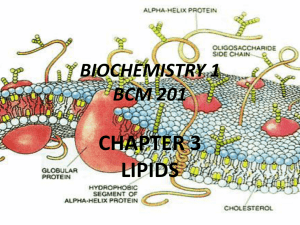
Lipids
... • The membrane that surrounds the cytoplasm of a cell; it is also called the plasma membrane or, in a more general sense, a unit membrane. This is a very thin, semifluid, sheet like structure made of four continuous monolayers of molecules. • The plasma membrane and the membranes making up all the i ...
... • The membrane that surrounds the cytoplasm of a cell; it is also called the plasma membrane or, in a more general sense, a unit membrane. This is a very thin, semifluid, sheet like structure made of four continuous monolayers of molecules. • The plasma membrane and the membranes making up all the i ...
The Bacterial Cell Wall. The Result of Adsorption
... of the peptide chains would be about 20-30A. Mucopeptides are the principal mechanical supports in both Gram-positive and Gram-negative micro-organisms, but whereas they form a major portion of preparations of walls of the former organisms, of the latter they may constitute only 5-10y0 of the weight ...
... of the peptide chains would be about 20-30A. Mucopeptides are the principal mechanical supports in both Gram-positive and Gram-negative micro-organisms, but whereas they form a major portion of preparations of walls of the former organisms, of the latter they may constitute only 5-10y0 of the weight ...
The Bacterial Cell Wall. The Result of Adsorption
... of the peptide chains would be about 20-30A. Mucopeptides are the principal mechanical supports in both Gram-positive and Gram-negative micro-organisms, but whereas they form a major portion of preparations of walls of the former organisms, of the latter they may constitute only 5-10y0 of the weight ...
... of the peptide chains would be about 20-30A. Mucopeptides are the principal mechanical supports in both Gram-positive and Gram-negative micro-organisms, but whereas they form a major portion of preparations of walls of the former organisms, of the latter they may constitute only 5-10y0 of the weight ...
Carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase deficiency: metabolic
... birth free fatty acids are mobilized from adipose tissue stores. A rapid increase in the activity of carnitine palmitoyltransferase I and II and a rise in the capacity to oxidize fatty acids is found in liver [2] and in heart [3] reflecting a prompt adaptation to lipid as the essential metabolic fue ...
... birth free fatty acids are mobilized from adipose tissue stores. A rapid increase in the activity of carnitine palmitoyltransferase I and II and a rise in the capacity to oxidize fatty acids is found in liver [2] and in heart [3] reflecting a prompt adaptation to lipid as the essential metabolic fue ...
M01
... hypoglycemia, hyperammoniemia) - secondary to many genetic / acquired disorders (episodic hypoketotic hypoglycemia, starting in infancy) Carnitine supplementation : supposed to increase energy production, because it facilitates the FA transport into mitochondria for oxidation, sparing glycogen from ...
... hypoglycemia, hyperammoniemia) - secondary to many genetic / acquired disorders (episodic hypoketotic hypoglycemia, starting in infancy) Carnitine supplementation : supposed to increase energy production, because it facilitates the FA transport into mitochondria for oxidation, sparing glycogen from ...
Lipid Metabolism Catabolism Overview
... acid phenyl derivatives and then analyzed their urine for the resulting metabolites. What metabolite was produced when dogs were fed ...
... acid phenyl derivatives and then analyzed their urine for the resulting metabolites. What metabolite was produced when dogs were fed ...
Comparison of cell-wall teichoic acid with high-molecular
... adherence test? All strains were gram-positive cocci and produced catalase but not coagulase. They were identified as S. epidermidis according to the scheme of Kloos and SchleiferlO by the API STAPH (API Grafton Way, Basingstoke, Hampshire) test kit. Isolation and purijication of extracellular high- ...
... adherence test? All strains were gram-positive cocci and produced catalase but not coagulase. They were identified as S. epidermidis according to the scheme of Kloos and SchleiferlO by the API STAPH (API Grafton Way, Basingstoke, Hampshire) test kit. Isolation and purijication of extracellular high- ...
2 Pyruvic Acid
... Negative feedback prevents too much product from being produced. The product of the metabolic pathway often inhibits the rate-limiting enzyme. ...
... Negative feedback prevents too much product from being produced. The product of the metabolic pathway often inhibits the rate-limiting enzyme. ...
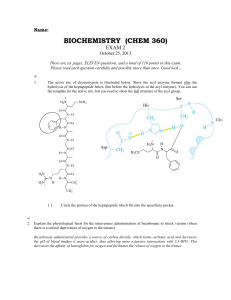
BIOCHEMISTRY (CHEM 360)
... Explain the physiological basis for the intravenous administration of bicarbonate to shock victims (when there is a critical deprivation of oxygen to the tissues) Bicarbonate administered provides a source of carbon dioxide, which forms carbonic acid and decreases the pH of blood (makes it more acid ...
... Explain the physiological basis for the intravenous administration of bicarbonate to shock victims (when there is a critical deprivation of oxygen to the tissues) Bicarbonate administered provides a source of carbon dioxide, which forms carbonic acid and decreases the pH of blood (makes it more acid ...
Alignment scoring statistics and scoring matrices
... • Why are they important? – Choice of scoring rule can dramatically influence the sequence alignments obtained and, therefore, the analysis being done – Different scoring matrices have been developed for different situations; using the wrong one can make a big difference. ...
... • Why are they important? – Choice of scoring rule can dramatically influence the sequence alignments obtained and, therefore, the analysis being done – Different scoring matrices have been developed for different situations; using the wrong one can make a big difference. ...
Fermentation: An Overview
... Precipitation by Metal Ions • Metal salts with lower solubilities can formed by enzymes and proteins • Nucleic acids, which are present in microbial cells, must be removed prior to this type of precipitation because they reduce the resolution of separation • Manganous salts can be used to selectivel ...
... Precipitation by Metal Ions • Metal salts with lower solubilities can formed by enzymes and proteins • Nucleic acids, which are present in microbial cells, must be removed prior to this type of precipitation because they reduce the resolution of separation • Manganous salts can be used to selectivel ...
Acid Carboxypeptidases: Their Occurrence in Plants, Intracellular
... In lemon the exocarp of very young fruits contains twice as much carboxypeptidase than the same tissue of mature fruits (Table 2). Thus the carboxypeptidase content seems to be related to the metabolic activity of cells. In citrus not only the fruit but ...
... In lemon the exocarp of very young fruits contains twice as much carboxypeptidase than the same tissue of mature fruits (Table 2). Thus the carboxypeptidase content seems to be related to the metabolic activity of cells. In citrus not only the fruit but ...
Lab12
... Halo around the streak (clearing of lipids) = complete hydrolysis of triglycerides, positive for lipase production (agar could be pale blue due to complete clearing of all fatty acids or dark blue because a few fatty acids remain) Pale blue agar, no halo = tributyrin present, negative for lipase pro ...
... Halo around the streak (clearing of lipids) = complete hydrolysis of triglycerides, positive for lipase production (agar could be pale blue due to complete clearing of all fatty acids or dark blue because a few fatty acids remain) Pale blue agar, no halo = tributyrin present, negative for lipase pro ...
Biochemistry of Cardiac Muscle and Lung
... LDH4 (H3M) – kidneys, placenta, pancreas, LDH5 (4M) – liver and striated muscles ...
... LDH4 (H3M) – kidneys, placenta, pancreas, LDH5 (4M) – liver and striated muscles ...
Metabolic Disorders
... Motor deficits Seizures Intermittent episodes of vomiting, acidosis, hypoglycaemia and/or coma triggered by stress e.g. infections, surgery. ...
... Motor deficits Seizures Intermittent episodes of vomiting, acidosis, hypoglycaemia and/or coma triggered by stress e.g. infections, surgery. ...
protein synthesis - Jannali
... The mRNA strand is then modified so that it only consists of the base sequence that will code for the protein. It removes the non-coding regions, introns, while still in the nucleus by splicing the coding regions, exons, together. The modified mRNA then moves from the nucleus into the cytoplasm ...
... The mRNA strand is then modified so that it only consists of the base sequence that will code for the protein. It removes the non-coding regions, introns, while still in the nucleus by splicing the coding regions, exons, together. The modified mRNA then moves from the nucleus into the cytoplasm ...
Antihyperlipoproteinemic Drugs
... - Inhibits HMG CoA Reductase, which is necessary for cholesterol synthesis. So, intracellular cholesterol goes down. As a result, LDL receptors goes up and uptake of circulating LDL by cell goes up lowering plasma cholesterol - HDL may go up in some pt. - Small decrease in TAG - Macrophages ingest o ...
... - Inhibits HMG CoA Reductase, which is necessary for cholesterol synthesis. So, intracellular cholesterol goes down. As a result, LDL receptors goes up and uptake of circulating LDL by cell goes up lowering plasma cholesterol - HDL may go up in some pt. - Small decrease in TAG - Macrophages ingest o ...
Proximate, Amino acid and Fatty acid profile of
... life. Amino acids play a vital role both as building blocks of proteins and as intermediates in metabolism. Fish oil is one of the most significant natural sources of polyunsaturated fatty acids. It is scientifically demonstrated to have functional effects on human diet (Saoud et al., 2008; Rafflenb ...
... life. Amino acids play a vital role both as building blocks of proteins and as intermediates in metabolism. Fish oil is one of the most significant natural sources of polyunsaturated fatty acids. It is scientifically demonstrated to have functional effects on human diet (Saoud et al., 2008; Rafflenb ...
3. Metabolism - Professor Monzir Abdel
... May occur when an inhibitor binds to the same active site on the enzyme as the substrate, but binds so tightly that it is effectively not released. Thus, the binding site is permanently blocked. May also occur when an inhibitor binds tightly (sometimes covalently) to a different site on the enzyme t ...
... May occur when an inhibitor binds to the same active site on the enzyme as the substrate, but binds so tightly that it is effectively not released. Thus, the binding site is permanently blocked. May also occur when an inhibitor binds tightly (sometimes covalently) to a different site on the enzyme t ...
Sphingolipids Sphingolipids
... Cerebrosides Cerebrosides contain galactose or glucose attached by a -glycosidic bond to the —OH group of ceramide are found in the brain and the myelin sheath are important in cellular recognition and tissue immunity ...
... Cerebrosides Cerebrosides contain galactose or glucose attached by a -glycosidic bond to the —OH group of ceramide are found in the brain and the myelin sheath are important in cellular recognition and tissue immunity ...
Organic chemistry and Biological chemistry for Health Sciences
... four steps again, and the process is repeated until no more two-carbon acetyl units can be made. The FADH2 and NADH produced by -oxidation fuel the respiratory chain directly. The acetyl groups fuel the respiratory chain indirectly passing through the citric acid cycle, or they enter the general po ...
... four steps again, and the process is repeated until no more two-carbon acetyl units can be made. The FADH2 and NADH produced by -oxidation fuel the respiratory chain directly. The acetyl groups fuel the respiratory chain indirectly passing through the citric acid cycle, or they enter the general po ...
Hepoxilin

Hepoxilins (HxA3 and HxB3) are nonclassic eicosanoid hormones involved in inflammation.