Amino Acid Catabolism - Chemistry Courses: About
... • Leucine is degraded to acetyl CoA and acetoacetate by a pathway whose first two seps are identical to those of valine degradation (Figure 18-11). The third step is the same as the first step of fatty acid oxidation. The fourth step involves an ATPdependent carboxylation, the fifth step is a hydrat ...
... • Leucine is degraded to acetyl CoA and acetoacetate by a pathway whose first two seps are identical to those of valine degradation (Figure 18-11). The third step is the same as the first step of fatty acid oxidation. The fourth step involves an ATPdependent carboxylation, the fifth step is a hydrat ...
cellular respiration
... • Glycolysis releases energy, but also needs energy (needs 2 ATP, makes 4) • 4 high energy electrons are removed and carried by NAD+ (NADP+ in psyth) to other molecules ...
... • Glycolysis releases energy, but also needs energy (needs 2 ATP, makes 4) • 4 high energy electrons are removed and carried by NAD+ (NADP+ in psyth) to other molecules ...
Lecture: 27 Fatty acid and triacyl glycerol biosynthesis Biosynthesis
... and a water molecule is removed to form α, β-unsaturated acyl ACP. vi) Formation of Acyl ACP The unsaturated acyl ACP is converted in the next step to a saturated acyl ACP by the enzyme α,β-unsaturated acyl ACP reductase using NADPH as the coenzyme. The resultant product contains two carbon atom ...
... and a water molecule is removed to form α, β-unsaturated acyl ACP. vi) Formation of Acyl ACP The unsaturated acyl ACP is converted in the next step to a saturated acyl ACP by the enzyme α,β-unsaturated acyl ACP reductase using NADPH as the coenzyme. The resultant product contains two carbon atom ...
Lecture 6
... 3. The Lone Pair of the alcohol oxygen can react with the carbonyl carbon to set the whole thing in motion 4. Remember your VSEPR Geometry ...
... 3. The Lone Pair of the alcohol oxygen can react with the carbonyl carbon to set the whole thing in motion 4. Remember your VSEPR Geometry ...
Lipids
... surface of the outer mitochondrial membrane, transfers a fatty acid from CoA to the OH on carnitine. 2.Carnitine acylcarnitine translocase in the inner mitochondrial membrane mediates exchange of carnitine for acylcarnitine. ...
... surface of the outer mitochondrial membrane, transfers a fatty acid from CoA to the OH on carnitine. 2.Carnitine acylcarnitine translocase in the inner mitochondrial membrane mediates exchange of carnitine for acylcarnitine. ...
Cellular Respiration - Cathkin High School
... Citrate is gradually broken down back to the original oxaloacetate by a series of enzyme controlled steps which involve : the removal of carbon as carbon dioxide hydrogen which is picked up by a carrier ...
... Citrate is gradually broken down back to the original oxaloacetate by a series of enzyme controlled steps which involve : the removal of carbon as carbon dioxide hydrogen which is picked up by a carrier ...
Acid/Base: Salicylate Toxicity
... An acidic pH promotes the movement of salicylate into the tissues ...
... An acidic pH promotes the movement of salicylate into the tissues ...
2 Lec 4 Muscle Metabolism V10
... • Fast pathway, but does not produce much ATP • Important for the first 30 – 40 sec. of strenuous activity if enzymes and fuel are available • Stored ATP, CP and glycolysis can support strenuous muscle activity for 60 sec. • At full speed lactic acid accumulates, lowering pH which halts reaction • A ...
... • Fast pathway, but does not produce much ATP • Important for the first 30 – 40 sec. of strenuous activity if enzymes and fuel are available • Stored ATP, CP and glycolysis can support strenuous muscle activity for 60 sec. • At full speed lactic acid accumulates, lowering pH which halts reaction • A ...
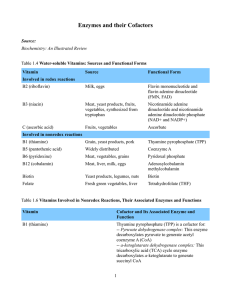
Enzymes and their Cofactors Source: Biochemistry: An Illustrated
... decarboxylases play a critical role in the synthesis of neurotransmitters (e.g., dopamine) -- Glycogen phosphorylase: This enzyme is involved in the breakdown of glycogen (glycogenolysis) -- Aminolevulinic acid (ALA) synthase: The ratelimiting step in heme and porphyrin synthesis is catalyzed by thi ...
... decarboxylases play a critical role in the synthesis of neurotransmitters (e.g., dopamine) -- Glycogen phosphorylase: This enzyme is involved in the breakdown of glycogen (glycogenolysis) -- Aminolevulinic acid (ALA) synthase: The ratelimiting step in heme and porphyrin synthesis is catalyzed by thi ...
Biology 233 - Request a Spot account
... 136-148 mEq/liter in plasma (10mEq in cells) Na/K pumps are responsible for high concentration in ECF accounts for nearly half of ECF osmolarity Sodium gain – diet (usually high) Sodium loss – urine, perspiration blood concentration is usually stable – balanced by osmosis (fluid level regulated main ...
... 136-148 mEq/liter in plasma (10mEq in cells) Na/K pumps are responsible for high concentration in ECF accounts for nearly half of ECF osmolarity Sodium gain – diet (usually high) Sodium loss – urine, perspiration blood concentration is usually stable – balanced by osmosis (fluid level regulated main ...
Final Review - Department of Chemistry ::: CALTECH
... because it contains half the carbons from glucose. Glycolysis can be broken down into two phases: the investment phase and the reward phase. What happens in gluconeogenesis? Now let’s say that you’re waking up from a nice 10 hour sleep. You haven’t eaten all night so there is no (or very little) ava ...
... because it contains half the carbons from glucose. Glycolysis can be broken down into two phases: the investment phase and the reward phase. What happens in gluconeogenesis? Now let’s say that you’re waking up from a nice 10 hour sleep. You haven’t eaten all night so there is no (or very little) ava ...
Respiration PowerPoint
... It’s a form of _____ production in O2-deprived cells (muscle) and red blood cells (no mitochondria) ...
... It’s a form of _____ production in O2-deprived cells (muscle) and red blood cells (no mitochondria) ...
Inborn Errors of Amino Acid Metabolism
... Prenatal diagnosis is done by detecting gene mutation in fetus Neonatal diagnosis in infants is done by measuring blood phe levels Treatment: Life long phe-restricted diet (low) If a pregnant mother is affected, the fetus is affected but the opposite will not affect the mother because the ...
... Prenatal diagnosis is done by detecting gene mutation in fetus Neonatal diagnosis in infants is done by measuring blood phe levels Treatment: Life long phe-restricted diet (low) If a pregnant mother is affected, the fetus is affected but the opposite will not affect the mother because the ...
OH - Whitesides Group
... growth regulatorsof this type would be facilitated by a convenient synthetic route to DAHP; such a route might also allow for the preparation of structural analoguesof DAHP. Most of the previous chemical synthesesof DAHPT-rl have employed 2-deoxy-o-glucose(a relatively costly carbohydrate at $17/g) ...
... growth regulatorsof this type would be facilitated by a convenient synthetic route to DAHP; such a route might also allow for the preparation of structural analoguesof DAHP. Most of the previous chemical synthesesof DAHPT-rl have employed 2-deoxy-o-glucose(a relatively costly carbohydrate at $17/g) ...
Respiratory chain is the most productive pathway to make ATP
... cycle). The chief purpose of the citric acid cycle is to supply chemical needs of respiratory chain. Citric acid cycle cannot run unless acetyl group is fed into the cycle through an enzyme cofactor, acetyl coenzyme A. The catabolism of molecules from all three major foodscarbohydrate, protein and l ...
... cycle). The chief purpose of the citric acid cycle is to supply chemical needs of respiratory chain. Citric acid cycle cannot run unless acetyl group is fed into the cycle through an enzyme cofactor, acetyl coenzyme A. The catabolism of molecules from all three major foodscarbohydrate, protein and l ...
Characterization of the receptors for the soluble pyocins S1, S2, and
... its versatility and adaptability to many different environments, and also the ability to produce a wide range of virulence factors which contribute to the virulence of P. aeruginosa. More than 90% of the P. aeruginosa strains are able to produce one or more pyocin (Michel-Briand & Baysse, 2000). Acc ...
... its versatility and adaptability to many different environments, and also the ability to produce a wide range of virulence factors which contribute to the virulence of P. aeruginosa. More than 90% of the P. aeruginosa strains are able to produce one or more pyocin (Michel-Briand & Baysse, 2000). Acc ...
Nutritional composition of Polyrhachis vicina Roger (Edible Chinese
... major antioxidant enzymes, SOD plays an important role in catalyzing the conversion of O2 to hydrogen and molecular oxygen, thereby helping to prevent tissue damage by O2 and its metabolites, and preventing the danger of Harber-Weiss reaction, which generates OH. In fact, SOD has been considered as ...
... major antioxidant enzymes, SOD plays an important role in catalyzing the conversion of O2 to hydrogen and molecular oxygen, thereby helping to prevent tissue damage by O2 and its metabolites, and preventing the danger of Harber-Weiss reaction, which generates OH. In fact, SOD has been considered as ...
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL
... essential to an understanding of human metabolism. For example, one might expect that a fasted individual would show a fall in all essential nutrient levels in the plasma pool. In many instances this is not the case initially because of the existence of storage pools, such as liver stores of iron or ...
... essential to an understanding of human metabolism. For example, one might expect that a fasted individual would show a fall in all essential nutrient levels in the plasma pool. In many instances this is not the case initially because of the existence of storage pools, such as liver stores of iron or ...
Hydroxy carboxylic acids
... Salicylic acid (from the Latin word for the willow tree, Salix, from whose bark it can be obtained) is a beta hydroxy acid (BHA) with the formula C6H4(OH)COOH, where the OH group is adjacent to the carboxyl group. This colorless crystalline organic acid is widely used in organic synthesis and functi ...
... Salicylic acid (from the Latin word for the willow tree, Salix, from whose bark it can be obtained) is a beta hydroxy acid (BHA) with the formula C6H4(OH)COOH, where the OH group is adjacent to the carboxyl group. This colorless crystalline organic acid is widely used in organic synthesis and functi ...
Short Answer Questions: a workshop
... Without ATP, cells (neurones, etc.) cannot carry out work and the brain and body cannot function properly. [ 60 words ] Possible answer: Caused by inadequate supply of ATP to neurones dependent on complete oxidation of glucose via PDH (16 words) ...
... Without ATP, cells (neurones, etc.) cannot carry out work and the brain and body cannot function properly. [ 60 words ] Possible answer: Caused by inadequate supply of ATP to neurones dependent on complete oxidation of glucose via PDH (16 words) ...
dutch national chemistry olympiad
... Many live organisms – plants as well as animals – are capable of producing vitamin C themselves. The most important reactions occurring during this so-called biosynthesis of vitamin C, can be described schematically as in figure 1: ...
... Many live organisms – plants as well as animals – are capable of producing vitamin C themselves. The most important reactions occurring during this so-called biosynthesis of vitamin C, can be described schematically as in figure 1: ...
Krebs cycle
... 5. Succinyl-CoA Synthetase • Free energy in thioester bond of succinyl CoA is conserved as GTP or ATP in higher animals (or ATP in plants, some bacteria) • Substrate level phosphorylation reaction ...
... 5. Succinyl-CoA Synthetase • Free energy in thioester bond of succinyl CoA is conserved as GTP or ATP in higher animals (or ATP in plants, some bacteria) • Substrate level phosphorylation reaction ...
Simulation of multiphase physico-chemical processes occurring in
... Within SPACCIM complex multiphase chemistry was coupled to a detailed microphysical model. The applied explicit aqueous phase radical mechanisms currently consists of CAPRAM 2.3 (Herrmann et al., 2000) and CAPRAM 2.4 (MODAC-mechanism, Ervens et al., 2003). The gas phase chemistry is described by the ...
... Within SPACCIM complex multiphase chemistry was coupled to a detailed microphysical model. The applied explicit aqueous phase radical mechanisms currently consists of CAPRAM 2.3 (Herrmann et al., 2000) and CAPRAM 2.4 (MODAC-mechanism, Ervens et al., 2003). The gas phase chemistry is described by the ...
SYNTHESIS OF OXOQUINOLINE DERIVATIVES COUPLED TO DIFFERENT AMINO ACID ESTERS
... formation as the coupling reagent, while HOBt was used to decrease racemization and to increase the yields [13]. Synthesis of 2-quinolone N acetyl -L-Tyr ethyl ester (D3) To a stirred solution of Tyr ethyl ester HCl (compound A1) (0.3mmol, 74mg) in (30ml) of DMF, (0.3mmol, 0.04ml) of NMM was added w ...
... formation as the coupling reagent, while HOBt was used to decrease racemization and to increase the yields [13]. Synthesis of 2-quinolone N acetyl -L-Tyr ethyl ester (D3) To a stirred solution of Tyr ethyl ester HCl (compound A1) (0.3mmol, 74mg) in (30ml) of DMF, (0.3mmol, 0.04ml) of NMM was added w ...
Hepoxilin

Hepoxilins (HxA3 and HxB3) are nonclassic eicosanoid hormones involved in inflammation.