Phys. Rev. B 76, 035315 (2007) - Petta Group
... hyperfine interaction.20,21,24 In this paper, we present a detailed theory describing coherent properties of coupled electrons in double quantum dots that was used to guide those experiments and analyze the results. The theory includes hyperfine interactions, external magnetic field, exchange terms, ...
... hyperfine interaction.20,21,24 In this paper, we present a detailed theory describing coherent properties of coupled electrons in double quantum dots that was used to guide those experiments and analyze the results. The theory includes hyperfine interactions, external magnetic field, exchange terms, ...
2.0 Chem 20 Final Review
... ▫ Hydrogen nucleus (proton) is simultaneously attracted to two pairs of electrons; one closer (in the same molecule) and one further away (a lone pair on the next molecule) Why do you need a strongly electronegative atom? It pulls the hydrogen’s ...
... ▫ Hydrogen nucleus (proton) is simultaneously attracted to two pairs of electrons; one closer (in the same molecule) and one further away (a lone pair on the next molecule) Why do you need a strongly electronegative atom? It pulls the hydrogen’s ...
Unit 1 Student Booklet
... reactant and product. 2. Write each element underneath the equation and keep a tally of the number of atoms of each element. 3. Use coefficients to balance metals first, then non-metals. 4. Leave single elements and diatomic molecules to balance last. 5. If possible, reduce the coefficients to the l ...
... reactant and product. 2. Write each element underneath the equation and keep a tally of the number of atoms of each element. 3. Use coefficients to balance metals first, then non-metals. 4. Leave single elements and diatomic molecules to balance last. 5. If possible, reduce the coefficients to the l ...
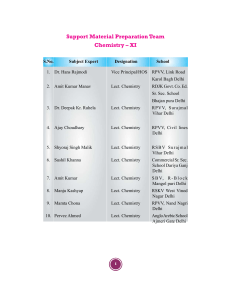
Support Material
... Discovery of Electron, Proton and Neutron, atomic number, isotopes and isobars. Thomson’s model and its limitations. Rutherford’s model and its limitations, Bohr’s model and its limitations, concept of shells and subshells, dual nature of matter and light, cle Broglie’s relationship, Heisenberg unce ...
... Discovery of Electron, Proton and Neutron, atomic number, isotopes and isobars. Thomson’s model and its limitations. Rutherford’s model and its limitations, Bohr’s model and its limitations, concept of shells and subshells, dual nature of matter and light, cle Broglie’s relationship, Heisenberg unce ...
Chemistry 2 Higher revision mark scheme
... forms an oxide that reacts with alkalis with chlorine forms a molecular chloride 1 of these for 1 mark semi-conductor suggests in between this, or any other for 1further mark [NB Maximum of 2 for arguing metal/non-metal only] Under each head 1 wrong reason → maximum of 1 available 2 wrong reasons → ...
... forms an oxide that reacts with alkalis with chlorine forms a molecular chloride 1 of these for 1 mark semi-conductor suggests in between this, or any other for 1further mark [NB Maximum of 2 for arguing metal/non-metal only] Under each head 1 wrong reason → maximum of 1 available 2 wrong reasons → ...
- Natural Sciences Publishing
... which corresponds to the absolute value of the sum of negative eigenvalues of ρ̂ TA [38] , and which vanishes for unentangled states, N(ρ ) does not increase under local operations and classical communications (LOCC), i.e., it is an entanglement monotone [39], and as such it can be used to quantify ...
... which corresponds to the absolute value of the sum of negative eigenvalues of ρ̂ TA [38] , and which vanishes for unentangled states, N(ρ ) does not increase under local operations and classical communications (LOCC), i.e., it is an entanglement monotone [39], and as such it can be used to quantify ...
2013 Avogadro Exam
... middle initial) on the STUDENT RESPONSE sheet. Also fill in the corresponding circles below your printed ...
... middle initial) on the STUDENT RESPONSE sheet. Also fill in the corresponding circles below your printed ...
Contents
... the Hamiltonian for this system and solve the Schrödinger equation associated with it. However, the Hamiltonian typically contains, besides the sums of single-particle kinetic energy and static potential, the interaction between pairs of particles. This makes the partial differential equation of ma ...
... the Hamiltonian for this system and solve the Schrödinger equation associated with it. However, the Hamiltonian typically contains, besides the sums of single-particle kinetic energy and static potential, the interaction between pairs of particles. This makes the partial differential equation of ma ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.