UNIT 1 WORKSHEET 1. Name three methods for the separation of
... 7.69 g Z. The second sample was 35.9% A and 64.1% Z. It was observed that 0.718 g A reacted with Z to form 2.00 g of the third sample. Show that these data illustrate the law of definite composition. ...
... 7.69 g Z. The second sample was 35.9% A and 64.1% Z. It was observed that 0.718 g A reacted with Z to form 2.00 g of the third sample. Show that these data illustrate the law of definite composition. ...
Hydrogen Atom Simulator – Exercises
... o Note how energy and frequency are directly proportional and energy and wavelength are inversely proportional. o On the slider are some of the energies which correspond to levels in the Lyman, Balmer, and Paschen series. o Clicking on the label will shoot a photon of that energy. ...
... o Note how energy and frequency are directly proportional and energy and wavelength are inversely proportional. o On the slider are some of the energies which correspond to levels in the Lyman, Balmer, and Paschen series. o Clicking on the label will shoot a photon of that energy. ...
4-1. 1 - Riverside Local Schools
... ● Calculations: Calculate the following and fill in the table on the front 1. Find the distance ( z ) from the diffraction grating to the image of the spectral line using the following equation: z = √ x2 + y2 ...
... ● Calculations: Calculate the following and fill in the table on the front 1. Find the distance ( z ) from the diffraction grating to the image of the spectral line using the following equation: z = √ x2 + y2 ...
Objective 6: TSW explain how the quantum
... • If light is being given off in bursts as Planck suggested in quantum mechanics, it is a stream of particles (photons) each with a specific amount of energy, E = hf • If the photon has sufficient energy to knock an electron out of an atom, then it will be ejected, if it isn’t of high enough energy ...
... • If light is being given off in bursts as Planck suggested in quantum mechanics, it is a stream of particles (photons) each with a specific amount of energy, E = hf • If the photon has sufficient energy to knock an electron out of an atom, then it will be ejected, if it isn’t of high enough energy ...
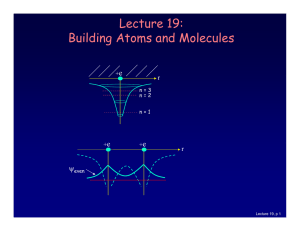
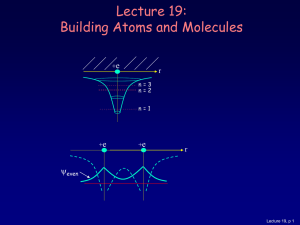
Lecture 19: Building Atoms and Molecules
... Let’s start building more complicated atoms to study the Periodic Table. For atoms with many electrons (e.g., carbon: 6, iron: 26, etc.) 4 What energies do the electrons have? “Pauli Exclusion Principle” (1925) No two electrons can be in the same quantum state. For example, in a given atom they cann ...
... Let’s start building more complicated atoms to study the Periodic Table. For atoms with many electrons (e.g., carbon: 6, iron: 26, etc.) 4 What energies do the electrons have? “Pauli Exclusion Principle” (1925) No two electrons can be in the same quantum state. For example, in a given atom they cann ...
Nature of Molecules and Water
... − O and N are more electronegative than C and H • Differences in electronegativity dictate how electrons are distributed in covalent bonds – Nonpolar covalent bonds = equal sharing of electrons – Polar covalent bonds = unequal sharing of electrons • Polar molecules have significant amounts of O or N ...
... − O and N are more electronegative than C and H • Differences in electronegativity dictate how electrons are distributed in covalent bonds – Nonpolar covalent bonds = equal sharing of electrons – Polar covalent bonds = unequal sharing of electrons • Polar molecules have significant amounts of O or N ...
Unit 4 - School District of Durand
... equipped with a dim red light so that your friend can see enough to handle the film and the developing solution. One day when the red bulb burned out, your friend replaced it with a dim yellow bulb that she found. She and several other students were later dismayed when they ruined their film while u ...
... equipped with a dim red light so that your friend can see enough to handle the film and the developing solution. One day when the red bulb burned out, your friend replaced it with a dim yellow bulb that she found. She and several other students were later dismayed when they ruined their film while u ...
+1/2 and
... geometric place of points with a given r value build a sphere. An orbital has n-l spheric nodal surfaces, one of them is in the infinity. The points with common q build a cone; at 90o cosq=0, cone deforms to a plane; their number is: l - m The points with common polar angle build planes (sin=0 or c ...
... geometric place of points with a given r value build a sphere. An orbital has n-l spheric nodal surfaces, one of them is in the infinity. The points with common q build a cone; at 90o cosq=0, cone deforms to a plane; their number is: l - m The points with common polar angle build planes (sin=0 or c ...
Energy level - Spring-Ford Area School District
... Electron Configurations… …are the way electrons are arranged in various orbitals around the nuclei of atoms. Three rules tell us how: 1) Aufbau principle - electrons enter the lowest energy first. • This causes difficulties because of the overlap of orbitals of different energies – follow the diagr ...
... Electron Configurations… …are the way electrons are arranged in various orbitals around the nuclei of atoms. Three rules tell us how: 1) Aufbau principle - electrons enter the lowest energy first. • This causes difficulties because of the overlap of orbitals of different energies – follow the diagr ...
Chapter 5 Electrons in Atoms
... Electron Configurations… …are the way electrons are arranged in various orbitals around the nuclei of atoms. Three rules tell us how: 1) Aufbau principle - electrons enter the lowest energy first. • This causes difficulties because of the overlap of orbitals of different energies – follow the diagr ...
... Electron Configurations… …are the way electrons are arranged in various orbitals around the nuclei of atoms. Three rules tell us how: 1) Aufbau principle - electrons enter the lowest energy first. • This causes difficulties because of the overlap of orbitals of different energies – follow the diagr ...
class slides for Chapter 39
... semiconductor, differing only in the size of their granules. Each granule serves as an electron trap. The lower sample has the larger granules and consequently the smaller spacing between energy levels and the lower photon energy threshold for the absorption of light. Light not absorbed is scattered ...
... semiconductor, differing only in the size of their granules. Each granule serves as an electron trap. The lower sample has the larger granules and consequently the smaller spacing between energy levels and the lower photon energy threshold for the absorption of light. Light not absorbed is scattered ...
Chemistry Nomenclature Notes
... Elements on the periodic table are classified and arranged according to four basic patterns: 1. Atomic number: the number of protons (positively charged particle) in the nucleus of an element. ...
... Elements on the periodic table are classified and arranged according to four basic patterns: 1. Atomic number: the number of protons (positively charged particle) in the nucleus of an element. ...
Review for Exam 1
... Determine how many of each ion type is needed for an overall charge of zero. When the cation and anion have different charges, use the ion charges to determine the number of ions of each needed. ...
... Determine how many of each ion type is needed for an overall charge of zero. When the cation and anion have different charges, use the ion charges to determine the number of ions of each needed. ...
Multi-Electron Atoms Helium Schrödinger Equation
... e.g. Expectation value of some measurable M: ...
... e.g. Expectation value of some measurable M: ...
Fall Exam 4 - Chemistry - University of Kentucky
... The total number of molecular orbitals formed does not always equal the number of atomic orbitals combined. In H2 molecules, the two 1s orbitals combine constructively, which results in one bonding orbital and one nonbonding orbital Electrons placed in antibonding orbitals stabilize the species. Whe ...
... The total number of molecular orbitals formed does not always equal the number of atomic orbitals combined. In H2 molecules, the two 1s orbitals combine constructively, which results in one bonding orbital and one nonbonding orbital Electrons placed in antibonding orbitals stabilize the species. Whe ...
Solon City Schools
... p, d, and f stand for names given to groups of lines in the spectra of 4s the alkali metals. Early chemists called the line groups sharp, principal, diffuse, and fundamental. ...
... p, d, and f stand for names given to groups of lines in the spectra of 4s the alkali metals. Early chemists called the line groups sharp, principal, diffuse, and fundamental. ...
Chapter 2
... p, d, and f stand for names given to groups of lines in the spectra of 4s the alkali metals. Early chemists called the line groups sharp, principal, diffuse, and fundamental. ...
... p, d, and f stand for names given to groups of lines in the spectra of 4s the alkali metals. Early chemists called the line groups sharp, principal, diffuse, and fundamental. ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.