III. Quantum Model of the Atom
... n = # of sublevels per level n2 = # of orbitals per level Sublevel sets: 1 s, 3 p, 5 d, 7 f C. Johannesson ...
... n = # of sublevels per level n2 = # of orbitals per level Sublevel sets: 1 s, 3 p, 5 d, 7 f C. Johannesson ...
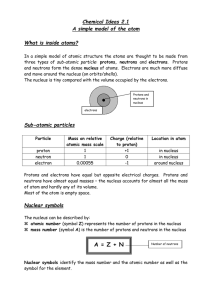
Notes - Organization of Matter
... • Compounds are pure substances that are composed of two or more atoms that are chemically combined • Compounds can only be changed into simpler substances called elements by chemical changes ...
... • Compounds are pure substances that are composed of two or more atoms that are chemically combined • Compounds can only be changed into simpler substances called elements by chemical changes ...
Chapter 8
... (covalent bonds, sharing of electrons). • Form between ions resulting in ionic cmps (ionic bonds, electron transfer). • Chemical bonding model assumes molecule consists of individual chemical bonds. • Bond strength varies and is measured by bond energy (kJ/mol) = energy required to break a mole of b ...
... (covalent bonds, sharing of electrons). • Form between ions resulting in ionic cmps (ionic bonds, electron transfer). • Chemical bonding model assumes molecule consists of individual chemical bonds. • Bond strength varies and is measured by bond energy (kJ/mol) = energy required to break a mole of b ...
Preview Sample 1
... Chemicals used as reagents, such as bromthymol blue or sodium iodide, may permanently stain clothing. Use with caution. ...
... Chemicals used as reagents, such as bromthymol blue or sodium iodide, may permanently stain clothing. Use with caution. ...
Instructor`s Notes Atomic Tiles: Play Your Way from Atoms to
... electrons. 3b. Students know that compounds are formed by combining two or more different elements and that compounds have properties that are different from their constituent elements. 5a. Students know reactant atoms and molecules interact to form products with different chemical properties. 5b. S ...
... electrons. 3b. Students know that compounds are formed by combining two or more different elements and that compounds have properties that are different from their constituent elements. 5a. Students know reactant atoms and molecules interact to form products with different chemical properties. 5b. S ...
Quantum Physics
... be explained by the classical wave theory of light. Describe how the photon model explains these characteristics. CLICK FOR ANSWER Light hits material and electron is ejected. (The electron is called a “photoelectron”.) ...
... be explained by the classical wave theory of light. Describe how the photon model explains these characteristics. CLICK FOR ANSWER Light hits material and electron is ejected. (The electron is called a “photoelectron”.) ...
Chapter 27
... and proton have the same momentum, they cannot have the same speed because of the difference in their masses. For the same reason, remembering that KE = p2/2m, they cannot have the same kinetic energy. Because the kinetic energy is the only type of energy an isolated particle can have, and we have a ...
... and proton have the same momentum, they cannot have the same speed because of the difference in their masses. For the same reason, remembering that KE = p2/2m, they cannot have the same kinetic energy. Because the kinetic energy is the only type of energy an isolated particle can have, and we have a ...
How Atoms Bond: Ionic Bonds
... And atoms themselves? Heads up – this next part contains information that might prove useful in a later quiz: Because atoms have equal numbers of positive protons and negative electrons , the electric charges cancel each other out. Net charge: zero. OK, now back to electrons. While the positive prot ...
... And atoms themselves? Heads up – this next part contains information that might prove useful in a later quiz: Because atoms have equal numbers of positive protons and negative electrons , the electric charges cancel each other out. Net charge: zero. OK, now back to electrons. While the positive prot ...
Chem 1411 Chapt2
... Molecular (covalent)- Consists of non-metals only. HCl, N2O4, C3H6O, C6H12O6 Note- All compounds can be molecules; not all molecules can be compounds. Ions- Are chemical species that have a net charge. Monatomic- cations: K+, Na+, Mg+2, Al+3 Anions: Cl-, O2-, BrThe monatomic ions like to take charge ...
... Molecular (covalent)- Consists of non-metals only. HCl, N2O4, C3H6O, C6H12O6 Note- All compounds can be molecules; not all molecules can be compounds. Ions- Are chemical species that have a net charge. Monatomic- cations: K+, Na+, Mg+2, Al+3 Anions: Cl-, O2-, BrThe monatomic ions like to take charge ...
AP Chemistry Summer Work Packet I have read and understand the i
... Orbitals; wave functions knowing (n) in electron shell N & 1 values = sub shells 4. Electron Configuration ! Hund’s Rules Know how to indicate electron configuration of an atom Main Groups Valence electrons vs. core electrons Transitions lanthanide actinide and F blocks elements Questi ...
... Orbitals; wave functions knowing (n) in electron shell N & 1 values = sub shells 4. Electron Configuration ! Hund’s Rules Know how to indicate electron configuration of an atom Main Groups Valence electrons vs. core electrons Transitions lanthanide actinide and F blocks elements Questi ...
10th Grade Chemistry - Ms. Luckasavitch
... Chapter 1 Introduction to Chemistry and Chapter 3 Scientific Measurement Objectives: Students will understand and demonstrate the role of chemistry in society, the use of the scientific method, measurement and errors, significant figures, and SI units. Essential Questions: In what ways is chemistry ...
... Chapter 1 Introduction to Chemistry and Chapter 3 Scientific Measurement Objectives: Students will understand and demonstrate the role of chemistry in society, the use of the scientific method, measurement and errors, significant figures, and SI units. Essential Questions: In what ways is chemistry ...
Document
... an electric field to accelerate a beam of positively charged ions – electrically charged plates attract the positive ions from the mixture in the ionisation chamber and accelerate them. By arranging the plates and choosing their voltage a fine beam of ions with only a narrow range of kinetic energie ...
... an electric field to accelerate a beam of positively charged ions – electrically charged plates attract the positive ions from the mixture in the ionisation chamber and accelerate them. By arranging the plates and choosing their voltage a fine beam of ions with only a narrow range of kinetic energie ...
lecture 5 radiation and matter
... However, practically speaking, electrons, atoms, and molecules all have individual environments that blurs the situation somewhat. For example, electrons in molecules have discreet electronic states and a wider variety of vibrational states that are dependent on their local environment (temperature, ...
... However, practically speaking, electrons, atoms, and molecules all have individual environments that blurs the situation somewhat. For example, electrons in molecules have discreet electronic states and a wider variety of vibrational states that are dependent on their local environment (temperature, ...
Chapter 7 – Quantum Theory and Atomic Structure Chapters 4 and 6
... De Broglie brought us a step closer to what the atom really looks like, but the best model of the atom to date throws out the concept of circular orbits for the electron altogether. Erwin Schrödinger developed an equation that treats the electron entirely as a wave and only at the very end takes int ...
... De Broglie brought us a step closer to what the atom really looks like, but the best model of the atom to date throws out the concept of circular orbits for the electron altogether. Erwin Schrödinger developed an equation that treats the electron entirely as a wave and only at the very end takes int ...
Midterm Review 4
... 47. It is possible to convert moles to particles by: a. multiplying by 6.02 x1023 b. dividing by 6.02 x1023 c. multiplying by the molar mass d. dividing by the molar mass 48. How many molecules of sulfur dioxide are present in 1.60 moles of sulfur dioxide? a. 9.63 x 1023 b. 102.1 x101 c. 7.62 x 101 ...
... 47. It is possible to convert moles to particles by: a. multiplying by 6.02 x1023 b. dividing by 6.02 x1023 c. multiplying by the molar mass d. dividing by the molar mass 48. How many molecules of sulfur dioxide are present in 1.60 moles of sulfur dioxide? a. 9.63 x 1023 b. 102.1 x101 c. 7.62 x 101 ...
Unit 2: Biochem Notes
... Na+Cl3. H2O has the ability to travel through small pores or to move upward through narrow vessels against the force of gravity. ________________________ - Water molecules and the molecules of solid surfaces are attracted to each other. 4. Water heats up and cools down at a slow rate (resists change ...
... Na+Cl3. H2O has the ability to travel through small pores or to move upward through narrow vessels against the force of gravity. ________________________ - Water molecules and the molecules of solid surfaces are attracted to each other. 4. Water heats up and cools down at a slow rate (resists change ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.