Atomic Physics 4
... • Within an atom energy is only absorbed or emitted when electrons change energy levels and this energy is QUANTIZED. • electrons are either in lowest energy state (ground state) or certain allowed levels (excited state). ...
... • Within an atom energy is only absorbed or emitted when electrons change energy levels and this energy is QUANTIZED. • electrons are either in lowest energy state (ground state) or certain allowed levels (excited state). ...
Relativity Problem Set 7 - Solutions Prof. J. Gerton October 24, 2011
... The energy spectrum is proportional to n2 as in the Hydrogen atom case, which is obvious because we are still treating a Coulomb field, but the number of the fundamental level E0 = 6.81 eV is different from the fundamental level of the Hydrogen system. Positronium has long being theoretically predic ...
... The energy spectrum is proportional to n2 as in the Hydrogen atom case, which is obvious because we are still treating a Coulomb field, but the number of the fundamental level E0 = 6.81 eV is different from the fundamental level of the Hydrogen system. Positronium has long being theoretically predic ...
Document
... i. To make writing names of the elements simple, chemists use abbreviations, or element symbols. ii. Many of these symbols consist of the first letter or the first two letters of the element name. c. 3.3 Dalton’s Atomic Theory i. In the early 1800’s English scientist John Dalton came up with an expl ...
... i. To make writing names of the elements simple, chemists use abbreviations, or element symbols. ii. Many of these symbols consist of the first letter or the first two letters of the element name. c. 3.3 Dalton’s Atomic Theory i. In the early 1800’s English scientist John Dalton came up with an expl ...
Honors Chemistry
... A substance composed of two or more elements chemically combined is called a. an isotope b. a compound c. an element ...
... A substance composed of two or more elements chemically combined is called a. an isotope b. a compound c. an element ...
Document
... a chemical reaction. Gasoline CO2 and H2O • The number of each type of element and their masses remain unchanged (balanced) in a chemical reaction. (Law of Conservation of Mass) • A chemical equation is a way to describe or represent what goes on in a chemical reaction and follows the Law of Conse ...
... a chemical reaction. Gasoline CO2 and H2O • The number of each type of element and their masses remain unchanged (balanced) in a chemical reaction. (Law of Conservation of Mass) • A chemical equation is a way to describe or represent what goes on in a chemical reaction and follows the Law of Conse ...
1) Which of the following concepts was discussed in Chapter 1
... 1) Increase the momentum of the particle 2) Decrease the momentum of the particle 3) Decrease the well width 4) Increase the well depth 5) Decrease the well depth ...
... 1) Increase the momentum of the particle 2) Decrease the momentum of the particle 3) Decrease the well width 4) Increase the well depth 5) Decrease the well depth ...
Revision worksheet 1
... (See www.chembook.co.uk/index.htm#answersheet1 for latest link to current answer sheet.) ...
... (See www.chembook.co.uk/index.htm#answersheet1 for latest link to current answer sheet.) ...
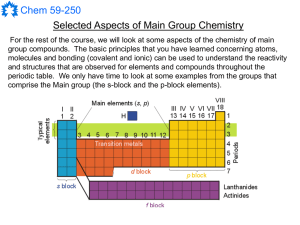
Main Group Notes 1
... Much of the important chemistry of the group 17 elements can be understood on the basis of their electronic structure and electronegativity. Since the elements have a [core]ns2 np5 electron configuration, neutral group 17 compounds can form up to seven bonds. This provides for several possible oxida ...
... Much of the important chemistry of the group 17 elements can be understood on the basis of their electronic structure and electronegativity. Since the elements have a [core]ns2 np5 electron configuration, neutral group 17 compounds can form up to seven bonds. This provides for several possible oxida ...
Ch 16 – Quantam Physics
... would be a continuous radiation of energy. The loss of energy would slow down the speed of the electron and eventually the electron would fall into the nucleus. But such a collapse does not occur. Rutherford's model was unable to explain it. ...
... would be a continuous radiation of energy. The loss of energy would slow down the speed of the electron and eventually the electron would fall into the nucleus. But such a collapse does not occur. Rutherford's model was unable to explain it. ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.