Anomalous Magnetoresistance in Dirty Magnetic Quantum Wells
... magnetoresistance oscillation originated from the QHFM formation are clearly observed down to B = 0.3 T and up to T = 1.5 K, despite very low mobility µ < 500 cm2 /Vs. At the same time transport becomes strongly nonlinear. Moreover, while at B = 0 and high excitation currents I exc the apparent meta ...
... magnetoresistance oscillation originated from the QHFM formation are clearly observed down to B = 0.3 T and up to T = 1.5 K, despite very low mobility µ < 500 cm2 /Vs. At the same time transport becomes strongly nonlinear. Moreover, while at B = 0 and high excitation currents I exc the apparent meta ...
PPT
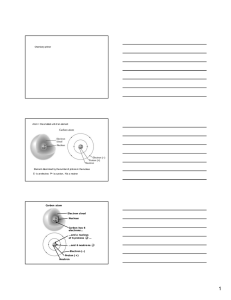
... Electron A falls from energy level n=2 to energy level n=1 (ground state), causing a photon to be emitted. Electron B falls from energy level n=3 to energy level n=1 (ground state), causing a photon to be emitted. ...
... Electron A falls from energy level n=2 to energy level n=1 (ground state), causing a photon to be emitted. Electron B falls from energy level n=3 to energy level n=1 (ground state), causing a photon to be emitted. ...
What You Need To Know for the Chemistry Regents Exam
... H and He only need 2 electrons to fill their valence level. The noble gasses (group 18) have filled valence levels. They do not normally bond with other atoms. 10. Electron-dot diagrams (Lewis structures) represent the valence electron arrangement in elements, compounds and ions. Electrons in ...
... H and He only need 2 electrons to fill their valence level. The noble gasses (group 18) have filled valence levels. They do not normally bond with other atoms. 10. Electron-dot diagrams (Lewis structures) represent the valence electron arrangement in elements, compounds and ions. Electrons in ...
Chapter 8 – Covalent Bonding
... Double Covalent Bond – a bond that involves two shared pairs of electrons Triple Covalent Bond – a bond that involves three shared pairs of electrons Let’s Practice ...
... Double Covalent Bond – a bond that involves two shared pairs of electrons Triple Covalent Bond – a bond that involves three shared pairs of electrons Let’s Practice ...
Need
... H and He only need 2 electrons to fill their valence level. The noble gasses (group 18) have filled valence levels. They do not normally bond with other atoms. 10. Electron-dot diagrams (Lewis structures) represent the valence electron arrangement in elements, compounds and ions. Electrons in ...
... H and He only need 2 electrons to fill their valence level. The noble gasses (group 18) have filled valence levels. They do not normally bond with other atoms. 10. Electron-dot diagrams (Lewis structures) represent the valence electron arrangement in elements, compounds and ions. Electrons in ...
Northgate High School Chemistry Department
... AS Unit F321: Atoms, Bonds and Groups Module 1.3.2 Group 2 describe the redox reactions of the Group 2 elements Mg → Ba: (i) with oxygen, (ii) with water; explain the trend in reactivity of Group 2 elements down the group due to the increasing ease of forming cations, in terms of atomic size, shield ...
... AS Unit F321: Atoms, Bonds and Groups Module 1.3.2 Group 2 describe the redox reactions of the Group 2 elements Mg → Ba: (i) with oxygen, (ii) with water; explain the trend in reactivity of Group 2 elements down the group due to the increasing ease of forming cations, in terms of atomic size, shield ...
Text Book: Fundamentals of Physics Authors: Halliday, Resnick
... three-dimensional structure called a lattice. •Solid such as wood, plastic, glass, and rubber whose atoms are not arranged in such repetitive patterns are not considered. •Three electrical properties that can be used to distinguish among crystalline solids are resistivity , temperature, coefficient ...
... three-dimensional structure called a lattice. •Solid such as wood, plastic, glass, and rubber whose atoms are not arranged in such repetitive patterns are not considered. •Three electrical properties that can be used to distinguish among crystalline solids are resistivity , temperature, coefficient ...
a non-perturbative approach for quantum field theory
... wavefunctions) for ground state (physical electron) and several low-lying excited states (excited electrons) Evaluate other observables (anomalous magnetic moment, parton distribution function) from electron wavefunction (vector-matrix-vector multiplication) ...
... wavefunctions) for ground state (physical electron) and several low-lying excited states (excited electrons) Evaluate other observables (anomalous magnetic moment, parton distribution function) from electron wavefunction (vector-matrix-vector multiplication) ...
Chemistry primer Atom = the smallest unit of an element Element
... Physical Properties of mineral related to crystalline structure and composit ion (The less reliable ones for mineral identification) Luster: How the mineral reflects light. Streak: Color in power form. This is more reliable than color due to uniformit y of grains. Color: Determined by the compositi ...
... Physical Properties of mineral related to crystalline structure and composit ion (The less reliable ones for mineral identification) Luster: How the mineral reflects light. Streak: Color in power form. This is more reliable than color due to uniformit y of grains. Color: Determined by the compositi ...
Chemistry Final Exam Review 2006-2007
... 21. What is the difference between the Bohr model and the Quantum mechanical model? 22. a. What are flame tests? b. What area of the electromagnetic radiation spectrum allows us to observe flame tests? c. Is energy released or absorbed when an electron falls from a higher energy level to a lower ene ...
... 21. What is the difference between the Bohr model and the Quantum mechanical model? 22. a. What are flame tests? b. What area of the electromagnetic radiation spectrum allows us to observe flame tests? c. Is energy released or absorbed when an electron falls from a higher energy level to a lower ene ...
Chapter 27: Summary
... to be emitted via the photoelectric effect. If we reduce the intensity of the light shining on the metal, without changing its wavelength, what happens? Explain your answer. 4. The work functions of gold, aluminum, and cesium are 5.1 eV, 4.1 eV, and 2.1 eV, respectively. If light of a particular fre ...
... to be emitted via the photoelectric effect. If we reduce the intensity of the light shining on the metal, without changing its wavelength, what happens? Explain your answer. 4. The work functions of gold, aluminum, and cesium are 5.1 eV, 4.1 eV, and 2.1 eV, respectively. If light of a particular fre ...
Chapter 6: Chemistry in Biology
... An __________ is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by physical or chemical means. ...
... An __________ is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by physical or chemical means. ...
國立嘉義大學九十七學年度轉學生招生考試試題
... 17. If the principal quantum number is 4, how many values of the angular momentum quantum number are possible? (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4 18. If the angular momentum quantum number is 4, how many values of the magnetic quantum number are possible? (A) 5 (B) 7 (C) 9 (D) 11 19. A f-orbital has an angular ...
... 17. If the principal quantum number is 4, how many values of the angular momentum quantum number are possible? (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4 18. If the angular momentum quantum number is 4, how many values of the magnetic quantum number are possible? (A) 5 (B) 7 (C) 9 (D) 11 19. A f-orbital has an angular ...
SOME ELEMENTS OF ATOMIC STRUCTURE THEORY
... spin angular momentum is Sz = ms h̄. Here ms is analogous to ml except that it has only two possible values: ms = ±1/2. We say that the spin must be either “up” or “down”. For reasons of convenience in speaking and writing, a historical system of letters instead of l values, known as spectroscopic n ...
... spin angular momentum is Sz = ms h̄. Here ms is analogous to ml except that it has only two possible values: ms = ±1/2. We say that the spin must be either “up” or “down”. For reasons of convenience in speaking and writing, a historical system of letters instead of l values, known as spectroscopic n ...
Midterm Review Date
... 37. What is the total number of oxygen atoms in the formula MgSO 4 • 7 H 2O? [The • represents seven units of H 2O attached to one unit of MgSO 4 .] A) 11 ...
... 37. What is the total number of oxygen atoms in the formula MgSO 4 • 7 H 2O? [The • represents seven units of H 2O attached to one unit of MgSO 4 .] A) 11 ...
North Haven Public Schools Curriculum
... Biological, chemical and physical properties of matter result from the ability of atoms to form bonds from electrostatic forces between electrons and protons and between atoms and molecules. Atoms combine to form molecules by sharing electrons to form covalent or metallic bonds or by exchanging el ...
... Biological, chemical and physical properties of matter result from the ability of atoms to form bonds from electrostatic forces between electrons and protons and between atoms and molecules. Atoms combine to form molecules by sharing electrons to form covalent or metallic bonds or by exchanging el ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.