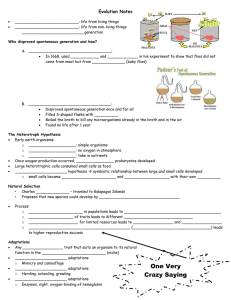
Spontaneous Generation
... D. proteins were present before amino acids 9. How do scientists explain the increase in oxygen in Earth’s early atmosphere? A. Microbes produced oxygen through photosynthesis. B. Ozone was dissolved, creating free oxygen in the atmosphere. C. Greenhouse gas molecules were separated into atmospheric ...
... D. proteins were present before amino acids 9. How do scientists explain the increase in oxygen in Earth’s early atmosphere? A. Microbes produced oxygen through photosynthesis. B. Ozone was dissolved, creating free oxygen in the atmosphere. C. Greenhouse gas molecules were separated into atmospheric ...
Origin of Life
... years (first human life) •20 years would take you back to the Cambrian age (500million years ago) ...
... years (first human life) •20 years would take you back to the Cambrian age (500million years ago) ...
BSC 1005
... • Led to the conclusion that the earth can be understood in terms of universal laws ...
... • Led to the conclusion that the earth can be understood in terms of universal laws ...
15-1 The Puzzle of Life*s Diversity
... different types of beaks adapted to their type of food gathering ...
... different types of beaks adapted to their type of food gathering ...
Chapters 14-15 Reading Notes Key
... He proposed that individuals could acquire traits during their lifetimes as a result of experience or behavior, and then pass these traits to offspring Is this idea still accepted? Why or why not? No, it is not – because only characteristics that are genetically determined can be inherited (by gamet ...
... He proposed that individuals could acquire traits during their lifetimes as a result of experience or behavior, and then pass these traits to offspring Is this idea still accepted? Why or why not? No, it is not – because only characteristics that are genetically determined can be inherited (by gamet ...
Unit Three - Owen County Schools
... Homologous Structures - body parts that are similar in structure, but have different functions. Analogous Structures - body parts that are different in structure, but have the same function. ...
... Homologous Structures - body parts that are similar in structure, but have different functions. Analogous Structures - body parts that are different in structure, but have the same function. ...
1 History of Micro
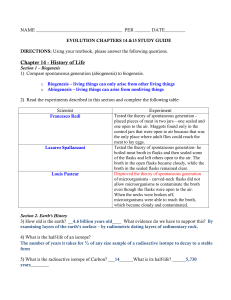
... • Francesco Redi and rotten meat (1668) • Lazarro Spallazani and chicken broth (1765) • Pasteur and swan-necked flasks (1861) • Tyndall and Sterility •The Golden Age of Microbiology (1857-1914) • Fermentation and Pasteurization • Germ Theory of Disease (Koch) ...
... • Francesco Redi and rotten meat (1668) • Lazarro Spallazani and chicken broth (1765) • Pasteur and swan-necked flasks (1861) • Tyndall and Sterility •The Golden Age of Microbiology (1857-1914) • Fermentation and Pasteurization • Germ Theory of Disease (Koch) ...
Blank Jeopardy
... Name of the scientist that came up with the same theory of Darwin about natural selection but got secondary credit only. ...
... Name of the scientist that came up with the same theory of Darwin about natural selection but got secondary credit only. ...
Darwinian Evolution Summative Assessment Review Define
... 17. What is the idea developed by Lyell which states that the geologic processes that shaped Earth in the past continue to operate in the same way today? 18. What do farmers look for when they select plants or animals to use for breeding? ...
... 17. What is the idea developed by Lyell which states that the geologic processes that shaped Earth in the past continue to operate in the same way today? 18. What do farmers look for when they select plants or animals to use for breeding? ...
Unit 8 Test Review
... 14. What kind of rocks are fossils found in? 15. Explain relative dating of fossils 16. Explain radioactive dating 17. What is a half life? 18. What was Lamarck’s (incorrect) theory called and what did it say? 19. What was Darwin’s theory called and what were its four points? 20. What were the Galap ...
... 14. What kind of rocks are fossils found in? 15. Explain relative dating of fossils 16. Explain radioactive dating 17. What is a half life? 18. What was Lamarck’s (incorrect) theory called and what did it say? 19. What was Darwin’s theory called and what were its four points? 20. What were the Galap ...
Review for Unit 1 Test on Nature of Science and History of Biology
... *Be able to list and give an example of each of the 8 characteristics of life* -Made up of cells (single cells,tissues, organs, organ systems, etc) -Pass on their genetic code (DNA) ((Heredity)) -Reproduce (at some point the population produces offspring) -Adapt and Evolve as a population -Grow and ...
... *Be able to list and give an example of each of the 8 characteristics of life* -Made up of cells (single cells,tissues, organs, organ systems, etc) -Pass on their genetic code (DNA) ((Heredity)) -Reproduce (at some point the population produces offspring) -Adapt and Evolve as a population -Grow and ...