energy - U of L Class Index
... The Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom In 1913, Neils Bohr (1885-1962) proposed explanation H hydrogen based on three postulates: ...
... The Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom In 1913, Neils Bohr (1885-1962) proposed explanation H hydrogen based on three postulates: ...
Orbitals Package Examples Introduction Initialization
... one or two parameters are left symbolic, plots readily show the variation with the parameter(s), e.g., overlap integrals as a function of internuclear distance. Legal Notice: The copyright for this application is owned by the author(s). Neither Maplesoft nor the author are responsible for any errors ...
... one or two parameters are left symbolic, plots readily show the variation with the parameter(s), e.g., overlap integrals as a function of internuclear distance. Legal Notice: The copyright for this application is owned by the author(s). Neither Maplesoft nor the author are responsible for any errors ...
ch04_sec3_as - LCMR School District
... In an atom, an energy level is an area around the nucleus where electrons are located. Each energy level may contain only a certain number of electrons. The electrons in an atom’s outer energy level are called valence electrons, which determine the chemical properties of an atom. The diagram below s ...
... In an atom, an energy level is an area around the nucleus where electrons are located. Each energy level may contain only a certain number of electrons. The electrons in an atom’s outer energy level are called valence electrons, which determine the chemical properties of an atom. The diagram below s ...
Orbitals
... 1. No electrons are emitted if the frequency of light used is less than νo, regardless of the intensity of the light. 2. For light with a frequency≥ νo , electrons are emitted. The number of electrons increases with the intensity of the light. 3. For light with a frequency > νo , the electrons are e ...
... 1. No electrons are emitted if the frequency of light used is less than νo, regardless of the intensity of the light. 2. For light with a frequency≥ νo , electrons are emitted. The number of electrons increases with the intensity of the light. 3. For light with a frequency > νo , the electrons are e ...
4. - period2chem
... a. 0.652 dm, b. 2,300 kg, c. 65 mL, d. 50,200 cm 1900 mL 8.7 hours slope = (mass) (volume) = density always record one estimate digit 1200 m 4.84 10-19 J Hydrogen atoms have specific energy levels. Therefore, the atoms can only gain or lose certain amounts of energy. When atoms lose energy, they ...
... a. 0.652 dm, b. 2,300 kg, c. 65 mL, d. 50,200 cm 1900 mL 8.7 hours slope = (mass) (volume) = density always record one estimate digit 1200 m 4.84 10-19 J Hydrogen atoms have specific energy levels. Therefore, the atoms can only gain or lose certain amounts of energy. When atoms lose energy, they ...
Chapter 2 – Atoms and Elements - U of L Class Index
... charged nucleus so, as it slows, the electron should spiral in toward the nucleus. This does not happen! Why not? ...
... charged nucleus so, as it slows, the electron should spiral in toward the nucleus. This does not happen! Why not? ...
Honors Chemistry Unit 1 Outline – 2012-2013
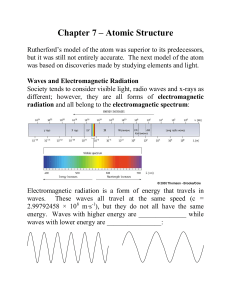
... Chm 1.1.3 Chapter 4 a. Understand that energy exists in discrete units called quanta b. Describe the concepts of excited and ground state electrons in the atom c. Articulate that electromagnetic radiation is made up of photons d. Understand the relationship between wavelength and frequency e. Use th ...
... Chm 1.1.3 Chapter 4 a. Understand that energy exists in discrete units called quanta b. Describe the concepts of excited and ground state electrons in the atom c. Articulate that electromagnetic radiation is made up of photons d. Understand the relationship between wavelength and frequency e. Use th ...
1411-Practice Exam 3 (ch6-8)
... Sodium and potassium have similar chemical and physical properties. This is best explained by the fact that both elements A) are active metals. B) are in Period 1 of the periodic table. C) have the same ground-state valence-electron configuration. D) have low relative atomic masses. E) have relative ...
... Sodium and potassium have similar chemical and physical properties. This is best explained by the fact that both elements A) are active metals. B) are in Period 1 of the periodic table. C) have the same ground-state valence-electron configuration. D) have low relative atomic masses. E) have relative ...
Science 9
... A) are composed of metal ions bonded to other metal ions. B) are formed when metal react with non-metals. C) are substances with low melting points. D) are usually insoluble in water. 3. Molecular compounds… A) are combinations of metals and non-metals. B) form when electrons are shared. C) are good ...
... A) are composed of metal ions bonded to other metal ions. B) are formed when metal react with non-metals. C) are substances with low melting points. D) are usually insoluble in water. 3. Molecular compounds… A) are combinations of metals and non-metals. B) form when electrons are shared. C) are good ...
PA304 QUANTUM MECHANICS
... Hamiltonian by solving the Schrödinger time-independent equation H > = E > . ...
... Hamiltonian by solving the Schrödinger time-independent equation H > = E > . ...
Regents Review Packet B2 Answer Key
... 4. Identify the physical property in the table that could be used to differentiate the samples of the three elements from each other. ...
... 4. Identify the physical property in the table that could be used to differentiate the samples of the three elements from each other. ...
Thornton/Rex Chp 4 Structure of the Atom
... The Rydberg constant for infinite nuclear mass is replaced by R. ...
... The Rydberg constant for infinite nuclear mass is replaced by R. ...
Chapter 2: Data Analysis
... Bohr’s Model of Hydrogen Atom quantum – quantity of energy gained or lost by an atom when electrons are excited photon – a quantum of light ground state – lowest energy level of an atom excited state – a heightened state of energy in an atom Electrons of hydrogen circle the nucleus in orbits 1. orb ...
... Bohr’s Model of Hydrogen Atom quantum – quantity of energy gained or lost by an atom when electrons are excited photon – a quantum of light ground state – lowest energy level of an atom excited state – a heightened state of energy in an atom Electrons of hydrogen circle the nucleus in orbits 1. orb ...
Bohr`s Model of the Atom - Mr. Walsh`s AP Chemistry
... The Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom The Bohr model worked well for hydrogen. However, the equations could not be solved exactly for atoms with more than one electron, because of the additional effects that electrons exert on each other (Coulomb force kq q F d12 2 ). By the mid-1920s, quantum physi ...
... The Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom The Bohr model worked well for hydrogen. However, the equations could not be solved exactly for atoms with more than one electron, because of the additional effects that electrons exert on each other (Coulomb force kq q F d12 2 ). By the mid-1920s, quantum physi ...
ChemicalBondingTestAnswers
... The charge on the nucleus – On moving from left to right, the effective nuclear charge increases. The distance of the electron from the nucleus – On moving from left to right in a period, the distance of the electron from the nucleus decreases a little . The number of electrons between the outer ele ...
... The charge on the nucleus – On moving from left to right, the effective nuclear charge increases. The distance of the electron from the nucleus – On moving from left to right in a period, the distance of the electron from the nucleus decreases a little . The number of electrons between the outer ele ...
Document
... classical mechanics, which predict that electrons in orbit would fall towards and collide with the nucleus. Stable Bohr atoms are not possible. • Modern quantum mechanics, with orbitals rather than orbits, provides the only reasonable explanation for the observed properties of the atoms ...
... classical mechanics, which predict that electrons in orbit would fall towards and collide with the nucleus. Stable Bohr atoms are not possible. • Modern quantum mechanics, with orbitals rather than orbits, provides the only reasonable explanation for the observed properties of the atoms ...
Chapter 7 Quantum Theory of the Atom
... Building on de Broglie’s work, in 1926, Erwin Schrödinger devised a theory that could be used to explain the wave properties of electrons in atoms and molecules. The branch of physics that mathematically describes the wave properties of submicroscopic particles is called quantum mechanics or wave m ...
... Building on de Broglie’s work, in 1926, Erwin Schrödinger devised a theory that could be used to explain the wave properties of electrons in atoms and molecules. The branch of physics that mathematically describes the wave properties of submicroscopic particles is called quantum mechanics or wave m ...
Periodic Trends/Patterns
... Trend of ionic radii The cation of an atom decreases in size while the anion of an atom increases in size. The trend can not be made according to the periodic table, but by the isoelectronic series. The more positive an ion is the smaller it is because Zeff increases, while the more negative an io ...
... Trend of ionic radii The cation of an atom decreases in size while the anion of an atom increases in size. The trend can not be made according to the periodic table, but by the isoelectronic series. The more positive an ion is the smaller it is because Zeff increases, while the more negative an io ...
Atomic orbital
An atomic orbital is a mathematical function that describes the wave-like behavior of either one electron or a pair of electrons in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus. The term may also refer to the physical region or space where the electron can be calculated to be present, as defined by the particular mathematical form of the orbital.Each orbital in an atom is characterized by a unique set of values of the three quantum numbers n, ℓ, and m, which respectively correspond to the electron's energy, angular momentum, and an angular momentum vector component (the magnetic quantum number). Any orbital can be occupied by a maximum of two electrons, each with its own spin quantum number. The simple names s orbital, p orbital, d orbital and f orbital refer to orbitals with angular momentum quantum number ℓ = 0, 1, 2 and 3 respectively. These names, together with the value of n, are used to describe the electron configurations of atoms. They are derived from the description by early spectroscopists of certain series of alkali metal spectroscopic lines as sharp, principal, diffuse, and fundamental. Orbitals for ℓ > 3 continue alphabetically, omitting j (g, h, i, k, …).Atomic orbitals are the basic building blocks of the atomic orbital model (alternatively known as the electron cloud or wave mechanics model), a modern framework for visualizing the submicroscopic behavior of electrons in matter. In this model the electron cloud of a multi-electron atom may be seen as being built up (in approximation) in an electron configuration that is a product of simpler hydrogen-like atomic orbitals. The repeating periodicity of the blocks of 2, 6, 10, and 14 elements within sections of the periodic table arises naturally from the total number of electrons that occupy a complete set of s, p, d and f atomic orbitals, respectively.