2.8 Atomic Spectra of Hydrogen For some time scientist had known
... electromagnetic radiation. Bohr assumed that the observed spectrum of the hydrogen atom is due to transition from one allowed energy state to another and he predicted that the allowed energy difference is given by ΔE = hυ = me4Z2/8ε02h2 [1/n12 - 1/n22] Thus, the simple explanation for the line spect ...
... electromagnetic radiation. Bohr assumed that the observed spectrum of the hydrogen atom is due to transition from one allowed energy state to another and he predicted that the allowed energy difference is given by ΔE = hυ = me4Z2/8ε02h2 [1/n12 - 1/n22] Thus, the simple explanation for the line spect ...
Pre-Knowledge: Chemistry and Physics Vocabulary Atomic Number
... overall negative charge. Cations have lost one or more electrons, so they have more protons than electrons and an overall positive charge. Nuclide A general term referring to all known isotopes of the chemical elements. There are 279 stable nuclides and approximately 2700 unstable nuclides. Radioact ...
... overall negative charge. Cations have lost one or more electrons, so they have more protons than electrons and an overall positive charge. Nuclide A general term referring to all known isotopes of the chemical elements. There are 279 stable nuclides and approximately 2700 unstable nuclides. Radioact ...
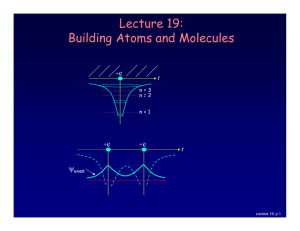
Lecture 19: Building Atoms and Molecules
... For atoms with many electrons (e.g., carbon: 6, iron: 26, etc.) 4 What energies do the electrons have? “Pauli Exclusion Principle” (1925) No two electrons can be in the same quantum state. For example, in a given atom they cannot have the same set of quantum numbers n, l, ml, ms. This means that eac ...
... For atoms with many electrons (e.g., carbon: 6, iron: 26, etc.) 4 What energies do the electrons have? “Pauli Exclusion Principle” (1925) No two electrons can be in the same quantum state. For example, in a given atom they cannot have the same set of quantum numbers n, l, ml, ms. This means that eac ...
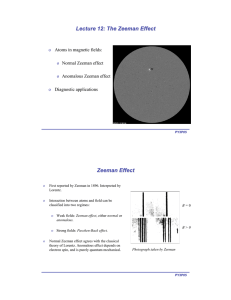
o Atoms in magnetic fields: Normal Zeeman effect Anomalous Zeeman effect
... Normal Zeeman effect agrees with the classical theory of Lorentz. Anomalous effect depends on electron spin, and is purely quantum mechanical. ...
... Normal Zeeman effect agrees with the classical theory of Lorentz. Anomalous effect depends on electron spin, and is purely quantum mechanical. ...
1. dia
... Quantum numbers describe values of conserved quantities in the dynamics of the quantum system. They often describe specifically the energies of electrons in atoms, but other possibilities include angular momentum, spin etc. It is already known from the Bohr’s atom model that the energy of the electr ...
... Quantum numbers describe values of conserved quantities in the dynamics of the quantum system. They often describe specifically the energies of electrons in atoms, but other possibilities include angular momentum, spin etc. It is already known from the Bohr’s atom model that the energy of the electr ...
Density of States Derivation
... The allowed states can be plotted as a grid of points in k space, a 3-D visualization of the directions of electron wavevectors. Allowed states are separated by / Lx , y , z in the 3 directions in k space. The k space volume taken up by each allowed state is 3 / Lx Ly Lz . The reciprocal is the ...
... The allowed states can be plotted as a grid of points in k space, a 3-D visualization of the directions of electron wavevectors. Allowed states are separated by / Lx , y , z in the 3 directions in k space. The k space volume taken up by each allowed state is 3 / Lx Ly Lz . The reciprocal is the ...
Chemical reactions occur with outer level electrons so that is the
... The most stable atoms have a full outer level or shell The Octet Rule: Atoms will combine to form compounds to reach 8 electrons in their outer energy level. Atoms with less than 4 electrons will lose electrons For Na it is easier to lose 1 electron than to gain 7 electrons A Na atom has 11+ and 11- ...
... The most stable atoms have a full outer level or shell The Octet Rule: Atoms will combine to form compounds to reach 8 electrons in their outer energy level. Atoms with less than 4 electrons will lose electrons For Na it is easier to lose 1 electron than to gain 7 electrons A Na atom has 11+ and 11- ...
Physics 102: Lecture 24 Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle Physics
... Plum pudding theory: – electrons in “cloud” of uniformly if l distributed di t ib t d + charge h Æ electric field felt by alpha never gets too large To scatter at large angles, need positive charge concentrated in small region (the nucleus) ...
... Plum pudding theory: – electrons in “cloud” of uniformly if l distributed di t ib t d + charge h Æ electric field felt by alpha never gets too large To scatter at large angles, need positive charge concentrated in small region (the nucleus) ...
K,7th Grade Test Review: Atoms and Chemical Reactions PART
... 1. __________ is the smallest unit of an element that is still that element. 2. __________ is a substance that cannot be broken down into similar substances by physical or chemical changes. 3. Protons and neutrons have a __________ of 1 unit. Electrons have almost none. 4. An atom with more protons ...
... 1. __________ is the smallest unit of an element that is still that element. 2. __________ is a substance that cannot be broken down into similar substances by physical or chemical changes. 3. Protons and neutrons have a __________ of 1 unit. Electrons have almost none. 4. An atom with more protons ...
Atomic 1
... The pole pieces of the magnetic are situated such that there is a channel in which there is a non-uniform field in the z-direction. The magnetic field in the x and y (horizontal) is uniform so there is no force in the x and y direction. Atoms produced from a metal (Ag) heated in an oven are sent dow ...
... The pole pieces of the magnetic are situated such that there is a channel in which there is a non-uniform field in the z-direction. The magnetic field in the x and y (horizontal) is uniform so there is no force in the x and y direction. Atoms produced from a metal (Ag) heated in an oven are sent dow ...
B - Piazza
... molecules—the positive and negative charges both behave like point sources and so their fields cancel out perfectly! So how do molecules form? ...
... molecules—the positive and negative charges both behave like point sources and so their fields cancel out perfectly! So how do molecules form? ...
Quantum (wave) mechanics
... The Rutherford-Bohr model of the atom described the electron orbiting around the nucleus in circular orbits. This is a planetary model like the planets orbiting the Sun. However, in terms of Quantum Mechanics the electron has to be regarded as a wave so that experimental observations agree with theo ...
... The Rutherford-Bohr model of the atom described the electron orbiting around the nucleus in circular orbits. This is a planetary model like the planets orbiting the Sun. However, in terms of Quantum Mechanics the electron has to be regarded as a wave so that experimental observations agree with theo ...
Atomic History Notes.notebook
... 3) Atoms combine chemically in simple whole number ratios, H2O is a 2:1 ratio of hydrogen and oxygen. - A chemical compound is a distinct substance made up of atoms or two or more elements (like water above) 4) Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined or rearranged. 5) Atoms of one ...
... 3) Atoms combine chemically in simple whole number ratios, H2O is a 2:1 ratio of hydrogen and oxygen. - A chemical compound is a distinct substance made up of atoms or two or more elements (like water above) 4) Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined or rearranged. 5) Atoms of one ...
Chemistry - Halifax County Public Schools
... The mass of zinc used and hydrogen production are directly proportional. The mass of zinc used and hydrogen production are inversely proportional. The mass of zinc used and hydrogen production are related, but not proportional. The mass of zinc used and hydrogen production are unrelated. ...
... The mass of zinc used and hydrogen production are directly proportional. The mass of zinc used and hydrogen production are inversely proportional. The mass of zinc used and hydrogen production are related, but not proportional. The mass of zinc used and hydrogen production are unrelated. ...
non-born–oppenheimer effects between electrons and protons
... We performed initial NEO-RXCHF calculations on proton-containing systems on Blue Waters. We analyzed the nuclear densities of the protons and compared them to highly accurate grid-based densities. Our calculations illustrate that this approach can provide accurate descriptions of the protons that ar ...
... We performed initial NEO-RXCHF calculations on proton-containing systems on Blue Waters. We analyzed the nuclear densities of the protons and compared them to highly accurate grid-based densities. Our calculations illustrate that this approach can provide accurate descriptions of the protons that ar ...
Atomic orbital
An atomic orbital is a mathematical function that describes the wave-like behavior of either one electron or a pair of electrons in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus. The term may also refer to the physical region or space where the electron can be calculated to be present, as defined by the particular mathematical form of the orbital.Each orbital in an atom is characterized by a unique set of values of the three quantum numbers n, ℓ, and m, which respectively correspond to the electron's energy, angular momentum, and an angular momentum vector component (the magnetic quantum number). Any orbital can be occupied by a maximum of two electrons, each with its own spin quantum number. The simple names s orbital, p orbital, d orbital and f orbital refer to orbitals with angular momentum quantum number ℓ = 0, 1, 2 and 3 respectively. These names, together with the value of n, are used to describe the electron configurations of atoms. They are derived from the description by early spectroscopists of certain series of alkali metal spectroscopic lines as sharp, principal, diffuse, and fundamental. Orbitals for ℓ > 3 continue alphabetically, omitting j (g, h, i, k, …).Atomic orbitals are the basic building blocks of the atomic orbital model (alternatively known as the electron cloud or wave mechanics model), a modern framework for visualizing the submicroscopic behavior of electrons in matter. In this model the electron cloud of a multi-electron atom may be seen as being built up (in approximation) in an electron configuration that is a product of simpler hydrogen-like atomic orbitals. The repeating periodicity of the blocks of 2, 6, 10, and 14 elements within sections of the periodic table arises naturally from the total number of electrons that occupy a complete set of s, p, d and f atomic orbitals, respectively.