PHYS-2020: General Physics II Course Lecture Notes Section X Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser
... F. The Bohr Model of Hydrogen. 1. Work that lead to an understanding of the spectrum of the hydrogen atom took place at the end of the 19th and beginning of the 20th century. As such, the work described here is presented in the cgs unit system since those are the units that were being used in physic ...
... F. The Bohr Model of Hydrogen. 1. Work that lead to an understanding of the spectrum of the hydrogen atom took place at the end of the 19th and beginning of the 20th century. As such, the work described here is presented in the cgs unit system since those are the units that were being used in physic ...
Oleg Teryaev
... Newtonian – “Falling elevator” – well known and checked Post-Newtonian – gravity action on SPIN – known since 1962 (Kobzarev and Okun) – not checked on purpose but in fact checked in atomic spins experiments at % level (Silenko,OT’07) Anomalous gravitomagnetic moment iz ZERO or Classical and QUANTUM ...
... Newtonian – “Falling elevator” – well known and checked Post-Newtonian – gravity action on SPIN – known since 1962 (Kobzarev and Okun) – not checked on purpose but in fact checked in atomic spins experiments at % level (Silenko,OT’07) Anomalous gravitomagnetic moment iz ZERO or Classical and QUANTUM ...
Research Poster 24 x 48
... splitting in the energies of spin-up and spin-down electrons. •In case of ferromagnets, which can maintain their own B-field, this energy splitting can occur without any external field. This so-called exchange splitting can be on the order of an eV, and explains unequal density of states of electron ...
... splitting in the energies of spin-up and spin-down electrons. •In case of ferromagnets, which can maintain their own B-field, this energy splitting can occur without any external field. This so-called exchange splitting can be on the order of an eV, and explains unequal density of states of electron ...
S4. Building Blocks of the Universe Agenda Lunar Reconnaissance
... • What is the exclusion principle? • Two fermions of the same type cannot occupy the same quantum state at the same time. (This principle does not apply to bosons.) • How is the exclusion principle important to our existence? • The exclusion principle explains the different energy levels in atoms, w ...
... • What is the exclusion principle? • Two fermions of the same type cannot occupy the same quantum state at the same time. (This principle does not apply to bosons.) • How is the exclusion principle important to our existence? • The exclusion principle explains the different energy levels in atoms, w ...
Chapter 7, Quantum Nos.
... For the H atom the orbital energy depends only on n, so all orbitals with the same value of n have the same energy. This is not true, however, for any other atom! The H atom orbitals may be used to approximate the orbitals for multi-electron atoms. But since these atoms have more than one electron, ...
... For the H atom the orbital energy depends only on n, so all orbitals with the same value of n have the same energy. This is not true, however, for any other atom! The H atom orbitals may be used to approximate the orbitals for multi-electron atoms. But since these atoms have more than one electron, ...
Chp7,Quantum_Num
... For the H atom the orbital energy depends only on n, so all orbitals with the same value of n have the same energy. This is not true, however, for any other atom! The H atom orbitals may be used to approximate the orbitals for multi-electron atoms. But since these atoms have more than one electron, ...
... For the H atom the orbital energy depends only on n, so all orbitals with the same value of n have the same energy. This is not true, however, for any other atom! The H atom orbitals may be used to approximate the orbitals for multi-electron atoms. But since these atoms have more than one electron, ...
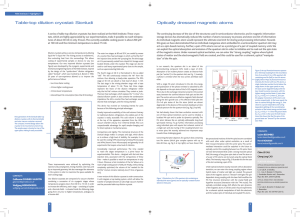
Optically dressed magnetic atoms
... The continuing decrease of the size of the structures used in semiconductor electronics and in magnetic informationstorage devices has dramatically reduced the number of atoms necessary to process and store one bit of information: An individual magnetic atom would represent the ultimate size limit f ...
... The continuing decrease of the size of the structures used in semiconductor electronics and in magnetic informationstorage devices has dramatically reduced the number of atoms necessary to process and store one bit of information: An individual magnetic atom would represent the ultimate size limit f ...
quantum number
... • Werner Heisenberg came up with the idea that, since little tiny things have both wave and particle properties, that you can’t know the position of the particle version and the energy of the wave version with any precision at the same time. ...
... • Werner Heisenberg came up with the idea that, since little tiny things have both wave and particle properties, that you can’t know the position of the particle version and the energy of the wave version with any precision at the same time. ...
2 1 2 3 2 5 2 4 1 2 2 1 1 3 5 4 1 2 2 1 1 4 1 2 2 1 2 2 1 2 1 2 2 2 1 2 1
... Now, since the largest eigenvalue m (ie, j) equals the sum of the largest eigenvalues m1 and m2, the largest quantum number j is clearly j1+j2, since mi’s can only be from the set of numbers ji to +ji in steps of 1. We can find the degeneracy of a given value of m by noting in how many ways it can ...
... Now, since the largest eigenvalue m (ie, j) equals the sum of the largest eigenvalues m1 and m2, the largest quantum number j is clearly j1+j2, since mi’s can only be from the set of numbers ji to +ji in steps of 1. We can find the degeneracy of a given value of m by noting in how many ways it can ...
Ramsey Interference in One-Dimensional Systems: The Full
... many-body origin of Ramsey fringe decay. In the following, we argue that unambiguous signatures of the multimode decoherence are found in the full distribution function of the Ramsey fringe amplitudes. Such distribution functions should be accessible in experiments with 1D quasicondensates realized ...
... many-body origin of Ramsey fringe decay. In the following, we argue that unambiguous signatures of the multimode decoherence are found in the full distribution function of the Ramsey fringe amplitudes. Such distribution functions should be accessible in experiments with 1D quasicondensates realized ...
Klicker-questions, chapter 1 1. The figure shows the probability
... If you measure the position of the particle where is the largest probability to find it? a) Around x=0. b) Depends of the time t. c) The probability to find the particle is the same everywhere. 4. The probability distribution for the position of a particle at time t is shown in the figure. At this t ...
... If you measure the position of the particle where is the largest probability to find it? a) Around x=0. b) Depends of the time t. c) The probability to find the particle is the same everywhere. 4. The probability distribution for the position of a particle at time t is shown in the figure. At this t ...
Quantum Mechanics of Fractional
... statistics, interpolating between bosons and fermions. Since interchange -of two of these particles can give any phase, I will cal. l. them generically anyons. In this paper some elementary examples in the quantum mechanics of anyons are worked out. Description of these particles requires some widen ...
... statistics, interpolating between bosons and fermions. Since interchange -of two of these particles can give any phase, I will cal. l. them generically anyons. In this paper some elementary examples in the quantum mechanics of anyons are worked out. Description of these particles requires some widen ...