Atomic Theory and the Atom
... Dalton’s Theory John Dalton published his atomic theory in 1803. His theory stated that all substances are made of atoms. Atoms are small particles that cannot be created, divided, or destroyed. Atoms of the same element are exactly alike, and atoms of different elements are different. Atoms join wi ...
... Dalton’s Theory John Dalton published his atomic theory in 1803. His theory stated that all substances are made of atoms. Atoms are small particles that cannot be created, divided, or destroyed. Atoms of the same element are exactly alike, and atoms of different elements are different. Atoms join wi ...
Skeleton of - Science802
... 3. Atoms of different elements have different properties: their masses are different, and their chemical reactions are different. ...
... 3. Atoms of different elements have different properties: their masses are different, and their chemical reactions are different. ...
Nuclear and Hadron physics
... • Both real and virtual photons can have polarization • Determining azimuthal distribution of reaction products around these polarization directions gives powerful information. ...
... • Both real and virtual photons can have polarization • Determining azimuthal distribution of reaction products around these polarization directions gives powerful information. ...
Atomic Spectroscopy and the Bohr Model
... Calculate the frequency of the green light. c=λν c 2.998X108 m/s ν = --- = --------------------- = 5.82X1014 Hz λ 5.15X10-7 m ...
... Calculate the frequency of the green light. c=λν c 2.998X108 m/s ν = --- = --------------------- = 5.82X1014 Hz λ 5.15X10-7 m ...
PP_Cosm_2b
... Physicists went on mountain tops for experiments! 1937: New particle discovered: negative charge, ~ 200 me Very longe range in matter !? Not Yukawa’s “pion” ! ...
... Physicists went on mountain tops for experiments! 1937: New particle discovered: negative charge, ~ 200 me Very longe range in matter !? Not Yukawa’s “pion” ! ...
electron arrangement in atoms
... rainbows and coloured light to emphasise the process being observed. The actual observation of line spectra can be startling - it's as if the atoms had signed their name! The difference between an absorption and an emission spectrum is illustrated with an explanation of line spectra in terms of disc ...
... rainbows and coloured light to emphasise the process being observed. The actual observation of line spectra can be startling - it's as if the atoms had signed their name! The difference between an absorption and an emission spectrum is illustrated with an explanation of line spectra in terms of disc ...
Mass Spectroscopy
... a charged particle passing through a magnetic field is deflected along a circular path on a radius that is proportional to the mass to charge ratio, m/e. ...
... a charged particle passing through a magnetic field is deflected along a circular path on a radius that is proportional to the mass to charge ratio, m/e. ...
Article3-Dirac - Inframatter Research Center
... of the electron, but rather in its size. An interpretation of Compton’s scattering produces an electron with an effective radius of 386 fm. Putting that in perspective, the Hydrogen atom has a radius of 52918 fm, and no known nucleus has a radius over 12 fm (with a radius under 8 fm being typical). ...
... of the electron, but rather in its size. An interpretation of Compton’s scattering produces an electron with an effective radius of 386 fm. Putting that in perspective, the Hydrogen atom has a radius of 52918 fm, and no known nucleus has a radius over 12 fm (with a radius under 8 fm being typical). ...
Ch 2 Atomic History
... containing a small hole. As the oil drops fall through the hole, they are given a negative charge. Gravity forces the drops downward. The applied electric field forces the drops upward. When a drop is perfectly balanced, the weight of the drop is equal to the electrostatic force of attraction betwee ...
... containing a small hole. As the oil drops fall through the hole, they are given a negative charge. Gravity forces the drops downward. The applied electric field forces the drops upward. When a drop is perfectly balanced, the weight of the drop is equal to the electrostatic force of attraction betwee ...
HW 4 - Seattle Central College
... voltage is multiplied by a factor of 4, then the potential energy is increased by a factor of 4 also. Then, by energy conservation, we assume that all of the potential energy is converted to kinetic energy during the acceleration process. Thus the kinetic energy has increased by a factor of 4 also. ...
... voltage is multiplied by a factor of 4, then the potential energy is increased by a factor of 4 also. Then, by energy conservation, we assume that all of the potential energy is converted to kinetic energy during the acceleration process. Thus the kinetic energy has increased by a factor of 4 also. ...
History of the Atom File
... centimeter in diameter, then the electrons and quarks would be less than the diameter of a hair and the entire atom's diameter would be greater than the length of thirty football fields! 99.999999999999% of an atom's volume is just empty space! ...
... centimeter in diameter, then the electrons and quarks would be less than the diameter of a hair and the entire atom's diameter would be greater than the length of thirty football fields! 99.999999999999% of an atom's volume is just empty space! ...
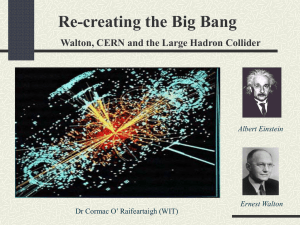
Recreating the Big Bang
... Discovery of electron Crooke’s tube cathode rays Perrin’s paddle wheel mass and momentum Thompson’s B-field e/m Milikan’s oil drop electron charge Result: me = 9.1 x 10-31 kg: TINY ...
... Discovery of electron Crooke’s tube cathode rays Perrin’s paddle wheel mass and momentum Thompson’s B-field e/m Milikan’s oil drop electron charge Result: me = 9.1 x 10-31 kg: TINY ...
Document
... “. . .Our understanding does not advance just by slow and steady building on previous work. Sometimes as with Copernicus and Einstein, we have to make a leap to new world picture. Maybe Newton should have said “I used the shoulders of giants as a springboard.” - Stephan Hawking in “On the Shoulder o ...
... “. . .Our understanding does not advance just by slow and steady building on previous work. Sometimes as with Copernicus and Einstein, we have to make a leap to new world picture. Maybe Newton should have said “I used the shoulders of giants as a springboard.” - Stephan Hawking in “On the Shoulder o ...
Quantum Mechanics
... 2. The hydrogen atom wave function may be written as R(r)Y`m (θ, φ), where R is the radial function and Y`m are the spherical harmonics. a. What is the differential equation for R(r)? b. The differential equation may be simplified somewhat by changing r and E into ρ = r/a0 and W = E/[ke2 /(2a0 )], w ...
... 2. The hydrogen atom wave function may be written as R(r)Y`m (θ, φ), where R is the radial function and Y`m are the spherical harmonics. a. What is the differential equation for R(r)? b. The differential equation may be simplified somewhat by changing r and E into ρ = r/a0 and W = E/[ke2 /(2a0 )], w ...
subatomic-particles
... from classical physics. But it also reflects the modern understanding that at the quantum scale matter and energy behave very differently from what much of everyday experience would lead us to expect. The idea of a particle underwent serious rethinking when experiments showed that light could behave ...
... from classical physics. But it also reflects the modern understanding that at the quantum scale matter and energy behave very differently from what much of everyday experience would lead us to expect. The idea of a particle underwent serious rethinking when experiments showed that light could behave ...
Electron scattering

Electron scattering occurs when electrons are deviated from their original trajectory. This is due to the electrostatic forces within matter interaction or, if an external magnetic field is present, the electron may be deflected by the Lorentz force. This scattering typically happens with solids such as metals, semiconductors and insulators; and is a limiting factor in integrated circuits and transistors.The application of electron scattering is such that it can be used as a high resolution microscope for hadronic systems, that allows the measurement of the distribution of charges for nucleons and nuclear structure. The scattering of electrons has allowed us to understand that protons and neutrons are made up of the smaller elementary subatomic particles called quarks.Electrons may be scattered through a solid in several ways:Not at all: no electron scattering occurs at all and the beam passes straight through.Single scattering: when an electron is scattered just once.Plural scattering: when electron(s) scatter several times.Multiple scattering: when electron(s) scatter very many times over.The likelihood of an electron scattering and the proliferance of the scattering is a probability function of the specimen thickness to the mean free path.