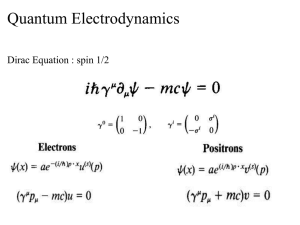
key - gcisd
... 10. Rutherford - Gold foil experiment- expected all of the radiation to pass through and was very surprised when some of the particles were deflected led to the discovery of the NUCLEUS (centrally located positive charge) and the concept that the atom is mostly empty space. Also discovered the proto ...
... 10. Rutherford - Gold foil experiment- expected all of the radiation to pass through and was very surprised when some of the particles were deflected led to the discovery of the NUCLEUS (centrally located positive charge) and the concept that the atom is mostly empty space. Also discovered the proto ...
PROBset2_2014 - University of Toronto, Particle Physics and
... angle in the LAB frame that the pions can make with the K 0 line of flight. Hint: use a Lorentz transformation to take the pions from the K 0 rest frame to the LAB. Then get the tan of the angle required and find its maximum. ...
... angle in the LAB frame that the pions can make with the K 0 line of flight. Hint: use a Lorentz transformation to take the pions from the K 0 rest frame to the LAB. Then get the tan of the angle required and find its maximum. ...
Document
... What is the de Broglie wavelength of a 50 kg person traveling at 15 m/s? (h = 6.6 x 10-34 J s) comparable to spacing ...
... What is the de Broglie wavelength of a 50 kg person traveling at 15 m/s? (h = 6.6 x 10-34 J s) comparable to spacing ...
SSPD Chapter 1_Part 5_Story of Atom-Solar
... Here it will be appropriate to mention that Alpha , Beta and Gamma Rays accompany Radioactivity. Gamma Rays are very short energetic Electromagnetic Waves of wavelength (1/100)Å, Beta Rays are electron beam whereas Alpha Rays are the nuclei of He atoms with two protons and two neutrons. On the basis ...
... Here it will be appropriate to mention that Alpha , Beta and Gamma Rays accompany Radioactivity. Gamma Rays are very short energetic Electromagnetic Waves of wavelength (1/100)Å, Beta Rays are electron beam whereas Alpha Rays are the nuclei of He atoms with two protons and two neutrons. On the basis ...
A modern view of forces - HEP Educational Outreach
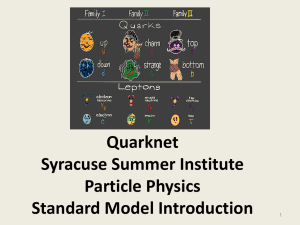
... All fundamental particles to date are found to be fermions (spin 1/2) of type: Quarks (q=+2/3[u,c,t] or -1/3[d,s,b]) Leptons (q=0 or -1) Antiparticles have opposite charge and same mass as these particles. ...
... All fundamental particles to date are found to be fermions (spin 1/2) of type: Quarks (q=+2/3[u,c,t] or -1/3[d,s,b]) Leptons (q=0 or -1) Antiparticles have opposite charge and same mass as these particles. ...
08_lecture_ppt
... Quantum Mechanics • Bohr theory only modeled the line spectrum of H • Further experiments established waveparticle duality of light and matter – Young’s two slit experiment produced interference patterns for both photons and electrons. ...
... Quantum Mechanics • Bohr theory only modeled the line spectrum of H • Further experiments established waveparticle duality of light and matter – Young’s two slit experiment produced interference patterns for both photons and electrons. ...
James Chadwick
... • James Chadwick used scattering data to calculate the mass of this neutral particle • Since Rutherford, it had been known that the atomic mass number of a nuclei is a little more than twice the atomic number for most atoms and that essentially all the mass of the atom is concentrated in the relativ ...
... • James Chadwick used scattering data to calculate the mass of this neutral particle • Since Rutherford, it had been known that the atomic mass number of a nuclei is a little more than twice the atomic number for most atoms and that essentially all the mass of the atom is concentrated in the relativ ...
Linear particle accelerator (LINAC)
... Within the chamber, electrically isolated cylindrical electrodes (“drift tubes” in Figure 2) are placed, whose length varies with the distance along the pipe. The length of each electrode is determined by the frequency and power of the driving power source and the nature of the particle to be accele ...
... Within the chamber, electrically isolated cylindrical electrodes (“drift tubes” in Figure 2) are placed, whose length varies with the distance along the pipe. The length of each electrode is determined by the frequency and power of the driving power source and the nature of the particle to be accele ...
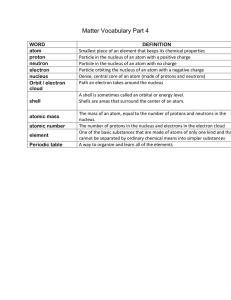
Matter Vocab Part 4
... Particle in the nucleus of an atom with a positive charge Particle in the nucleus of an atom with no charge Particle orbiting the nucleus of an atom with a negative charge Dense, central core of an atom (made of protons and neutrons) Path an electron takes around the nucleus A shell is sometimes cal ...
... Particle in the nucleus of an atom with a positive charge Particle in the nucleus of an atom with no charge Particle orbiting the nucleus of an atom with a negative charge Dense, central core of an atom (made of protons and neutrons) Path an electron takes around the nucleus A shell is sometimes cal ...
Atomic Radius and Ionization Energy
... • The pattern of properties within a period repeats as you move across a period from left to right… When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their physical and chemical properties ...
... • The pattern of properties within a period repeats as you move across a period from left to right… When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their physical and chemical properties ...
Lecture 8a
... • The electronic Zeeman effect arises from an unpaired electron, which possesses a magnetic moment that assumes one of two orientations in an external magnetic field • The energy separation between these two states, is given as DE = hn = gbH where h, g, and b are Planck's constant, the Lande spectro ...
... • The electronic Zeeman effect arises from an unpaired electron, which possesses a magnetic moment that assumes one of two orientations in an external magnetic field • The energy separation between these two states, is given as DE = hn = gbH where h, g, and b are Planck's constant, the Lande spectro ...
nuc_alchemy_talk-fgs-dec07
... Making Gold : Nuclear Alchemy Dr. Paddy Regan Department of Physics University of Surrey Guildford, GU2 7XH [email protected] ...
... Making Gold : Nuclear Alchemy Dr. Paddy Regan Department of Physics University of Surrey Guildford, GU2 7XH [email protected] ...
Atoms and Molecules 2012
... – neutral charge; holds the protons in the center of the atom (nucleus); largest Proton -- positively charged particles; determines the identity of the element; Electron – negatively charged particles; smallest; rapidly move around the nucleus ...
... – neutral charge; holds the protons in the center of the atom (nucleus); largest Proton -- positively charged particles; determines the identity of the element; Electron – negatively charged particles; smallest; rapidly move around the nucleus ...
Atoms and Molecules with charges
... – neutral charge; holds the protons in the center of the atom (nucleus); largest Proton -- positively charged particles; determines the identity of the element; Electron – negatively charged particles; smallest; rapidly move around the nucleus ...
... – neutral charge; holds the protons in the center of the atom (nucleus); largest Proton -- positively charged particles; determines the identity of the element; Electron – negatively charged particles; smallest; rapidly move around the nucleus ...
More on Characterization
... Processes in which volume not conserved Condensation, evaporation, nucleation, sedimentation, ...
... Processes in which volume not conserved Condensation, evaporation, nucleation, sedimentation, ...
Exam #2 from 2010
... 16. Extra Credit (5 pts): A proton in a one-dimensional box (infinite square well potential) is in a state that does not have definite energy, but rather it is a superposition (combination) of energies E a=2 eV and Eb=8 eV. The expectation value of the energy is = 4 eV.
a) Find the probability t ...
... 16. Extra Credit (5 pts): A proton in a one-dimensional box (infinite square well potential) is in a state that does not have definite energy, but rather it is a superposition (combination) of energies E a=2 eV and Eb=8 eV. The expectation value of the energy is
D NAME: 1. Which of the following phenomena could not be expla
... Prove that, given a pair of normalized but not orthogonal functions ψ1 and ψ2, the function ψ3 = ψ2 – Sψ1 is orthogonal to ψ1 if S is the overlap integral of ψ1 and ψ2. Is ψ3 normalized? (Use the back of the page if necessary). ...
... Prove that, given a pair of normalized but not orthogonal functions ψ1 and ψ2, the function ψ3 = ψ2 – Sψ1 is orthogonal to ψ1 if S is the overlap integral of ψ1 and ψ2. Is ψ3 normalized? (Use the back of the page if necessary). ...
Basics of Electron Storage Rings
... 3. Synchrotron and storage ring - Figure shows the basic idea of synchrotron: it consists of vacuum pipes, magnets, and radio frequency (rf) accelerating cavities. Beam is injected into the synchrotron and extracted from it. - Storage ring is a kind of synchrotron, where injected beam is stored and ...
... 3. Synchrotron and storage ring - Figure shows the basic idea of synchrotron: it consists of vacuum pipes, magnets, and radio frequency (rf) accelerating cavities. Beam is injected into the synchrotron and extracted from it. - Storage ring is a kind of synchrotron, where injected beam is stored and ...
Intro to Particle Physics and High Energy Astrophysics
... multiplied by the square of twice the Lorentz factor (where the Lorentz factor squared is given by 2 =1 / [1-(v/c)2] and v is the electron velocity): ...
... multiplied by the square of twice the Lorentz factor (where the Lorentz factor squared is given by 2 =1 / [1-(v/c)2] and v is the electron velocity): ...
By convention magnetic momentum of a current loop is calculated by
... Where M is the calculated magnetic momentum of the loop, i is equal to the current in the loop and A is the area enclosed of the loop. An elementary particle like for instance the proton particle, may be regarded as a closed current loop. Because the particle has an electric unit charge, we can writ ...
... Where M is the calculated magnetic momentum of the loop, i is equal to the current in the loop and A is the area enclosed of the loop. An elementary particle like for instance the proton particle, may be regarded as a closed current loop. Because the particle has an electric unit charge, we can writ ...
Electron scattering

Electron scattering occurs when electrons are deviated from their original trajectory. This is due to the electrostatic forces within matter interaction or, if an external magnetic field is present, the electron may be deflected by the Lorentz force. This scattering typically happens with solids such as metals, semiconductors and insulators; and is a limiting factor in integrated circuits and transistors.The application of electron scattering is such that it can be used as a high resolution microscope for hadronic systems, that allows the measurement of the distribution of charges for nucleons and nuclear structure. The scattering of electrons has allowed us to understand that protons and neutrons are made up of the smaller elementary subatomic particles called quarks.Electrons may be scattered through a solid in several ways:Not at all: no electron scattering occurs at all and the beam passes straight through.Single scattering: when an electron is scattered just once.Plural scattering: when electron(s) scatter several times.Multiple scattering: when electron(s) scatter very many times over.The likelihood of an electron scattering and the proliferance of the scattering is a probability function of the specimen thickness to the mean free path.