Document
... N.B. in contrast, Bosons ‘like’ to be in same state! (laser cavity etc.) “Exchange’ interaction – no classical equivalent ...
... N.B. in contrast, Bosons ‘like’ to be in same state! (laser cavity etc.) “Exchange’ interaction – no classical equivalent ...
Quantum Notes (Chapter 16)(Powerpoint document)
... For each value of n (1, 2, 3 etc.) there are n2 different wave functions, any of which are valid for an electron of the H atom. First of all, what is a wavefunction? It is a mathematical description of the wave properties of an electron in the H atom. As a wavefunction, it has the properties of a wa ...
... For each value of n (1, 2, 3 etc.) there are n2 different wave functions, any of which are valid for an electron of the H atom. First of all, what is a wavefunction? It is a mathematical description of the wave properties of an electron in the H atom. As a wavefunction, it has the properties of a wa ...
Helium Atom
... The emission spectra of He consists of a number of series in the visible region of the spectrum as well as in the near & far UV regions. There are twice as many line series as for the alkalis; two principal series in the visible and near UV, as well as two diffuse, two sharp and two fundamental seri ...
... The emission spectra of He consists of a number of series in the visible region of the spectrum as well as in the near & far UV regions. There are twice as many line series as for the alkalis; two principal series in the visible and near UV, as well as two diffuse, two sharp and two fundamental seri ...
NASA Space Radiation Laboratory
... a number of years at the LBNL Bevalac and BNL AGS [Zeitlin (1998)]. Instruments to be exposed to beam are mounted on a simple and stable rail system with adjustable attachments to which instrument holders can be readily adapted. Positioning is done by means of a laser system. The beam is steered, fo ...
... a number of years at the LBNL Bevalac and BNL AGS [Zeitlin (1998)]. Instruments to be exposed to beam are mounted on a simple and stable rail system with adjustable attachments to which instrument holders can be readily adapted. Positioning is done by means of a laser system. The beam is steered, fo ...
Kein Folientitel - Max Planck Institute for Solar System
... The neutral collision frequency, n, i.e. number of collisions per second, is proportional to the number of neutral particles in a column with a cross section of an atom or molecule, nnn, where nn is the density and n= d02 ( 10-20 m2) the atomic cross section, and to the average speed, < > ( ...
... The neutral collision frequency, n, i.e. number of collisions per second, is proportional to the number of neutral particles in a column with a cross section of an atom or molecule, nnn, where nn is the density and n= d02 ( 10-20 m2) the atomic cross section, and to the average speed, < > ( ...
In 1913 Bohr proposed his quantized shell model of the atom to
... Bohr noticed, however, that the quantum constant formulated by the German physicist Max Planck has dimensions which, when combined with the mass and charge of the electron, produce a measure of length. Numerically, the measure is close to the known size of atoms. This encouraged Bohr to use Planck's ...
... Bohr noticed, however, that the quantum constant formulated by the German physicist Max Planck has dimensions which, when combined with the mass and charge of the electron, produce a measure of length. Numerically, the measure is close to the known size of atoms. This encouraged Bohr to use Planck's ...
TAP 521- 6: Rutherford experiment and atomic structure
... that he called the nucleus, and that the negatively charged particles, the electrons, were in orbit around the nucleus. Most of the mass was in the nucleus ...
... that he called the nucleus, and that the negatively charged particles, the electrons, were in orbit around the nucleus. Most of the mass was in the nucleus ...
File
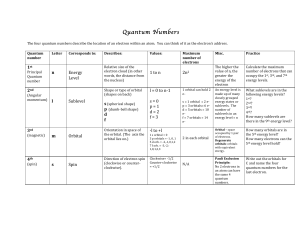
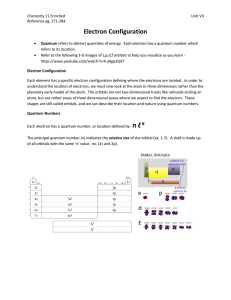
... 4 quantum numbers define energy of an electron electrons arranged in shells shells described by principal quantum number, n n = 1, closest to nucleus; second shell n = 2 the higher n, the higher the potential energy associated the shell and the further from the nucleus the electron likely to be foun ...
... 4 quantum numbers define energy of an electron electrons arranged in shells shells described by principal quantum number, n n = 1, closest to nucleus; second shell n = 2 the higher n, the higher the potential energy associated the shell and the further from the nucleus the electron likely to be foun ...
Honors Chemistry
... Students should be able to identify these elements simply based on total number of electrons Significance of electron configurations Valence shell electrons - outermost electrons involved with bonding for n = 5, pattern is very complicated - no atom has more than 8 valence electrons Noble gases - 8 ...
... Students should be able to identify these elements simply based on total number of electrons Significance of electron configurations Valence shell electrons - outermost electrons involved with bonding for n = 5, pattern is very complicated - no atom has more than 8 valence electrons Noble gases - 8 ...
midterm answers
... the square of the wave function is the probability density, since the wave function is approaching zero without reaching it as long as x is finite, the square of the wave function will not reach zero either, this being the probability density in the barrier, the particle has a probability to be ther ...
... the square of the wave function is the probability density, since the wave function is approaching zero without reaching it as long as x is finite, the square of the wave function will not reach zero either, this being the probability density in the barrier, the particle has a probability to be ther ...
Lecture5.EMfield
... “field” was a superposition of an infinite number of individual “plane wave” particles, with momentum k . The second quantization fell out naturally. ...
... “field” was a superposition of an infinite number of individual “plane wave” particles, with momentum k . The second quantization fell out naturally. ...
Biomimetic folding particle chains
... colloids [1] with full control over the sequence of particles on the single particle level. Our goal is to experimentally observe and control the self-folding of colloidal chains [2]. In analogy to how the sequence of amino acids determines the folded 3-D structure of proteins, we aim to control the ...
... colloids [1] with full control over the sequence of particles on the single particle level. Our goal is to experimentally observe and control the self-folding of colloidal chains [2]. In analogy to how the sequence of amino acids determines the folded 3-D structure of proteins, we aim to control the ...
Electron scattering

Electron scattering occurs when electrons are deviated from their original trajectory. This is due to the electrostatic forces within matter interaction or, if an external magnetic field is present, the electron may be deflected by the Lorentz force. This scattering typically happens with solids such as metals, semiconductors and insulators; and is a limiting factor in integrated circuits and transistors.The application of electron scattering is such that it can be used as a high resolution microscope for hadronic systems, that allows the measurement of the distribution of charges for nucleons and nuclear structure. The scattering of electrons has allowed us to understand that protons and neutrons are made up of the smaller elementary subatomic particles called quarks.Electrons may be scattered through a solid in several ways:Not at all: no electron scattering occurs at all and the beam passes straight through.Single scattering: when an electron is scattered just once.Plural scattering: when electron(s) scatter several times.Multiple scattering: when electron(s) scatter very many times over.The likelihood of an electron scattering and the proliferance of the scattering is a probability function of the specimen thickness to the mean free path.