LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... standard integral 0 exp(-bx2) dx = (1/2)(/b)1/2.] 19. Define or explain the three parts that make an atomic term symbol and formulate the term symbols for the ground state configuration of F atom. 20. In solving the H2+ problem using the LCAO method, the lowest energy obtained is given by E+ = (H ...
... standard integral 0 exp(-bx2) dx = (1/2)(/b)1/2.] 19. Define or explain the three parts that make an atomic term symbol and formulate the term symbols for the ground state configuration of F atom. 20. In solving the H2+ problem using the LCAO method, the lowest energy obtained is given by E+ = (H ...
Experimental Verification of Filter Characteristics Using
... 2. The value of e/m can be calculated if we can measure the accelerating potential, the radius of the orbit, and the magnetic field. 3. By using a special arrangement of coils called Helmholtz coils, we can calculate the magnetic field if we know the radius of the coils, the number of turns in each ...
... 2. The value of e/m can be calculated if we can measure the accelerating potential, the radius of the orbit, and the magnetic field. 3. By using a special arrangement of coils called Helmholtz coils, we can calculate the magnetic field if we know the radius of the coils, the number of turns in each ...
Standard model of particle physics
... i.e. all of them are colorless, we can conclude that the color of the quarks annihilate each other. Therefore the two quarks in mesons have one color and the corresponding anticolor. And the (anti)baryons there appear either all three colors or all three anticolors. Because of the additive color mix ...
... i.e. all of them are colorless, we can conclude that the color of the quarks annihilate each other. Therefore the two quarks in mesons have one color and the corresponding anticolor. And the (anti)baryons there appear either all three colors or all three anticolors. Because of the additive color mix ...
PROBLEM 1 [25 PTS] A system consists of N distinquishable
... part a)? You should have one answer for each possible value of j from part a), with the total adding up to your answer from part c). ...
... part a)? You should have one answer for each possible value of j from part a), with the total adding up to your answer from part c). ...
ATOMIC STRUCTURE
... En = (-RH)(1/n2) n = 1,2,3,4…. RH = Rydberg constant (2.18 x 10-18 J) n = principle quantun number ...
... En = (-RH)(1/n2) n = 1,2,3,4…. RH = Rydberg constant (2.18 x 10-18 J) n = principle quantun number ...
Radioactivity_Topic
... Radioactivity Topic Many atoms have an unstable nucleus. Such atoms are said to be radioactive and will undergo decay. All radioactive isotopes (radioisotopes) will turn into stable atoms by decaying, but as they do so they give out radiation. ...
... Radioactivity Topic Many atoms have an unstable nucleus. Such atoms are said to be radioactive and will undergo decay. All radioactive isotopes (radioisotopes) will turn into stable atoms by decaying, but as they do so they give out radiation. ...
Exam #: Printed Name: Signature: PHYSICS DEPARTMENT
... b. The n = 2 state splits into six states which can be labelled by their orbital angular momentum (L), total spin (S ), and total angular momentum (J )|for example, as in n 2S+1LJ = 2 3 S1. What are the labels n 2S+1 LJ for each of the six states? c. Consider the transitions from each of the six sta ...
... b. The n = 2 state splits into six states which can be labelled by their orbital angular momentum (L), total spin (S ), and total angular momentum (J )|for example, as in n 2S+1LJ = 2 3 S1. What are the labels n 2S+1 LJ for each of the six states? c. Consider the transitions from each of the six sta ...
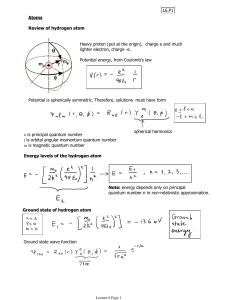
Lecture 6 - physics.udel.edu
... Is ground state of helium triplet, singlet, or can be either one and can not be determined from the given information? The helium excited states have form one electron in the ground state and one electron in the excited state. Do these states have to be singlet, triplet states, or can be both? ...
... Is ground state of helium triplet, singlet, or can be either one and can not be determined from the given information? The helium excited states have form one electron in the ground state and one electron in the excited state. Do these states have to be singlet, triplet states, or can be both? ...
10. Nuclear fusion in stars
... In the quantum-mechanical theory forces between particles act by the transfer of virtual particles, that do not satisfy Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle and can thus not be observed. Written in terms of the particle energy, the uncertainty principle states for the lifetime of particles δt · δE ≥ ~ ...
... In the quantum-mechanical theory forces between particles act by the transfer of virtual particles, that do not satisfy Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle and can thus not be observed. Written in terms of the particle energy, the uncertainty principle states for the lifetime of particles δt · δE ≥ ~ ...
The Second Law of Thermodynamics
... The physical and chemical properties of elements is determined by the atomic structure. The atomic structure is, in turn, determined by the electrons and which shells, subshells and orbitals they reside in. The rules of placing electrons within shells is known as the Aufbau principle. As protons are ...
... The physical and chemical properties of elements is determined by the atomic structure. The atomic structure is, in turn, determined by the electrons and which shells, subshells and orbitals they reside in. The rules of placing electrons within shells is known as the Aufbau principle. As protons are ...
Hunter Hatfield Bullock A-4 12-13-12 Vocabulary of Instruction
... conservative forceelectrical energya vector quantity from which is determined the magnitude and direction of the force on a charged particle due to the presence of other charged particles, accelerated charged particles ...
... conservative forceelectrical energya vector quantity from which is determined the magnitude and direction of the force on a charged particle due to the presence of other charged particles, accelerated charged particles ...
The relation between the ( hypothetical) intrinsic vibrational motion
... particle. We have shown that if these particles are simply considered as loops of current( a useful image, as noted earlier), the corresponding magnetodynamic trapped energy matches their rest energies to a precision of a factor of at most 2. This seems to be valid for fundamental as well as to comp ...
... particle. We have shown that if these particles are simply considered as loops of current( a useful image, as noted earlier), the corresponding magnetodynamic trapped energy matches their rest energies to a precision of a factor of at most 2. This seems to be valid for fundamental as well as to comp ...
Enrichment Opportunities: Atoms
... curiosity has shown us things smaller than anyone thought existed – first the atom and then subatomic particles. But scientists didn’t stop with protons, electrons, and neutrons. Instead, they devised sophisticated instruments called particle accelerators to take a close look at subatomic particles. ...
... curiosity has shown us things smaller than anyone thought existed – first the atom and then subatomic particles. But scientists didn’t stop with protons, electrons, and neutrons. Instead, they devised sophisticated instruments called particle accelerators to take a close look at subatomic particles. ...
Chapter 7:The Quantum-Mechanical Model of
... Dalton’s Indivisible Atom explained the Law of Constant Composition and the Law of Conservation of Mass and led to the Law of Multiple Proportions. J.J. Thomson, through Cathode Ray Tube experiments, discovered that electrons are small negatively charged particles inside a divisible atom and came up ...
... Dalton’s Indivisible Atom explained the Law of Constant Composition and the Law of Conservation of Mass and led to the Law of Multiple Proportions. J.J. Thomson, through Cathode Ray Tube experiments, discovered that electrons are small negatively charged particles inside a divisible atom and came up ...
Problem Set 1
... 4. An electron is in the n = 2, l = 1 state of the hydrogen atom. Write down the passible wave functions of the electron including its intrinsic spin. The wave function ~ J~ and Jz where J~ is the total angular momentum operator must be eigenfunctions of J. and Jz is its z-component. ( You have a to ...
... 4. An electron is in the n = 2, l = 1 state of the hydrogen atom. Write down the passible wave functions of the electron including its intrinsic spin. The wave function ~ J~ and Jz where J~ is the total angular momentum operator must be eigenfunctions of J. and Jz is its z-component. ( You have a to ...
Word
... 1. The up quark (+ /3 e) and the down quark (– /3 e). A proton, charge +1e, is made of two up quarks and one down quark uud. A neutron, charge 0, is made of one up quark and two down quarks udd. A meson consists of a quark and an antiquark. For example, a meson consists of an up or a down quark a ...
... 1. The up quark (+ /3 e) and the down quark (– /3 e). A proton, charge +1e, is made of two up quarks and one down quark uud. A neutron, charge 0, is made of one up quark and two down quarks udd. A meson consists of a quark and an antiquark. For example, a meson consists of an up or a down quark a ...
Quantum theory or radiation
... in Keil in 1885 before moving to Berlin in 1889. He described his radiation formula as "lucky" but it involved one vital new proposal - that radiation was emitted not in a continuous stream of energy but in bundles of energy that he called quanta. He even related the energy of a quantum to its frequ ...
... in Keil in 1885 before moving to Berlin in 1889. He described his radiation formula as "lucky" but it involved one vital new proposal - that radiation was emitted not in a continuous stream of energy but in bundles of energy that he called quanta. He even related the energy of a quantum to its frequ ...
Quantum Mechanics Physics
... quanta between the different levels of excited electron energy orbitals? And what are the frequencies and wavelengths of the energy? • Hypothesis: The amount of energy given off is calculated by the colors of the quanta of light given off when the electrons “cascade” from upper energy levels to the ...
... quanta between the different levels of excited electron energy orbitals? And what are the frequencies and wavelengths of the energy? • Hypothesis: The amount of energy given off is calculated by the colors of the quanta of light given off when the electrons “cascade” from upper energy levels to the ...
Thesis Presentation Mr. Joshuah T. Heath Department of Physics
... analytical expression can be derived for the partition function at any density and chemical potential. In the canonical ensemble, the total number of particles, N, is fixed and an expression for the partition function can only be generated via a complicated recursion relation. In this work we apply ...
... analytical expression can be derived for the partition function at any density and chemical potential. In the canonical ensemble, the total number of particles, N, is fixed and an expression for the partition function can only be generated via a complicated recursion relation. In this work we apply ...
Electron scattering

Electron scattering occurs when electrons are deviated from their original trajectory. This is due to the electrostatic forces within matter interaction or, if an external magnetic field is present, the electron may be deflected by the Lorentz force. This scattering typically happens with solids such as metals, semiconductors and insulators; and is a limiting factor in integrated circuits and transistors.The application of electron scattering is such that it can be used as a high resolution microscope for hadronic systems, that allows the measurement of the distribution of charges for nucleons and nuclear structure. The scattering of electrons has allowed us to understand that protons and neutrons are made up of the smaller elementary subatomic particles called quarks.Electrons may be scattered through a solid in several ways:Not at all: no electron scattering occurs at all and the beam passes straight through.Single scattering: when an electron is scattered just once.Plural scattering: when electron(s) scatter several times.Multiple scattering: when electron(s) scatter very many times over.The likelihood of an electron scattering and the proliferance of the scattering is a probability function of the specimen thickness to the mean free path.



![PROBLEM 1 [25 PTS] A system consists of N distinquishable](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006063913_1-e1778e5c6114fd66466f556bb5f30c03-300x300.png)