Reality Final: Why Ask Why?
... system in this situation will have a value x for the measurable property is the square of the product of the system's state vector and an eigenvector of the operator in question with an eigenvalue x. This implies that the laws of probability as they apply to vectors, are really in control of non-eig ...
... system in this situation will have a value x for the measurable property is the square of the product of the system's state vector and an eigenvector of the operator in question with an eigenvalue x. This implies that the laws of probability as they apply to vectors, are really in control of non-eig ...
Report - IISER Pune
... if we pass a stream of atoms possessing nonzero magnetic moments is directed to pass through a nonuniform magnetic field, the magnetic forces involved will split up the stream into a number of substreams , with one substream for each possible value of the z-component of µ (usually written as µz ). S ...
... if we pass a stream of atoms possessing nonzero magnetic moments is directed to pass through a nonuniform magnetic field, the magnetic forces involved will split up the stream into a number of substreams , with one substream for each possible value of the z-component of µ (usually written as µz ). S ...
URL - StealthSkater
... Could also gauge bosons correspond to wormhole contacts? (03/27/2007) Inner automorphisms of hyper-finite factors as universal local gauge symmetries? (03/22/2007) Planar algebras and generalized Feynman diagrams (03/21/2007) TGD Universe from the condition that all possible statistics are possible ...
... Could also gauge bosons correspond to wormhole contacts? (03/27/2007) Inner automorphisms of hyper-finite factors as universal local gauge symmetries? (03/22/2007) Planar algebras and generalized Feynman diagrams (03/21/2007) TGD Universe from the condition that all possible statistics are possible ...
F - Course ON-LINE
... SI system: In the SI system of units, mass is a base unit and weight is a derived unit. Typically, mass is specified in kilograms (kg), and weight is calculated from W = mg. If the gravitational acceleration (g) is specified in units of m/s2, then the weight is expressed in newtons (N). On the earth ...
... SI system: In the SI system of units, mass is a base unit and weight is a derived unit. Typically, mass is specified in kilograms (kg), and weight is calculated from W = mg. If the gravitational acceleration (g) is specified in units of m/s2, then the weight is expressed in newtons (N). On the earth ...
Newton`s Second Law - Philadelphia University
... SI system: In the SI system of units, mass is a base unit and weight is a derived unit. Typically, mass is specified in kilograms (kg), and weight is calculated from W = mg. If the gravitational acceleration (g) is specified in units of m/s2, then the weight is expressed in newtons (N). On the earth ...
... SI system: In the SI system of units, mass is a base unit and weight is a derived unit. Typically, mass is specified in kilograms (kg), and weight is calculated from W = mg. If the gravitational acceleration (g) is specified in units of m/s2, then the weight is expressed in newtons (N). On the earth ...
CHAPTER 1 SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
... Thus all we have learned about mechanical oscillators can be carried over to electrical oscillators. Moreover we can see a direct correspondence between the two sets of physical quantities involved: • q takes the place of x; • L takes the place of m; • 1/C takes the place of k. For example, the indu ...
... Thus all we have learned about mechanical oscillators can be carried over to electrical oscillators. Moreover we can see a direct correspondence between the two sets of physical quantities involved: • q takes the place of x; • L takes the place of m; • 1/C takes the place of k. For example, the indu ...
Hydrogen 2
... solutions to the Schrodinger equation for a particle confined to move on the surface s a sphere of unit radius. The first few are tabulated on the ...
... solutions to the Schrodinger equation for a particle confined to move on the surface s a sphere of unit radius. The first few are tabulated on the ...
ENGR-440, Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics 1 2001
... 1. Define intensive and extensive properties. 2. Know Gibb's Phase Rule. 3. Apply Gibb's Phase Rule to determine the degrees of freedom of a system. ...
... 1. Define intensive and extensive properties. 2. Know Gibb's Phase Rule. 3. Apply Gibb's Phase Rule to determine the degrees of freedom of a system. ...
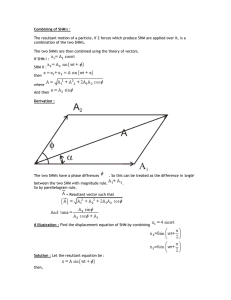
Combining of SHM`s
... frequency. At a certain instant, they both are found at a distance A/n from origin (y>1) and they are on opposite sides of the origin. Their velocities are found to be in same direction. Find the phase diference between two ? Solution :- The problem becomes very simple if we represent both SHM's on ...
... frequency. At a certain instant, they both are found at a distance A/n from origin (y>1) and they are on opposite sides of the origin. Their velocities are found to be in same direction. Find the phase diference between two ? Solution :- The problem becomes very simple if we represent both SHM's on ...
Lecture 3 : ultracold Fermi Gases Lecture 3 : ultracold Fermi Gases
... We have measured the grand potential of a tunable Fermi gas S. Nascimbène et al., Nature, 463, 1057, (2010), arxiv 0911.0747 ...
... We have measured the grand potential of a tunable Fermi gas S. Nascimbène et al., Nature, 463, 1057, (2010), arxiv 0911.0747 ...
Impulse and Momentum
... object and the time interval over which it acts (measures in Newton-seconds) Momentum: mv, or the product of the object’s mass and the objects velocity Impulse-momentum Theorem: FΔt= pf –pi ; The impulse on an object is equal to the object’s final momentum mines the object’s initial momentum (p= ...
... object and the time interval over which it acts (measures in Newton-seconds) Momentum: mv, or the product of the object’s mass and the objects velocity Impulse-momentum Theorem: FΔt= pf –pi ; The impulse on an object is equal to the object’s final momentum mines the object’s initial momentum (p= ...