No Slide Title - Weizmann Institute of Science
... Single particle superposition A single particle in a superposition of two locations is prepared in a double well potential and then the potential is turned off. The wavepackets expand and overlap after t=pMdw/h Initial state of probe+ Target: ...
... Single particle superposition A single particle in a superposition of two locations is prepared in a double well potential and then the potential is turned off. The wavepackets expand and overlap after t=pMdw/h Initial state of probe+ Target: ...
Many-Minds Quantum Mechanics
... wave function according to the wave functions of the other electrons. I refer to this version as Many-Minds Quantum Mechanics (MMQM) with each electron representing a (simple) mind seeking to solve its own Schrödinger equation. This is to be compared with the accepted view according to the Copenhag ...
... wave function according to the wave functions of the other electrons. I refer to this version as Many-Minds Quantum Mechanics (MMQM) with each electron representing a (simple) mind seeking to solve its own Schrödinger equation. This is to be compared with the accepted view according to the Copenhag ...
On The Copenhagen Interpretation of Quantum Mechanics
... mathematical objects, but looked very much like the equations all physicists had indeed learned in school to describe things like fluids in motion, or electric fields that pervaded space. Motions in fields are well described by waves, and so Schrödinger’s theory was called wave mechanics. Not long a ...
... mathematical objects, but looked very much like the equations all physicists had indeed learned in school to describe things like fluids in motion, or electric fields that pervaded space. Motions in fields are well described by waves, and so Schrödinger’s theory was called wave mechanics. Not long a ...
Schrödinger equation for the nuclear potential
... In one dimension the Schrödinger equation is a differential equation of a single variable: the single position coordinate of a particle. In three dimensions there are three coordinates defining position of a particle. Thus the Schrödinger equation relevant to nuclear and atomic sciences (thus also ...
... In one dimension the Schrödinger equation is a differential equation of a single variable: the single position coordinate of a particle. In three dimensions there are three coordinates defining position of a particle. Thus the Schrödinger equation relevant to nuclear and atomic sciences (thus also ...
Lecture 6: QUANTUM CIRCUITS 1. Simple Quantum Circuits We`ve
... In general, Eq. (22) is equivalent to the differential equation for operator U (t, t0 ), ih̄ ...
... In general, Eq. (22) is equivalent to the differential equation for operator U (t, t0 ), ih̄ ...
Introduction to Wave Mechanics
... . Around the turn of the last century it was noticed that certain experiments on atomic systems could not be understood using classical physics. Instead, new theories were required. This led to the creation of quantum theory. There are really two quantum theories. “Old quantum theory” (pre-1925) w ...
... . Around the turn of the last century it was noticed that certain experiments on atomic systems could not be understood using classical physics. Instead, new theories were required. This led to the creation of quantum theory. There are really two quantum theories. “Old quantum theory” (pre-1925) w ...
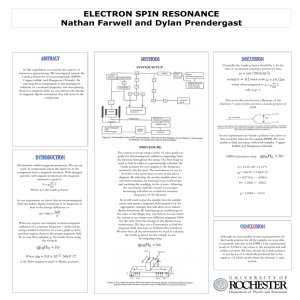
Poster: ESR
... All materials exhibit magnetic properties. We can see easily in compounds where the electrons in the compound have a magnetic moment. With charged particles with angular momentum the magnetic moment is equal to: Where g is the Lande g-factor. In our experiment we know that an electromagnetic field c ...
... All materials exhibit magnetic properties. We can see easily in compounds where the electrons in the compound have a magnetic moment. With charged particles with angular momentum the magnetic moment is equal to: Where g is the Lande g-factor. In our experiment we know that an electromagnetic field c ...
Physics 8805: Nuclear Few- and Many-Body Physics
... (f) Compare 1 S0 to 1 D2 and use the results to estimate the radial extent of the repulsive core for a local potential. (Hint: What does the centrifugal barrier in the D state do? You can use a classical argument.) [It would be great to test out such an argument with the numerical calculations!] (g) ...
... (f) Compare 1 S0 to 1 D2 and use the results to estimate the radial extent of the repulsive core for a local potential. (Hint: What does the centrifugal barrier in the D state do? You can use a classical argument.) [It would be great to test out such an argument with the numerical calculations!] (g) ...
Bringing Together Gravity and the Quanta
... initial conditions, follow the same path. Such universality of response — usually referred to as universality of free fall — is the most fundamental characteristic of the gravitational interaction. It is unique, peculiar to gravitation: no other basic interaction of Nature has it. On the other hand, ...
... initial conditions, follow the same path. Such universality of response — usually referred to as universality of free fall — is the most fundamental characteristic of the gravitational interaction. It is unique, peculiar to gravitation: no other basic interaction of Nature has it. On the other hand, ...
Interpretation of quantum mechanics by the double solution theory
... only exist in the theoretician’s mind, and that as long as they are not separated by a physical process which destroys the initial superposition, the superposition is the physical reality. Just after submitting my thesis, I therefore had to generalize the guiding ideas by considering, on one hand, a ...
... only exist in the theoretician’s mind, and that as long as they are not separated by a physical process which destroys the initial superposition, the superposition is the physical reality. Just after submitting my thesis, I therefore had to generalize the guiding ideas by considering, on one hand, a ...