The nucleus, a unique many-body system - IPN Orsay
... Both action and quantality can be used to describe when a system behaves like a quantum liquid (QL) rather than a crystal. Large quantum effects in a system (action close to ~) correspond to A& 1 and Λ . 1. This is the quantum liquid case. When quantum effects are smaller, such as in the crystal cas ...
... Both action and quantality can be used to describe when a system behaves like a quantum liquid (QL) rather than a crystal. Large quantum effects in a system (action close to ~) correspond to A& 1 and Λ . 1. This is the quantum liquid case. When quantum effects are smaller, such as in the crystal cas ...
the full course notes are available here in book form for downloading
... and discuss central forces. Using these two ideas, we will write down, and solve, the equations of motion for two bodies interacting through gravity. This enables us to prove Kepler’s empirical laws of planetary motion from first principles. Using the same ideas, we will examine the dynamics of spac ...
... and discuss central forces. Using these two ideas, we will write down, and solve, the equations of motion for two bodies interacting through gravity. This enables us to prove Kepler’s empirical laws of planetary motion from first principles. Using the same ideas, we will examine the dynamics of spac ...
ppt - UBC Computer Science
... Friction slows down the relative tangential velocity Causes a tangential force FT that opposes sliding, according to Magnitude of normal force FN pressing on particle ...
... Friction slows down the relative tangential velocity Causes a tangential force FT that opposes sliding, according to Magnitude of normal force FN pressing on particle ...
Gravity originates from variable energy density of
... fields, elementary particles and massive objects still exists on its own and so must have some concrete physical origin. The so-called “empty space” is a type of energy that is “full” of itself, having here its own independent physical existence. We do not “resurrect” the idea of ether, at least in ...
... fields, elementary particles and massive objects still exists on its own and so must have some concrete physical origin. The so-called “empty space” is a type of energy that is “full” of itself, having here its own independent physical existence. We do not “resurrect” the idea of ether, at least in ...
Introduction CHAPTER 1
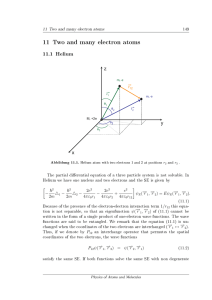
... diffusivity. This equation also describes heat conduction in incompressible liquids if the convective term is negligibly small compared to the conductive term and is the case when the liquid is at rest or the temperature of the liquid changes much faster than the liquid flows. The heat conduction eq ...
... diffusivity. This equation also describes heat conduction in incompressible liquids if the convective term is negligibly small compared to the conductive term and is the case when the liquid is at rest or the temperature of the liquid changes much faster than the liquid flows. The heat conduction eq ...
Magnetic Susceptibility
... Electrons have a magnetic moment that can be aligned either with or in opposition to an applied magnetic field, depending on whether the spin magnetic quantum number, ms, is +½ or –½. For an atom or ion with only paired electrons, the individual electron contributions to the overall spin magnetic qu ...
... Electrons have a magnetic moment that can be aligned either with or in opposition to an applied magnetic field, depending on whether the spin magnetic quantum number, ms, is +½ or –½. For an atom or ion with only paired electrons, the individual electron contributions to the overall spin magnetic qu ...
Big Bang Nucleosynthesis - Chalmers
... of each member of the above mentioned families are shown in table 3. It shall also be noted that both particles in an particle-antiparticle pair have the same mass and spin, yet opposite charge. As in the case of baryons, there exists a so called lepton number, which equals 1 for leptons, -1 for the ...
... of each member of the above mentioned families are shown in table 3. It shall also be noted that both particles in an particle-antiparticle pair have the same mass and spin, yet opposite charge. As in the case of baryons, there exists a so called lepton number, which equals 1 for leptons, -1 for the ...
Entangled Bell states of two electrons in coupled quantum dots
... Finally, the interaction Hc ðtÞ ¼ P ez F ðtÞ represents the coupling by a timei i¼1;2 dependent electric field F ðtÞ applied along the z direction. In the calculations we use the GaAs parameters m ¼ 0:067m0 with m0 the free electron mass, and k ¼ 13:1: We use the Hund–Mulliken method [28] of molecula ...
... Finally, the interaction Hc ðtÞ ¼ P ez F ðtÞ represents the coupling by a timei i¼1;2 dependent electric field F ðtÞ applied along the z direction. In the calculations we use the GaAs parameters m ¼ 0:067m0 with m0 the free electron mass, and k ¼ 13:1: We use the Hund–Mulliken method [28] of molecula ...
Chapter 7
... and the length of the wire is 1.20 m. Find the velocity (magnitude and direction) of the ball (a) just before the collision, and (b) just after the collision. ...
... and the length of the wire is 1.20 m. Find the velocity (magnitude and direction) of the ball (a) just before the collision, and (b) just after the collision. ...
Magnetoresistance.
... orbital angular momentum. Orbital angular momentum is the qunatum number that changes in the quantum Hall effect. When polycrystalline samples (or arbitrary angles of the applied magnetic field to the atomic planes) are used in the Hall experiment it is necessary for electrons to cross from one atom ...
... orbital angular momentum. Orbital angular momentum is the qunatum number that changes in the quantum Hall effect. When polycrystalline samples (or arbitrary angles of the applied magnetic field to the atomic planes) are used in the Hall experiment it is necessary for electrons to cross from one atom ...
Primitive ontology and quantum state in the GRW matter density theory
... four-dimensional space-time, at least not if one considers N-particle systems with N > 1. One then has to regard the quantum state either as a field on 3N-dimensional configuration space or as what Belot calls a “multi-field”, an object assigning properties to N-tuples of points in space. The second ...
... four-dimensional space-time, at least not if one considers N-particle systems with N > 1. One then has to regard the quantum state either as a field on 3N-dimensional configuration space or as what Belot calls a “multi-field”, an object assigning properties to N-tuples of points in space. The second ...