Chapter 2 Name___________________________________
... MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) If an atom of sulfur (atomic number 16) were allowed to react with atoms of hydrogen (atomic number 1), which of the molecules below would be formed? H A) S H B) H S H C) H S H D) E) H S H ...
... MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) If an atom of sulfur (atomic number 16) were allowed to react with atoms of hydrogen (atomic number 1), which of the molecules below would be formed? H A) S H B) H S H C) H S H D) E) H S H ...
c2 atomic structure f pmh
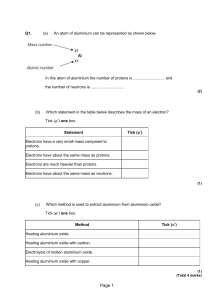
... Which statement in the table below describes the mass of an electron? Tick ( ) one box. ...
... Which statement in the table below describes the mass of an electron? Tick ( ) one box. ...
Chapter 10: Multi-‐Electron Atoms – Optical Excitations
... The structure of atoms with several optical electrons is more complicated. The energy levels of such atoms can be determined using the Hartree approximation which shows that the energy level of each electron in the outer shell is determined by two quantum numbers n and . Since there are ( 2 + 1) ...
... The structure of atoms with several optical electrons is more complicated. The energy levels of such atoms can be determined using the Hartree approximation which shows that the energy level of each electron in the outer shell is determined by two quantum numbers n and . Since there are ( 2 + 1) ...
The Spin Quantum Number
... that were clearly different colors but very close together. A fourth and final quantum number was added to the Bohr model to account for these light waves that differed by only a small amount of energy. ...
... that were clearly different colors but very close together. A fourth and final quantum number was added to the Bohr model to account for these light waves that differed by only a small amount of energy. ...
Presentation - University of Colorado Boulder
... Use superposition to calculate 2n values of function simultaneously and do not read out the result until a useful outout is expected with reasonably high probability. Use entanglement: measurement of states can be highly correlated ...
... Use superposition to calculate 2n values of function simultaneously and do not read out the result until a useful outout is expected with reasonably high probability. Use entanglement: measurement of states can be highly correlated ...
4.1Atoms and Isotopes
... An atom is composed of a central nucleus which consists of protons and neutrons, along with orbiting electrons that exist within ‘clouds’ or orbitals. These protons, neutrons, and electrons are commonly known as SUB-ATOMIC PARTICLES. ...
... An atom is composed of a central nucleus which consists of protons and neutrons, along with orbiting electrons that exist within ‘clouds’ or orbitals. These protons, neutrons, and electrons are commonly known as SUB-ATOMIC PARTICLES. ...
Document
... a Bunsen burner. Using any combination of these substances and common lab equipment, suggest a procedure below which will produce at least one new compound. Write a reaction to show how the new compound(s) form(s). Also, identify the formula for the new compound. NOTE: There are several acceptable p ...
... a Bunsen burner. Using any combination of these substances and common lab equipment, suggest a procedure below which will produce at least one new compound. Write a reaction to show how the new compound(s) form(s). Also, identify the formula for the new compound. NOTE: There are several acceptable p ...
Luminescence model with quantum impact parameter for low energy ions H.S. Cruz-Galindo
... interactions (nuclear stopping) between the incident ion and the material nuclei (excitations and reactions). The first is observed when, in the luminescent material, several atoms of the solid interact simultaneously with the ion. The collective effect of these on the energy deposition is considered ...
... interactions (nuclear stopping) between the incident ion and the material nuclei (excitations and reactions). The first is observed when, in the luminescent material, several atoms of the solid interact simultaneously with the ion. The collective effect of these on the energy deposition is considered ...
Course summary for Unit 4 "Interactions of Light and
... diffraction pattern was observed, identical to that produced by X-rays of the same calculated wavelength. Explain a model of quantised energy levels of the atom in which electrons are found in standing wave states; The Bohr Model of the Atom Bohr proposed that since electrons had a wavelength associ ...
... diffraction pattern was observed, identical to that produced by X-rays of the same calculated wavelength. Explain a model of quantised energy levels of the atom in which electrons are found in standing wave states; The Bohr Model of the Atom Bohr proposed that since electrons had a wavelength associ ...
Physics Today
... The ontological and epistemological bridge between the classical and quantum mechanical domains is embodied in Niels Bohr’s correspondence principle. It stipulates that semiclassical results—specifically, those based on Bohr’s old quantum theory, in which orbital electrons have quantized energy but ...
... The ontological and epistemological bridge between the classical and quantum mechanical domains is embodied in Niels Bohr’s correspondence principle. It stipulates that semiclassical results—specifically, those based on Bohr’s old quantum theory, in which orbital electrons have quantized energy but ...
o Atoms in magnetic fields: Normal Zeeman effect Anomalous Zeeman effect
... o The z-component (!ml = 0) is therefore absent and only observe !ml = ± 1. o Termed !-components and are circularly polarized. ...
... o The z-component (!ml = 0) is therefore absent and only observe !ml = ± 1. o Termed !-components and are circularly polarized. ...
Lecture: Resonance and Atomic
... allows for m = n ± 1 which mean that there are transitions from state n to state m. So, classically, there is the possibility of exciting an electron to a higher orbit, a higher oscillator state but only for higher harmonics in the driving frequency resonance. The quantum description allows for stat ...
... allows for m = n ± 1 which mean that there are transitions from state n to state m. So, classically, there is the possibility of exciting an electron to a higher orbit, a higher oscillator state but only for higher harmonics in the driving frequency resonance. The quantum description allows for stat ...
Physical Chemistry II – Exam 1 SOLUTIONS
... one property of the system that exhibits quantization. Make sure to include in your discussion an equation that illustrates quantization of the property of interest. Quantization is the idea that a physical property may take only certain allowed (discrete) values. Such properties would be predicted ...
... one property of the system that exhibits quantization. Make sure to include in your discussion an equation that illustrates quantization of the property of interest. Quantization is the idea that a physical property may take only certain allowed (discrete) values. Such properties would be predicted ...
Optically polarized atoms_ch_2
... In this approximation, energy of a configuration is just sum of Ei No reference to projections of li or to spins degeneracy If we go beyond the central-field approximation some of the degeneracies will be lifted Also spin-orbit (ls) interaction lifts some degeneracies In general, both effects nee ...
... In this approximation, energy of a configuration is just sum of Ei No reference to projections of li or to spins degeneracy If we go beyond the central-field approximation some of the degeneracies will be lifted Also spin-orbit (ls) interaction lifts some degeneracies In general, both effects nee ...
3UE-Exam Review-June2010 - Savita Pall and Chemistry
... a) when both atoms have low ionization energy and low electron affinity b) when both atoms have high ionization energy and low electron affinity c) when both atoms have high ionization energy and high electron affinity d) when one atom has high ionization energy and high electron affinity, and the o ...
... a) when both atoms have low ionization energy and low electron affinity b) when both atoms have high ionization energy and low electron affinity c) when both atoms have high ionization energy and high electron affinity d) when one atom has high ionization energy and high electron affinity, and the o ...
Exam Review
... A) Subatomic particles a. What are the atomic mass units for protons, neutrons, and electrons? Protons and neutrons = 1 amu; electrons about 0 amu What does the atomic number represent? # of protons b. What does the mass number represent? # of protons + # of neutrons c. What particles are in equal n ...
... A) Subatomic particles a. What are the atomic mass units for protons, neutrons, and electrons? Protons and neutrons = 1 amu; electrons about 0 amu What does the atomic number represent? # of protons b. What does the mass number represent? # of protons + # of neutrons c. What particles are in equal n ...
Atoms and Molecules - New Age International
... ∴ a sin kl + b cos kl = 0 It can only be possible when, nπ l where x is called quantum number and is equal to 1, 2, 3 ... ∞. ...
... ∴ a sin kl + b cos kl = 0 It can only be possible when, nπ l where x is called quantum number and is equal to 1, 2, 3 ... ∞. ...
GENERAL CHEMISTRY SECTION I: ATOMIC THEORY
... For any general chemistry course taught with an “atoms up” approach, an overview of the first chapter requires an argument for how light interacting with matter paved the way for a quantum mechanical revolution, which ultimately revealed the electronic configuration of atoms. Here is a summary of th ...
... For any general chemistry course taught with an “atoms up” approach, an overview of the first chapter requires an argument for how light interacting with matter paved the way for a quantum mechanical revolution, which ultimately revealed the electronic configuration of atoms. Here is a summary of th ...
Advanced Lab: Rutherford Scattering
... the early 19th century, proposed the existence of a fundamental entity in an effort to describe contemporary chemistry1 . Dalton argued that if identical chemicals were formed as aggregates of dissimilar particles, there would be inconsistent specific gravities of materials. For this reason Dalton p ...
... the early 19th century, proposed the existence of a fundamental entity in an effort to describe contemporary chemistry1 . Dalton argued that if identical chemicals were formed as aggregates of dissimilar particles, there would be inconsistent specific gravities of materials. For this reason Dalton p ...
orbit - Seattle Central College
... • We can model the attraction of the H atom’s single electron to its single proton with a “Coulombic” potential curve: ...
... • We can model the attraction of the H atom’s single electron to its single proton with a “Coulombic” potential curve: ...
Bohr model
In atomic physics, the Rutherford–Bohr model or Bohr model, introduced by Niels Bohr in 1913, depicts the atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons that travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, but with attraction provided by electrostatic forces rather than gravity. After the cubic model (1902), the plum-pudding model (1904), the Saturnian model (1904), and the Rutherford model (1911) came the Rutherford–Bohr model or just Bohr model for short (1913). The improvement to the Rutherford model is mostly a quantum physical interpretation of it. The Bohr model has been superseded, but the quantum theory remains sound.The model's key success lay in explaining the Rydberg formula for the spectral emission lines of atomic hydrogen. While the Rydberg formula had been known experimentally, it did not gain a theoretical underpinning until the Bohr model was introduced. Not only did the Bohr model explain the reason for the structure of the Rydberg formula, it also provided a justification for its empirical results in terms of fundamental physical constants.The Bohr model is a relatively primitive model of the hydrogen atom, compared to the valence shell atom. As a theory, it can be derived as a first-order approximation of the hydrogen atom using the broader and much more accurate quantum mechanics and thus may be considered to be an obsolete scientific theory. However, because of its simplicity, and its correct results for selected systems (see below for application), the Bohr model is still commonly taught to introduce students to quantum mechanics or energy level diagrams before moving on to the more accurate, but more complex, valence shell atom. A related model was originally proposed by Arthur Erich Haas in 1910, but was rejected. The quantum theory of the period between Planck's discovery of the quantum (1900) and the advent of a full-blown quantum mechanics (1925) is often referred to as the old quantum theory.