Plasmon electron energy-gain spectroscopy
... of all multipoles [25]; notice that both calculations are in excellent agreement, except for the ⇠580 nm quadrupolar plasmon of silver, which is obviously absent from the dipolar results). It is important to realize that only the component of the electric field along z contributes to the photon–elec ...
... of all multipoles [25]; notice that both calculations are in excellent agreement, except for the ⇠580 nm quadrupolar plasmon of silver, which is obviously absent from the dipolar results). It is important to realize that only the component of the electric field along z contributes to the photon–elec ...
quantum cryptography - 123SeminarsOnly.com
... So far this conforms to the accepted Newtonian universe model; but it was found that if the light was instead used to repeatedly emit just a single photon (a quantum of light) over a period of time, exactly the same interference pattern was formed on the screen. This was a startling result, and com ...
... So far this conforms to the accepted Newtonian universe model; but it was found that if the light was instead used to repeatedly emit just a single photon (a quantum of light) over a period of time, exactly the same interference pattern was formed on the screen. This was a startling result, and com ...
Multiphoton ionization of hydrogen in parallel simulations
... root mesh and a Numerov approximation for the kinetic energy operator. Typically, the wavefunction was contained within a spherical region with a radius of 7000 au; a mask was used to absorb outgoing electron probability and prevent the reflection of outgoing electrons from the spherical boundary. T ...
... root mesh and a Numerov approximation for the kinetic energy operator. Typically, the wavefunction was contained within a spherical region with a radius of 7000 au; a mask was used to absorb outgoing electron probability and prevent the reflection of outgoing electrons from the spherical boundary. T ...
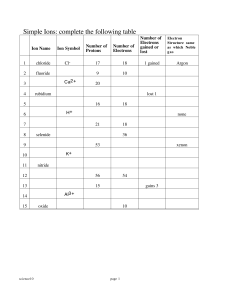
CHEM 1411 EXAM I (Chapters 1, 2, 3): 25
... Hint: For 11th ed.: p.p. 95‐97 and Examples 3.13 and 3.14 (application of Figure 3.8); for 9th edition: p.p. 97‐101. Examples 3.13. and 3.14. Figure 3.8. For 10th edition: p.p.99‐103: Examples 3.13. &3.14. Stoichiometrey. Method One (ratio approach): From the equation, the involving spec ...
... Hint: For 11th ed.: p.p. 95‐97 and Examples 3.13 and 3.14 (application of Figure 3.8); for 9th edition: p.p. 97‐101. Examples 3.13. and 3.14. Figure 3.8. For 10th edition: p.p.99‐103: Examples 3.13. &3.14. Stoichiometrey. Method One (ratio approach): From the equation, the involving spec ...
Magnetic Excitations of Stripes near a Quantum Critical Point
... stripes [17], and (2) Why is the high energy response of YBCO so similar to that of stripe-ordered LBCO, when YBCO does not show evidence of long-range magnetic order? Concerning the first question, the similarity may be due to the proximity to a quantum critical point with small critical exponent ! ...
... stripes [17], and (2) Why is the high energy response of YBCO so similar to that of stripe-ordered LBCO, when YBCO does not show evidence of long-range magnetic order? Concerning the first question, the similarity may be due to the proximity to a quantum critical point with small critical exponent ! ...
Entanglement, which-way measurements, and a quantum erasure Christian Ferrari Bernd Braunecker
... We have presented a simple model that requires knowledge only of two-level systems. Nonetheless, it allows us to explain interesting effects about one-particle quantum interference: Quantum interference appears when a particle can take different indistinguishable paths to arrive at a detector. The k ...
... We have presented a simple model that requires knowledge only of two-level systems. Nonetheless, it allows us to explain interesting effects about one-particle quantum interference: Quantum interference appears when a particle can take different indistinguishable paths to arrive at a detector. The k ...
VALIDITY OF SEMICLASSICAL GRAVITY
... Stochastic Gravity includes the two point function of Tmn in the Einstein-Langevin equation It is the lowest order in the hierarchy of correlation functions. The full hierarchy gives full information about the matter field. At each level of the hierarchy there is a linkage with the gravity sector. T ...
... Stochastic Gravity includes the two point function of Tmn in the Einstein-Langevin equation It is the lowest order in the hierarchy of correlation functions. The full hierarchy gives full information about the matter field. At each level of the hierarchy there is a linkage with the gravity sector. T ...
Direct Characterization of Quantum Dynamics
... [2]. A task of general and crucial importance is the characterization of the dynamics of a quantum system that has an unknown interaction with its embedding environment. Knowledge of this dynamics is indispensable, e.g., for verifying the performance of an information-processing device, and for the ...
... [2]. A task of general and crucial importance is the characterization of the dynamics of a quantum system that has an unknown interaction with its embedding environment. Knowledge of this dynamics is indispensable, e.g., for verifying the performance of an information-processing device, and for the ...
here
... variable that is constant along trajectories is called a constant of motion. Its value may differ from trajectory to trajectory. The hamiltonian H = T + V is a conserved quantity for conservative systems (i.e. where the force is the negative gradient of a scalar potential). ẋ = ...
... variable that is constant along trajectories is called a constant of motion. Its value may differ from trajectory to trajectory. The hamiltonian H = T + V is a conserved quantity for conservative systems (i.e. where the force is the negative gradient of a scalar potential). ẋ = ...
Maximal attainable boost and energy of elementary particles as a
... As for the predictions of a suggested scenario, the only clear one is the cut-off of beam of particles/flux of cosmic rays at limiting value EP ∼ 1018 GeV, energy, which is not accessible by modern accelerators and the cosmic rays observatories. Up to EP , i.e. up to Γmax when the localization regio ...
... As for the predictions of a suggested scenario, the only clear one is the cut-off of beam of particles/flux of cosmic rays at limiting value EP ∼ 1018 GeV, energy, which is not accessible by modern accelerators and the cosmic rays observatories. Up to EP , i.e. up to Γmax when the localization regio ...
The Vibrational-Rotational Spectrum of HCl
... spectroscopic constants; the Equilibrium Fundamental Vibrational Frequency and the Anharmonicity Constant . Finally, we will assume the HCl molecule is behaving approximately as two masses connected by a stiff spring of constant k rotating with internuclear distance r. We will then extract these mol ...
... spectroscopic constants; the Equilibrium Fundamental Vibrational Frequency and the Anharmonicity Constant . Finally, we will assume the HCl molecule is behaving approximately as two masses connected by a stiff spring of constant k rotating with internuclear distance r. We will then extract these mol ...
Hydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the elemental (baryonic) mass of the universe.In everyday life on Earth, isolated hydrogen atoms (usually called ""atomic hydrogen"" or, more precisely, ""monatomic hydrogen"") are extremely rare. Instead, hydrogen tends to combine with other atoms in compounds, or with itself to form ordinary (diatomic) hydrogen gas, H2. ""Atomic hydrogen"" and ""hydrogen atom"" in ordinary English use have overlapping, yet distinct, meanings. For example, a water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms, but does not contain atomic hydrogen (which would refer to isolated hydrogen atoms).