PreAP Biology
... Only edit existing variations, limited by historical constraints, adaptations are often compromises A change in allele frequency Dog and coyote Structures which come from the same embryonic tissue ...
... Only edit existing variations, limited by historical constraints, adaptations are often compromises A change in allele frequency Dog and coyote Structures which come from the same embryonic tissue ...
unnatural selection or artificial selection or selective breeding
... but simply a statement of facts that I have gathered. The principles are clearly Darwinian. One has to be very careful not to equate genes with human traits since most human behavior and traits are usually multifactorial genetic and environmental in nature, but gene frequency in a population in the ...
... but simply a statement of facts that I have gathered. The principles are clearly Darwinian. One has to be very careful not to equate genes with human traits since most human behavior and traits are usually multifactorial genetic and environmental in nature, but gene frequency in a population in the ...
The theory of evolution by natural selection, first formulated in
... "macroevolution." It can turn dinosaurs into birds, amphibious mammals into whales and the ancestors of apes into humans. Take the example of whales — using evolution as their guide and knowing how natural selection works, biologists knew that the transition of early whales from land to water occurr ...
... "macroevolution." It can turn dinosaurs into birds, amphibious mammals into whales and the ancestors of apes into humans. Take the example of whales — using evolution as their guide and knowing how natural selection works, biologists knew that the transition of early whales from land to water occurr ...
SBI3U – Evolution Unit Test Name
... c. Evolution is the progression towards a perfect species d. Mutations are rare events that can occur randomly or be the result of external factors 4. Genetic drift occurs due to: a. Random chance b. Natural selection c. Migration d. Artificial selection ...
... c. Evolution is the progression towards a perfect species d. Mutations are rare events that can occur randomly or be the result of external factors 4. Genetic drift occurs due to: a. Random chance b. Natural selection c. Migration d. Artificial selection ...
Evolution
... The ability of an organism to survive long enough to reproduce. Natural pressures "weed-out" those individuals "less fit" to survive. Thus changing a species over time. ...
... The ability of an organism to survive long enough to reproduce. Natural pressures "weed-out" those individuals "less fit" to survive. Thus changing a species over time. ...
Genetics and evolution
... Genetics and evolution ____populations___ evolve, NOT individuals! Evolution = changes in a populations genes overtime Helpful definitions Gene pool = a collection of all of the possible genes in a population Allelic frequency = the % of an allele in a gene pool Genetic equilibrium = occurs when all ...
... Genetics and evolution ____populations___ evolve, NOT individuals! Evolution = changes in a populations genes overtime Helpful definitions Gene pool = a collection of all of the possible genes in a population Allelic frequency = the % of an allele in a gene pool Genetic equilibrium = occurs when all ...
Evolution Test
... survives, reproduces, and passes the favorable phenotype to the next generation. Organisms without the favorable phenotype are less likely to survive and reproduce A. Directional Selection B. Natural Selection C. Disruptive Selection D. Structural Adaptation 10. A population in which the frequency o ...
... survives, reproduces, and passes the favorable phenotype to the next generation. Organisms without the favorable phenotype are less likely to survive and reproduce A. Directional Selection B. Natural Selection C. Disruptive Selection D. Structural Adaptation 10. A population in which the frequency o ...
Evolution - Houston Independent School District
... All organisms tend to over-reproduce There is a struggle for survival The fittest survive The environment determines who is the fittest ...
... All organisms tend to over-reproduce There is a struggle for survival The fittest survive The environment determines who is the fittest ...
File
... 4. I am the process in which unrelated species evolve similar traits while adapting to similar environments.________________________ ____________________________ 5. I am a pattern of evolution that is seen in the fossil record; I consist of short periods with lots of evolutionary activity, followed ...
... 4. I am the process in which unrelated species evolve similar traits while adapting to similar environments.________________________ ____________________________ 5. I am a pattern of evolution that is seen in the fossil record; I consist of short periods with lots of evolutionary activity, followed ...
The Evolutionary Synthesis
... Genetical Theory of Natural Selection (1930) • First half of book involved developing Fisher’s concepts of genetics at the population level: – Idea of a “gene pool” – Fitness of alleles – Role of selection ...
... Genetical Theory of Natural Selection (1930) • First half of book involved developing Fisher’s concepts of genetics at the population level: – Idea of a “gene pool” – Fitness of alleles – Role of selection ...
VESTIGIAL STRUCTURE - mvhs
... from a common ancestor, when the environment presents many new opportunities and selective forces. ...
... from a common ancestor, when the environment presents many new opportunities and selective forces. ...
int_2015_Bio_9
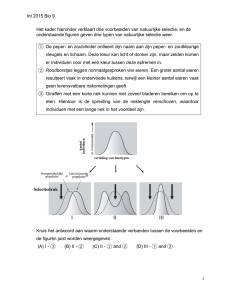
... Directional selection (I): a mode of natural selection in which a single phenotype is favored, causing the allele frequency to continuously shift in one direction. The genetic variance of the population shifts toward a new phenotype when exposed to environmental changes. In the case of such selectio ...
... Directional selection (I): a mode of natural selection in which a single phenotype is favored, causing the allele frequency to continuously shift in one direction. The genetic variance of the population shifts toward a new phenotype when exposed to environmental changes. In the case of such selectio ...
CHAPTER 16 EVOLUTION OF POPULATIONS
... - all members of a population have an equal opportunity to produce offspring and an equal chance of passing on its alleles - in natural populations, it is rarely random Ex. lions and wolves select mates on certain traits such as size or strength making genes for these traits not in equilibrium and u ...
... - all members of a population have an equal opportunity to produce offspring and an equal chance of passing on its alleles - in natural populations, it is rarely random Ex. lions and wolves select mates on certain traits such as size or strength making genes for these traits not in equilibrium and u ...
Sequence Differences between COII Genes in Some Animals Animal
... In North America, the eastern spotted skunk mates in late winter, and the western spotted skunk mates in late summer. Even though their geographic ranges overlap, the species do not mate with each other. What most likely prevents these two species from interbreeding? A. habitat isolation B. gametic ...
... In North America, the eastern spotted skunk mates in late winter, and the western spotted skunk mates in late summer. Even though their geographic ranges overlap, the species do not mate with each other. What most likely prevents these two species from interbreeding? A. habitat isolation B. gametic ...
evoluton
... People have always wondered how life originated and how so many different kinds of plants and animals arose. Stories of a supernatural creation of life developed among many peoples. The Bible, for example, tells of God's creation of humans and other higher ...
... People have always wondered how life originated and how so many different kinds of plants and animals arose. Stories of a supernatural creation of life developed among many peoples. The Bible, for example, tells of God's creation of humans and other higher ...
Natural Selection vs. Selective Breeding
... colored with dark spots. As the industrial revolution progressed, the tree trunks became covered with soot and turned dark. Over a period of 45 years, the dark variety of the peppered moth became more common. ...
... colored with dark spots. As the industrial revolution progressed, the tree trunks became covered with soot and turned dark. Over a period of 45 years, the dark variety of the peppered moth became more common. ...
Evolution PowerPoint
... • ((1785) James Hutton: Using geological examples, 85) Ja es utto : Us g geo og ca e a p es, concluded that the earth must be much older than a few thousand years. • (1798) Thomas Malthus: Reasoned that if the human population grew unchecked, their wouldn’t be enough space and food for everyone ...
... • ((1785) James Hutton: Using geological examples, 85) Ja es utto : Us g geo og ca e a p es, concluded that the earth must be much older than a few thousand years. • (1798) Thomas Malthus: Reasoned that if the human population grew unchecked, their wouldn’t be enough space and food for everyone ...
How Evolution Works: 1. Random mutations cause changes, or
... 1. Random mutations cause changes, or variation, in a population of organisms. 2. These different organisms then compete to survive and reproduce. 3. Those which are best able to survive and reproduce do so, and tend to leave the most offspring. This is called “natural selection.” 4. Over time, if s ...
... 1. Random mutations cause changes, or variation, in a population of organisms. 2. These different organisms then compete to survive and reproduce. 3. Those which are best able to survive and reproduce do so, and tend to leave the most offspring. This is called “natural selection.” 4. Over time, if s ...
Chapters 2 and 3
... ◦ R.A. Fisher – mathematician showed variability in populations could be explained using Mendel’s laws Genetical Theory of Natural Selection Believed selection was favored in large populations because variability remains high due to mutation and genetic recombination Selection acts uniformly a ...
... ◦ R.A. Fisher – mathematician showed variability in populations could be explained using Mendel’s laws Genetical Theory of Natural Selection Believed selection was favored in large populations because variability remains high due to mutation and genetic recombination Selection acts uniformly a ...
Chapter 22 – Descent with Modification: A Darwinian View of Life
... How is Darwin’s “descent with modification” unique as compared to the ideas of the individuals in question #1? 1 pt ...
... How is Darwin’s “descent with modification” unique as compared to the ideas of the individuals in question #1? 1 pt ...
File
... 2. What is meant by chemical evolution? Organic molecules formed from inorganic in the beginning of the earth. 3. Which scientists performed experiments simulating Earth’s early conditions and the formation of organic compounds from inorganic compounds? Miller and Urey 4. In terms of the first life ...
... 2. What is meant by chemical evolution? Organic molecules formed from inorganic in the beginning of the earth. 3. Which scientists performed experiments simulating Earth’s early conditions and the formation of organic compounds from inorganic compounds? Miller and Urey 4. In terms of the first life ...
EvolPract 2014
... ____ 23. The allele frequencies of a population are more likely to remain unchanged if a. the population size is reduced. b. frequent movement into and out of the population occurs. c. all mating is random. d. the mutation rate increases. ____ 24. An orchid lives at the top of a tree and gets expose ...
... ____ 23. The allele frequencies of a population are more likely to remain unchanged if a. the population size is reduced. b. frequent movement into and out of the population occurs. c. all mating is random. d. the mutation rate increases. ____ 24. An orchid lives at the top of a tree and gets expose ...
Evolution
... Ignored in Darwin’s time (and by Darwin himself!) Solved the problem of inheritance by demonstrating that it was particulate in nature, not “blended” ...
... Ignored in Darwin’s time (and by Darwin himself!) Solved the problem of inheritance by demonstrating that it was particulate in nature, not “blended” ...
Natural selection

Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype; it is a key mechanism of evolution. The term ""natural selection"" was popularised by Charles Darwin, who intended it to be compared with artificial selection, now more commonly referred to as selective breeding.Variation exists within all populations of organisms. This occurs partly because random mutations arise in the genome of an individual organism, and these mutations can be passed to offspring. Throughout the individuals’ lives, their genomes interact with their environments to cause variations in traits. (The environment of a genome includes the molecular biology in the cell, other cells, other individuals, populations, species, as well as the abiotic environment.) Individuals with certain variants of the trait may survive and reproduce more than individuals with other, less successful, variants. Therefore, the population evolves. Factors that affect reproductive success are also important, an issue that Darwin developed in his ideas on sexual selection, which was redefined as being included in natural selection in the 1930s when biologists considered it not to be very important, and fecundity selection, for example.Natural selection acts on the phenotype, or the observable characteristics of an organism, but the genetic (heritable) basis of any phenotype that gives a reproductive advantage may become more common in a population (see allele frequency). Over time, this process can result in populations that specialise for particular ecological niches (microevolution) and may eventually result in the emergence of new species (macroevolution). In other words, natural selection is an important process (though not the only process) by which evolution takes place within a population of organisms. Natural selection can be contrasted with artificial selection, in which humans intentionally choose specific traits (although they may not always get what they want). In natural selection there is no intentional choice. In other words, artificial selection is teleological and natural selection is not teleological.Natural selection is one of the cornerstones of modern biology. The concept was published by Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace in a joint presentation of papers in 1858, and set out in Darwin's influential 1859 book On the Origin of Species, in which natural selection was described as analogous to artificial selection, a process by which animals and plants with traits considered desirable by human breeders are systematically favoured for reproduction. The concept of natural selection was originally developed in the absence of a valid theory of heredity; at the time of Darwin's writing, nothing was known of modern genetics. The union of traditional Darwinian evolution with subsequent discoveries in classical and molecular genetics is termed the modern evolutionary synthesis. Natural selection remains the primary explanation for adaptive evolution.