Evolution Test
... 8. There are millions of species of organisms living at this time and new species are still being discovered. Based on Darwin’s theory of evolution, which of the following best describes how millions of species have developed? A. Organisms passed on acquired characteristics to evolve from lower life ...
... 8. There are millions of species of organisms living at this time and new species are still being discovered. Based on Darwin’s theory of evolution, which of the following best describes how millions of species have developed? A. Organisms passed on acquired characteristics to evolve from lower life ...
No Slide Title
... Inference 3. Because variation is heritable, differences between individuals in their reproductive success lead to changes in the characteristics of the next generation. Evolution occurs. ...
... Inference 3. Because variation is heritable, differences between individuals in their reproductive success lead to changes in the characteristics of the next generation. Evolution occurs. ...
natural selection
... • The blue-footed booby has many specialized characteristics that are very functional in water but less useful on land • Such evolutionary adaptations are inherited traits that enhance an organism's ability to survive and reproduce in its particular environment • Evolution is the changes in organism ...
... • The blue-footed booby has many specialized characteristics that are very functional in water but less useful on land • Such evolutionary adaptations are inherited traits that enhance an organism's ability to survive and reproduce in its particular environment • Evolution is the changes in organism ...
natural selections
... contribution eyes have made to the survival of humans. But when it comes to the purpose of humans themselves, or of the mechanism of natural selection that made them, the theory says nothing. If Darwin is right, we have been sired by blind chance out of the laws of physics. We testify to nothing but ...
... contribution eyes have made to the survival of humans. But when it comes to the purpose of humans themselves, or of the mechanism of natural selection that made them, the theory says nothing. If Darwin is right, we have been sired by blind chance out of the laws of physics. We testify to nothing but ...
CSP_evolution_7-17
... a. Individuals within a population often have more offspring than will simply replace the parents. 3. Over time, populations do not increase in size. Generally, the size along with their resources remain fairly constant over time . 4. Variation among individuals within a population exists and is inh ...
... a. Individuals within a population often have more offspring than will simply replace the parents. 3. Over time, populations do not increase in size. Generally, the size along with their resources remain fairly constant over time . 4. Variation among individuals within a population exists and is inh ...
evidence of evolution
... occurred and continues to occur. All life forms, including people, evolved from earlier species. Furthermore, all still living species of organisms continue to evolve today. We now understand that there are a number of different natural processes that can cause evolution to occur. These are presente ...
... occurred and continues to occur. All life forms, including people, evolved from earlier species. Furthermore, all still living species of organisms continue to evolve today. We now understand that there are a number of different natural processes that can cause evolution to occur. These are presente ...
Lecture 11: Evolution 1. Review of Geology Genesis
... The Galapagos: nearly missing the crucial observations Australia and its marsupials 6. Darwin: The Path to Origin of Species Gentleman geologist Early suspicions and radicalism Malthus and natural selection The great delay, 1839-1859 Wallace and simultaneous discovery Atheism and Romanticism ...
... The Galapagos: nearly missing the crucial observations Australia and its marsupials 6. Darwin: The Path to Origin of Species Gentleman geologist Early suspicions and radicalism Malthus and natural selection The great delay, 1839-1859 Wallace and simultaneous discovery Atheism and Romanticism ...
Welcome to Science 3/1
... • Organisms have variations that make them different. • Over time, nature will “select” the organisms with beneficial variations to survive and reproduce. • Over a long, long, time natural selection can lead to evolution. Helpful variations, gradually accumulate in a species, while unfavorable ones ...
... • Organisms have variations that make them different. • Over time, nature will “select” the organisms with beneficial variations to survive and reproduce. • Over a long, long, time natural selection can lead to evolution. Helpful variations, gradually accumulate in a species, while unfavorable ones ...
AP Bio Evolution Study Guide (Ch 22-25)
... o How is the evolutionary fitness of an individual or a species evaluated? How do the various types of selection (stabilizing, directional, diversifying) affect the makeup of a population of organisms? Speciation and Extinction Be familiar with the major definitions of a species (especially know ...
... o How is the evolutionary fitness of an individual or a species evaluated? How do the various types of selection (stabilizing, directional, diversifying) affect the makeup of a population of organisms? Speciation and Extinction Be familiar with the major definitions of a species (especially know ...
Evolution Jeopardy
... What was the significance of the Cambrian explosion to the evolution of life on Earth? A. It was a mass extinction during which nearly 90% of marine species were lost. B. It was a rapid diversification of the ancestors of most major animal groups. C. It was caused by tectonic instability, res ...
... What was the significance of the Cambrian explosion to the evolution of life on Earth? A. It was a mass extinction during which nearly 90% of marine species were lost. B. It was a rapid diversification of the ancestors of most major animal groups. C. It was caused by tectonic instability, res ...
Genetical theory of natural selection
... Amount by which the fitness of one genotype is reduced relative to the reference genotype WA = 0.75, s = 0.25 Overall fitness Fitness depends not only on reproductive success, especially when species reproduce sexually and have more than one reproductive event Age of reproduction Selection ...
... Amount by which the fitness of one genotype is reduced relative to the reference genotype WA = 0.75, s = 0.25 Overall fitness Fitness depends not only on reproductive success, especially when species reproduce sexually and have more than one reproductive event Age of reproduction Selection ...
Chapter 5
... Evolution in __________ populations of animals is believed to occur extremely rarely. sympatric parapatric allopatric small reproductively isolated ...
... Evolution in __________ populations of animals is believed to occur extremely rarely. sympatric parapatric allopatric small reproductively isolated ...
Power Point Notes
... • Thomas Malthus, a clergyman and economist, wrote essay that Darwin read on his return to England • Argued that as population size increases, resources dwindle, the struggle to live intensifies, and conflict increases ...
... • Thomas Malthus, a clergyman and economist, wrote essay that Darwin read on his return to England • Argued that as population size increases, resources dwindle, the struggle to live intensifies, and conflict increases ...
FREE Sample Here
... B. These examples of natural selection in action indicate that certain common principles apply. 1. A trait must be inherited if natural selection is to act on it. 2. Natural selection cannot occur without variation in inherited characteristics. 3. Fitness is a relative measure that will change as th ...
... B. These examples of natural selection in action indicate that certain common principles apply. 1. A trait must be inherited if natural selection is to act on it. 2. Natural selection cannot occur without variation in inherited characteristics. 3. Fitness is a relative measure that will change as th ...
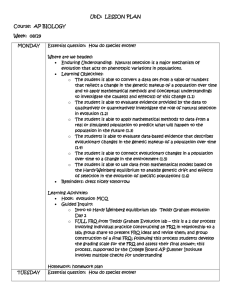
UbD: LESSON PLAN Course: AP BIOLOGY Week: 08/29 MONDAY
... o The student is able to convert a data set from a table of numbers that reflect a change in the genetic makeup of a population over time and to apply mathematical methods and conceptual understandings to investigate the cause(s) and effect(s) of this change (1.1) o The student is able to evaluate e ...
... o The student is able to convert a data set from a table of numbers that reflect a change in the genetic makeup of a population over time and to apply mathematical methods and conceptual understandings to investigate the cause(s) and effect(s) of this change (1.1) o The student is able to evaluate e ...
Evolution of Populations
... middle or at the other end Stabilizing selection- when individuals near the center of the curve have higher fitness than individuals at either end of the curve Disruptive selection- when individuals at the upper and lower ends of the curve have higher fitness than individuals near the middle ...
... middle or at the other end Stabilizing selection- when individuals near the center of the curve have higher fitness than individuals at either end of the curve Disruptive selection- when individuals at the upper and lower ends of the curve have higher fitness than individuals near the middle ...
File - Siegel Science
... 1. Overproduction – Many more offspring are born than can be supported by the environments’ food, space, and resources. These offspring then compete for survival. 2. Individual variation – Individuals within a species have different traits Sources of variation: a. Mutations (rare) b. Sexual re ...
... 1. Overproduction – Many more offspring are born than can be supported by the environments’ food, space, and resources. These offspring then compete for survival. 2. Individual variation – Individuals within a species have different traits Sources of variation: a. Mutations (rare) b. Sexual re ...
Natural Selection By Cindy Grigg 1 In 1831, Darwin was the ship`s
... breeding land mammals, and found that if a single female survived and reproduced at the same rate, after 750 years there could be 19,000,000 descendants of this single mother! ...
... breeding land mammals, and found that if a single female survived and reproduced at the same rate, after 750 years there could be 19,000,000 descendants of this single mother! ...
Ch15 16 17 evolution2
... Reasoned that if the human population continued to grow unchecked, sooner or later there would be insufficient living space and food for everyone ...
... Reasoned that if the human population continued to grow unchecked, sooner or later there would be insufficient living space and food for everyone ...
DescentText - Bryn Mawr College
... Darwin had consciously avoided any discussion of how humans fit into the evolutionary process in the Origin of Species, but as the 1861 Punch cartoon demonstrated, the topic was on everyone’s mind and he knew that he would have to address it eventually. During the 1860s, a number of other prominent ...
... Darwin had consciously avoided any discussion of how humans fit into the evolutionary process in the Origin of Species, but as the 1861 Punch cartoon demonstrated, the topic was on everyone’s mind and he knew that he would have to address it eventually. During the 1860s, a number of other prominent ...
Tecfa
... On the origin of species by means of Natural Selection or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life (Charles Darwin, 1859) ...
... On the origin of species by means of Natural Selection or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life (Charles Darwin, 1859) ...
Natural selection

Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype; it is a key mechanism of evolution. The term ""natural selection"" was popularised by Charles Darwin, who intended it to be compared with artificial selection, now more commonly referred to as selective breeding.Variation exists within all populations of organisms. This occurs partly because random mutations arise in the genome of an individual organism, and these mutations can be passed to offspring. Throughout the individuals’ lives, their genomes interact with their environments to cause variations in traits. (The environment of a genome includes the molecular biology in the cell, other cells, other individuals, populations, species, as well as the abiotic environment.) Individuals with certain variants of the trait may survive and reproduce more than individuals with other, less successful, variants. Therefore, the population evolves. Factors that affect reproductive success are also important, an issue that Darwin developed in his ideas on sexual selection, which was redefined as being included in natural selection in the 1930s when biologists considered it not to be very important, and fecundity selection, for example.Natural selection acts on the phenotype, or the observable characteristics of an organism, but the genetic (heritable) basis of any phenotype that gives a reproductive advantage may become more common in a population (see allele frequency). Over time, this process can result in populations that specialise for particular ecological niches (microevolution) and may eventually result in the emergence of new species (macroevolution). In other words, natural selection is an important process (though not the only process) by which evolution takes place within a population of organisms. Natural selection can be contrasted with artificial selection, in which humans intentionally choose specific traits (although they may not always get what they want). In natural selection there is no intentional choice. In other words, artificial selection is teleological and natural selection is not teleological.Natural selection is one of the cornerstones of modern biology. The concept was published by Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace in a joint presentation of papers in 1858, and set out in Darwin's influential 1859 book On the Origin of Species, in which natural selection was described as analogous to artificial selection, a process by which animals and plants with traits considered desirable by human breeders are systematically favoured for reproduction. The concept of natural selection was originally developed in the absence of a valid theory of heredity; at the time of Darwin's writing, nothing was known of modern genetics. The union of traditional Darwinian evolution with subsequent discoveries in classical and molecular genetics is termed the modern evolutionary synthesis. Natural selection remains the primary explanation for adaptive evolution.