Evolution Review
... b) the process by which populations change biologically over time as organisms pass their traits to their offspring. c) the process by which individuals change biologically over time as organisms pass their traits to offspring. d) a characteristic that improves and organism’s chance of survival e) e ...
... b) the process by which populations change biologically over time as organisms pass their traits to their offspring. c) the process by which individuals change biologically over time as organisms pass their traits to offspring. d) a characteristic that improves and organism’s chance of survival e) e ...
Evolution 2
... Overpopulation Darwin observed that many species produce more offspring than can possibly survive. So many offspring are produced that there is not enough resources – food, water, and living space – for all of them. ...
... Overpopulation Darwin observed that many species produce more offspring than can possibly survive. So many offspring are produced that there is not enough resources – food, water, and living space – for all of them. ...
Evolution and Classification Homework Evolution: Theory Due
... b. Why is Lamarck’s hypothesis easily disproved? 3. Charles Darwin and Alfred Wallace independently proposed that species were modified by natural selection. What is natural selection? 4. Darwin collected 13 separate species of finches from the Galapagos Islands. The birds were similar in appearance ...
... b. Why is Lamarck’s hypothesis easily disproved? 3. Charles Darwin and Alfred Wallace independently proposed that species were modified by natural selection. What is natural selection? 4. Darwin collected 13 separate species of finches from the Galapagos Islands. The birds were similar in appearance ...
Slide 1
... Farmers and animal breeders have long known that the traits of a population could be changed by nonrandom mating. Example: Oranges with smaller and smaller seeds were bred until “seedless” oranges were created In this case, farmers did not allow “nature to take its course”. They selected a trait t ...
... Farmers and animal breeders have long known that the traits of a population could be changed by nonrandom mating. Example: Oranges with smaller and smaller seeds were bred until “seedless” oranges were created In this case, farmers did not allow “nature to take its course”. They selected a trait t ...
Theory of Evolution Power Point
... 2. Overproduction: some will survive, it increases competition for resources. A certain variation allows an individual to survive 3. Adaptation: better than other individuals it competes with. ...
... 2. Overproduction: some will survive, it increases competition for resources. A certain variation allows an individual to survive 3. Adaptation: better than other individuals it competes with. ...
5 Points of Darwin`s Natural Selection
... b. Darwin's 5 points: Identify the 5 points in the scenario above. Population has variations. _______________________________________________________________________ Some variations are favorable. ___________________________________________________________________ More offspring are produced than su ...
... b. Darwin's 5 points: Identify the 5 points in the scenario above. Population has variations. _______________________________________________________________________ Some variations are favorable. ___________________________________________________________________ More offspring are produced than su ...
DO NOT WRITE ON THE EXAM Test: changes over time (100 points
... a. eating the insecticide caused the bugs to become resistant to it b. eating the insecticide caused the bugs to become less resistant to it c. it destroyed organisms that cause disease in the insects, thus allowing them to live longer d. the pests developed physiological adaptations to the insectic ...
... a. eating the insecticide caused the bugs to become resistant to it b. eating the insecticide caused the bugs to become less resistant to it c. it destroyed organisms that cause disease in the insects, thus allowing them to live longer d. the pests developed physiological adaptations to the insectic ...
Document
... 18. A population of birds lives in an area where plants with medium sized seeds are wiped out by a fungal infection. Birds with unusually large or small beaks would have higher fitness than those with medium sized beaks. Over time the population splits into two subgroups; one that eats small seeds ...
... 18. A population of birds lives in an area where plants with medium sized seeds are wiped out by a fungal infection. Birds with unusually large or small beaks would have higher fitness than those with medium sized beaks. Over time the population splits into two subgroups; one that eats small seeds ...
Learning Objectives
... 1. The potential for reproductive rates that outpace the rate of increase of food supplies. 2. The presence of biological variation within all species. 3. Constant competition among individuals for survival. 4. Individuals with favorable traits are more likely to survive and reproduce. 5. The enviro ...
... 1. The potential for reproductive rates that outpace the rate of increase of food supplies. 2. The presence of biological variation within all species. 3. Constant competition among individuals for survival. 4. Individuals with favorable traits are more likely to survive and reproduce. 5. The enviro ...
Biol 178 Lecture 32
... The alleles of these founders will be very significant in the new population, even if they were rare in the original population. Eg. Galápagos Islands. ...
... The alleles of these founders will be very significant in the new population, even if they were rare in the original population. Eg. Galápagos Islands. ...
A1983RC02000002
... they are). We estimated that the human genome contained about 40,000 genes, with structural genes accounting for only about one percent of DNA. I held out for the provocative title, which indeed managed to provoke everyone. We were able to cite Kimura in our revision, and began what was to be a leng ...
... they are). We estimated that the human genome contained about 40,000 genes, with structural genes accounting for only about one percent of DNA. I held out for the provocative title, which indeed managed to provoke everyone. We were able to cite Kimura in our revision, and began what was to be a leng ...
Unit 4 Evolution
... Charles Darwin developed the “Theory of Evolution” which explained how the species we have today on Earth got here. He thought that Natural Selection was the mechanism of evolution, and it explained how, over a long period of time, species have evolved (or CHANGED) on our planet from ...
... Charles Darwin developed the “Theory of Evolution” which explained how the species we have today on Earth got here. He thought that Natural Selection was the mechanism of evolution, and it explained how, over a long period of time, species have evolved (or CHANGED) on our planet from ...
Study Questions for Exam 1 Biology 354 Lecture 1: Natural selection
... Imagine that you took opossums from the mainland of Georgia and from Sapelo Island and raised them in the laboratory from birth to death. You monitored their survival patterns and found that they were the same – in other words, they died at the same rate. How would this cause you to reinterpret figu ...
... Imagine that you took opossums from the mainland of Georgia and from Sapelo Island and raised them in the laboratory from birth to death. You monitored their survival patterns and found that they were the same – in other words, they died at the same rate. How would this cause you to reinterpret figu ...
Natural Selection
... dark color in moths is dominant (D) why did light moths (dd) continue to reappear? ...
... dark color in moths is dominant (D) why did light moths (dd) continue to reappear? ...
Human Adaptation and Variation The logic of selection
... • are all relevant molecular, biochemical, metabolic, etc. control systems working properly? • is organism surviving? • if so, are all relevant physiological and endocrine control systems working properly? • is organism growing and developing? • if so, are all relevant psychoneuroendocrine control s ...
... • are all relevant molecular, biochemical, metabolic, etc. control systems working properly? • is organism surviving? • if so, are all relevant physiological and endocrine control systems working properly? • is organism growing and developing? • if so, are all relevant psychoneuroendocrine control s ...
Day 25 – Carbohydrates
... 2. Adaptation: any inherited characteristic that increases an organism’s chance of survival. ...
... 2. Adaptation: any inherited characteristic that increases an organism’s chance of survival. ...
Chapter 22: Descent with Modification: A Darwinian View of Life
... o as an organism acquired a trait, the new trait would pass information to its germ cells so that the next generation could benefit from the trait o the process occurred slowly so that only over many generations would visible changes occur o organisms had an innate drive to become increasingly more ...
... o as an organism acquired a trait, the new trait would pass information to its germ cells so that the next generation could benefit from the trait o the process occurred slowly so that only over many generations would visible changes occur o organisms had an innate drive to become increasingly more ...
Grade 11 University Biology – Unit 3 Evolution
... year or two of drought in which there are fewer plants. All the beetles have the same chances of survival and reproduction, but because of food restrictions, the beetles in the population are a little smaller than the preceding generation of beetles. The difference in weight is NOT evolution. It was ...
... year or two of drought in which there are fewer plants. All the beetles have the same chances of survival and reproduction, but because of food restrictions, the beetles in the population are a little smaller than the preceding generation of beetles. The difference in weight is NOT evolution. It was ...
Section 16-2 - Xavier High School
... A. Natural Selection on Single-Gene Traits B. Natural Selection on Polygenic Traits ...
... A. Natural Selection on Single-Gene Traits B. Natural Selection on Polygenic Traits ...
Document
... Historically, the white peppered moth was the most common moth in England. It was very well adapted to blend in with the white birch trees that it lived on. Blending in with its environment helped the peppered moth hide from bats, robins, and other flying predators. Black moths were very rare. They ...
... Historically, the white peppered moth was the most common moth in England. It was very well adapted to blend in with the white birch trees that it lived on. Blending in with its environment helped the peppered moth hide from bats, robins, and other flying predators. Black moths were very rare. They ...
Biology Unit 7 Ch. 13, 14, 15, 16 Evolution CHAPTER 13:
... Earth’s History and The First Life Forms a. I can outline the modern scientific understanding of the formation of Earth. b. I can explain the evidence used to infer that the first cells were prokaryotic, anaerobic, and heterotrophic. c. I can compare the two types of autotrophy used by early cells. ...
... Earth’s History and The First Life Forms a. I can outline the modern scientific understanding of the formation of Earth. b. I can explain the evidence used to infer that the first cells were prokaryotic, anaerobic, and heterotrophic. c. I can compare the two types of autotrophy used by early cells. ...
How Populations Evolve
... B. A finch that lives to be 5 years old and has five offspring, one of which survives to reproduce C. A finch that lives to be 2 years old and has four offspring, all of which survive to reproduce themselves ...
... B. A finch that lives to be 5 years old and has five offspring, one of which survives to reproduce C. A finch that lives to be 2 years old and has four offspring, all of which survive to reproduce themselves ...
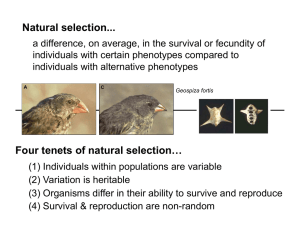
Four tenets of natural selection… Natural selection
... Probability of survival before and during the reproductive period ...
... Probability of survival before and during the reproductive period ...
Natural selection

Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype; it is a key mechanism of evolution. The term ""natural selection"" was popularised by Charles Darwin, who intended it to be compared with artificial selection, now more commonly referred to as selective breeding.Variation exists within all populations of organisms. This occurs partly because random mutations arise in the genome of an individual organism, and these mutations can be passed to offspring. Throughout the individuals’ lives, their genomes interact with their environments to cause variations in traits. (The environment of a genome includes the molecular biology in the cell, other cells, other individuals, populations, species, as well as the abiotic environment.) Individuals with certain variants of the trait may survive and reproduce more than individuals with other, less successful, variants. Therefore, the population evolves. Factors that affect reproductive success are also important, an issue that Darwin developed in his ideas on sexual selection, which was redefined as being included in natural selection in the 1930s when biologists considered it not to be very important, and fecundity selection, for example.Natural selection acts on the phenotype, or the observable characteristics of an organism, but the genetic (heritable) basis of any phenotype that gives a reproductive advantage may become more common in a population (see allele frequency). Over time, this process can result in populations that specialise for particular ecological niches (microevolution) and may eventually result in the emergence of new species (macroevolution). In other words, natural selection is an important process (though not the only process) by which evolution takes place within a population of organisms. Natural selection can be contrasted with artificial selection, in which humans intentionally choose specific traits (although they may not always get what they want). In natural selection there is no intentional choice. In other words, artificial selection is teleological and natural selection is not teleological.Natural selection is one of the cornerstones of modern biology. The concept was published by Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace in a joint presentation of papers in 1858, and set out in Darwin's influential 1859 book On the Origin of Species, in which natural selection was described as analogous to artificial selection, a process by which animals and plants with traits considered desirable by human breeders are systematically favoured for reproduction. The concept of natural selection was originally developed in the absence of a valid theory of heredity; at the time of Darwin's writing, nothing was known of modern genetics. The union of traditional Darwinian evolution with subsequent discoveries in classical and molecular genetics is termed the modern evolutionary synthesis. Natural selection remains the primary explanation for adaptive evolution.