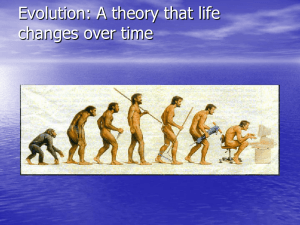
Species
... The amount of radioactive elements remaining in a rock can help scientists determine how much time has elapsed since the rock was formed and cooled. Common isotopes used for long-term dating (old rocks) include uranium as it decays to lead, and potassium as it decays to argon. The carbon-14 is ...
... The amount of radioactive elements remaining in a rock can help scientists determine how much time has elapsed since the rock was formed and cooled. Common isotopes used for long-term dating (old rocks) include uranium as it decays to lead, and potassium as it decays to argon. The carbon-14 is ...
Evolution Concept List Part 1 Chapter 15 1. Use the following terms
... 3. The word radiation is derived from the Latin radius, which means “rod” or “ray.” Using this information, explain the meaning of adaptive radiation. 4. Define the biological process of evolution. 5. Contrast Cuvier’s catastrophism with Lyell’s uniformitarianism. 6. Describe how the finch species o ...
... 3. The word radiation is derived from the Latin radius, which means “rod” or “ray.” Using this information, explain the meaning of adaptive radiation. 4. Define the biological process of evolution. 5. Contrast Cuvier’s catastrophism with Lyell’s uniformitarianism. 6. Describe how the finch species o ...
BIOE 103
... would a biologist explain how the ability to run fast evolved in cheetahs, assuming their ancestors could run only 20 miles per hour? Bowhead whales are the only species of the great whales that live their entire life in the cold water of the Arctic Ocean. Bowhead whales have a thick layer of fat ca ...
... would a biologist explain how the ability to run fast evolved in cheetahs, assuming their ancestors could run only 20 miles per hour? Bowhead whales are the only species of the great whales that live their entire life in the cold water of the Arctic Ocean. Bowhead whales have a thick layer of fat ca ...
Text S1.
... Ultimately we are interested in how the positive covariance observed here between strength of selection and expression of additive genetic variance (and heritability) influence the population’s ability to respond to selection. However, we would like to emphasize that predicting a response to selecti ...
... Ultimately we are interested in how the positive covariance observed here between strength of selection and expression of additive genetic variance (and heritability) influence the population’s ability to respond to selection. However, we would like to emphasize that predicting a response to selecti ...
Evolution - Byron High School
... 2. List the major events that led to Charles Darwin’s development of his theory of Evolution by means of Natural Selection 3. Summarize the major events of the Geologic Time Scale 4. Compare and contrast early experiments that support the concept of biogenesis and disproved spontaneous generation 5. ...
... 2. List the major events that led to Charles Darwin’s development of his theory of Evolution by means of Natural Selection 3. Summarize the major events of the Geologic Time Scale 4. Compare and contrast early experiments that support the concept of biogenesis and disproved spontaneous generation 5. ...
Evolution – Just A Theory?
... universe and of living things are best explained by an intelligent cause, not an undirected process such as natural selection.” A “creator” was responsible for the design of what exists on earth NOT a scientific theory/proposal due to the “fact” that there is a lack of evidence and should NOT be ...
... universe and of living things are best explained by an intelligent cause, not an undirected process such as natural selection.” A “creator” was responsible for the design of what exists on earth NOT a scientific theory/proposal due to the “fact” that there is a lack of evidence and should NOT be ...
evolution ppt
... All living things are highly adapted to their way of life. Many adaptations cannot be explained by environmental influence. Some adaptations are less than perfect. NS has been observed and has resulted in changes in natural populations. Artificial selection by “breeders” has produced many new adapta ...
... All living things are highly adapted to their way of life. Many adaptations cannot be explained by environmental influence. Some adaptations are less than perfect. NS has been observed and has resulted in changes in natural populations. Artificial selection by “breeders” has produced many new adapta ...
AP Biology Summer Assignment
... the following: Aristotle, Hutton, Cuvier, Lyell, Malthus, Wallace, Lamarck and Linnaeus. 2. Discuss how each of the researchers above influenced Charles Darwin? 3. Describe the observations and the inferences ...
... the following: Aristotle, Hutton, Cuvier, Lyell, Malthus, Wallace, Lamarck and Linnaeus. 2. Discuss how each of the researchers above influenced Charles Darwin? 3. Describe the observations and the inferences ...
Lesson plan - KBS GK12 Project
... B5.1d: explain how a new species or variety originates through the evolutionary process of natural selection B5.1e: explain how natural selection leads to organisms that are well suited for the environment B5.3A: explain how natural selection acts on individuals, but it is populations that evolve. R ...
... B5.1d: explain how a new species or variety originates through the evolutionary process of natural selection B5.1e: explain how natural selection leads to organisms that are well suited for the environment B5.3A: explain how natural selection acts on individuals, but it is populations that evolve. R ...
The Theory of Evolution
... • “survival of the fittest” (not Darwin’s words but Herbert Spencer’s) • organisms with a particular trait are better suited for their environment and survive, reproduce, and pass that trait on to the next generation ...
... • “survival of the fittest” (not Darwin’s words but Herbert Spencer’s) • organisms with a particular trait are better suited for their environment and survive, reproduce, and pass that trait on to the next generation ...
Origin of Life
... Find where Lamarck is using his two laws to falsely explain evolution in this case. ...
... Find where Lamarck is using his two laws to falsely explain evolution in this case. ...
Sample Review Material
... • Organisms share many conserved core processes and features that evolved and are widely distributed among organisms today. • Phylogenetic trees and cladograms are graphical representations of evolutionary history that can be tested. ...
... • Organisms share many conserved core processes and features that evolved and are widely distributed among organisms today. • Phylogenetic trees and cladograms are graphical representations of evolutionary history that can be tested. ...
What difference did Darwin make?
... Darwin was not only in recognising that evolution has occurred, but in discovering how it occurs through natural selection. Darwin once wrote that perhaps he chose the wrong word — perhaps he should have called this mechanism natural preservation. The problem with the word “selection” is that it may ...
... Darwin was not only in recognising that evolution has occurred, but in discovering how it occurs through natural selection. Darwin once wrote that perhaps he chose the wrong word — perhaps he should have called this mechanism natural preservation. The problem with the word “selection” is that it may ...
IB Evolution 2016
... population of a species become isolated from one another. Example: a species of butterfly is widely distributed across an area of grassland. ...
... population of a species become isolated from one another. Example: a species of butterfly is widely distributed across an area of grassland. ...
Darwin and Evolution 2
... Ideas That Influenced Darwin James Hutton – proposed that Earth is shaped by geological forces that took place over extremely long periods of time Charles Lyell – explained that processes occurring now have shaped Earth’s geological features over long periods of ...
... Ideas That Influenced Darwin James Hutton – proposed that Earth is shaped by geological forces that took place over extremely long periods of time Charles Lyell – explained that processes occurring now have shaped Earth’s geological features over long periods of ...
TYPES OF NATUR TYPES OF NATURAL SELECTION
... 3. In cross-fertilizing individuals: In cross-fertilising microorganisms no two individuals are alike genetically and every population possesses genes in different frequencies. Natural selection may increase the frequencies of some genes and decrease the frequency of others. Since new genotypes are ...
... 3. In cross-fertilizing individuals: In cross-fertilising microorganisms no two individuals are alike genetically and every population possesses genes in different frequencies. Natural selection may increase the frequencies of some genes and decrease the frequency of others. Since new genotypes are ...
Adaptation, Natural Selection and Evolution
... You must find out; - how your animal is adapted to it’s environment? - how does this adaptation affect the animal’s survival? ...
... You must find out; - how your animal is adapted to it’s environment? - how does this adaptation affect the animal’s survival? ...
AP Biology - TeacherWeb
... an individual makes to the gene pool of the next generation. 1. The term “fitness” does not mean how in shape you are physically. What does it mean? ...
... an individual makes to the gene pool of the next generation. 1. The term “fitness” does not mean how in shape you are physically. What does it mean? ...
Biology Unit 7 Ch. 13, 14, 15, 16 Evolution
... Earth’s History and The First Life Forms a. I can outline the modern scientific understanding of the formation of Earth. b. I can explain the evidence used to infer that the first cells were prokaryotic, anaerobic, and heterotrophic. c. I can compare the two types of autotrophy used by early cells. ...
... Earth’s History and The First Life Forms a. I can outline the modern scientific understanding of the formation of Earth. b. I can explain the evidence used to infer that the first cells were prokaryotic, anaerobic, and heterotrophic. c. I can compare the two types of autotrophy used by early cells. ...
Genetics and Evolution
... subgroup in a population. Hardy-Weinberg Principle: allele frequency will remain constant (genetic equilibrium) unless one or more factors cause frequencies to change. ...
... subgroup in a population. Hardy-Weinberg Principle: allele frequency will remain constant (genetic equilibrium) unless one or more factors cause frequencies to change. ...
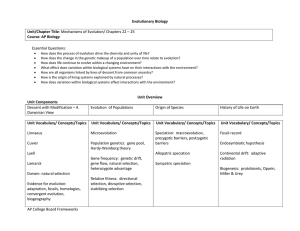
Evolutionary Biology Unit Design
... evaluate evidence provided by data /sets/ to qualitatively and quantitatively investigate the role of natural selection in evolution. use data from a real or simulated population, based on graphs or models of types of selection and apply mathematical methods to predict what will happen to the popula ...
... evaluate evidence provided by data /sets/ to qualitatively and quantitatively investigate the role of natural selection in evolution. use data from a real or simulated population, based on graphs or models of types of selection and apply mathematical methods to predict what will happen to the popula ...
WLHS / Biology / Monson Name Date Per READING GUIDE: 17.3
... 1) What is meant by REPRODUCTIVE ISOLATION? ...
... 1) What is meant by REPRODUCTIVE ISOLATION? ...
Natural selection

Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype; it is a key mechanism of evolution. The term ""natural selection"" was popularised by Charles Darwin, who intended it to be compared with artificial selection, now more commonly referred to as selective breeding.Variation exists within all populations of organisms. This occurs partly because random mutations arise in the genome of an individual organism, and these mutations can be passed to offspring. Throughout the individuals’ lives, their genomes interact with their environments to cause variations in traits. (The environment of a genome includes the molecular biology in the cell, other cells, other individuals, populations, species, as well as the abiotic environment.) Individuals with certain variants of the trait may survive and reproduce more than individuals with other, less successful, variants. Therefore, the population evolves. Factors that affect reproductive success are also important, an issue that Darwin developed in his ideas on sexual selection, which was redefined as being included in natural selection in the 1930s when biologists considered it not to be very important, and fecundity selection, for example.Natural selection acts on the phenotype, or the observable characteristics of an organism, but the genetic (heritable) basis of any phenotype that gives a reproductive advantage may become more common in a population (see allele frequency). Over time, this process can result in populations that specialise for particular ecological niches (microevolution) and may eventually result in the emergence of new species (macroevolution). In other words, natural selection is an important process (though not the only process) by which evolution takes place within a population of organisms. Natural selection can be contrasted with artificial selection, in which humans intentionally choose specific traits (although they may not always get what they want). In natural selection there is no intentional choice. In other words, artificial selection is teleological and natural selection is not teleological.Natural selection is one of the cornerstones of modern biology. The concept was published by Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace in a joint presentation of papers in 1858, and set out in Darwin's influential 1859 book On the Origin of Species, in which natural selection was described as analogous to artificial selection, a process by which animals and plants with traits considered desirable by human breeders are systematically favoured for reproduction. The concept of natural selection was originally developed in the absence of a valid theory of heredity; at the time of Darwin's writing, nothing was known of modern genetics. The union of traditional Darwinian evolution with subsequent discoveries in classical and molecular genetics is termed the modern evolutionary synthesis. Natural selection remains the primary explanation for adaptive evolution.