asexual reproduction
... elephants and whales, is to produce young. Animals need to reproduce to make sure that their species survives. There are two main aims in reproduction—to have as many young as possible and for those young to live long enough to reproduce themselves. To achieve these aims, some animals, such as many ...
... elephants and whales, is to produce young. Animals need to reproduce to make sure that their species survives. There are two main aims in reproduction—to have as many young as possible and for those young to live long enough to reproduce themselves. To achieve these aims, some animals, such as many ...
Scotland`s Freshwater Fish Populations: Stocking, Genetics and
... genetic populations or groups. In these groups breeding is more or less random, but among groups, interbreeding is limited or absent. These basic biological units have ...
... genetic populations or groups. In these groups breeding is more or less random, but among groups, interbreeding is limited or absent. These basic biological units have ...
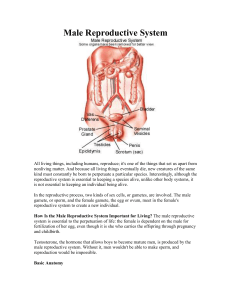
Male Reproductive System
... system is essential to the perpetuation of life: the female is dependent on the male for fertilization of her egg, even though it is she who carries the offspring through pregnancy and childbirth. Testosterone, the hormone that allows boys to become mature men, is produced by the male reproductive s ...
... system is essential to the perpetuation of life: the female is dependent on the male for fertilization of her egg, even though it is she who carries the offspring through pregnancy and childbirth. Testosterone, the hormone that allows boys to become mature men, is produced by the male reproductive s ...
Earthworm Dissection
... •This sac is carried by a worm until baby worms have developed, at which point the sac breaks open and they squirm free. ...
... •This sac is carried by a worm until baby worms have developed, at which point the sac breaks open and they squirm free. ...
Reproduction
... egg cell. The male structure is called the stamen. It consists of the filament and the pollenproducing anther. A new seed is formed when an egg cell joins with a pollen cell in the process of pollination. Pollination occurs when pollen grains are carried from the anther of the stamen to the stigma o ...
... egg cell. The male structure is called the stamen. It consists of the filament and the pollenproducing anther. A new seed is formed when an egg cell joins with a pollen cell in the process of pollination. Pollination occurs when pollen grains are carried from the anther of the stamen to the stigma o ...
REPRODUCTION IN ANIMALS
... lays only one egg at a time? Ans. Though these animals lay hundreds of eggs and release millions of sperms, all the eggs do not get fertilized and develop into new individuals. This is because the eggs and sperms get exposed to water movement, wind and rainfall. Also, there are other animals in the ...
... lays only one egg at a time? Ans. Though these animals lay hundreds of eggs and release millions of sperms, all the eggs do not get fertilized and develop into new individuals. This is because the eggs and sperms get exposed to water movement, wind and rainfall. Also, there are other animals in the ...
File
... Such as hydra and yeast reproduce asexually by budding. During budding, the parent produces a small “bud”, or a smaller version of itself. In most animals (like the hydra) and unicellular fungus (yeast), the bud detaches and becomes a new individual identical to its parent. In some (such as coral) t ...
... Such as hydra and yeast reproduce asexually by budding. During budding, the parent produces a small “bud”, or a smaller version of itself. In most animals (like the hydra) and unicellular fungus (yeast), the bud detaches and becomes a new individual identical to its parent. In some (such as coral) t ...
6.2 Sexual Reproduction
... 2. Temperature must not be too cold or too hot. 3. There must be enough moisture so that the embryo does not dry out. 4. Embryo must be protected from predators and items in the environment that can potentially harm it. ...
... 2. Temperature must not be too cold or too hot. 3. There must be enough moisture so that the embryo does not dry out. 4. Embryo must be protected from predators and items in the environment that can potentially harm it. ...
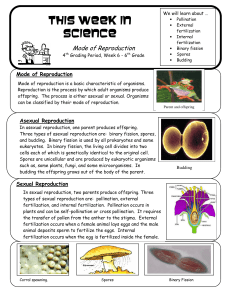
This week in science 6th - Reproduction
... fertilization, and internal fertilization. Pollination occurs in plants and can be self-pollination or cross pollination. It requires the transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma. External fertilization occurs when a female animal lays eggs and the male animal deposits sperm to fertilize the ...
... fertilization, and internal fertilization. Pollination occurs in plants and can be self-pollination or cross pollination. It requires the transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma. External fertilization occurs when a female animal lays eggs and the male animal deposits sperm to fertilize the ...
Methods of reproduction
... of water, food, right temperatures, etc., binary fission is a very effective way of producing many, many offspring. • For example, the cell of a Paramecium can divide, grow, and divide again in the space of 8 hours. ...
... of water, food, right temperatures, etc., binary fission is a very effective way of producing many, many offspring. • For example, the cell of a Paramecium can divide, grow, and divide again in the space of 8 hours. ...
Chapter 2 Lesson 1 Reproduction All living things must reproduce
... Like plants, animals that reproduce sexually develop into embryos. Some develop inside eggs. Different types of eggs are needed for different environments. Fish and frogs lay eggs in water to prevent them from drying out. Reptiles and birds have tough shells filled with watery liquid to keep it from ...
... Like plants, animals that reproduce sexually develop into embryos. Some develop inside eggs. Different types of eggs are needed for different environments. Fish and frogs lay eggs in water to prevent them from drying out. Reptiles and birds have tough shells filled with watery liquid to keep it from ...
- Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute
... When the female is ready to deposit the eggs in protected areas under rocks or in discarded shells, the female uses the arms to wipe the stored spermatophores onto each egg. Cuttlefish eggs are individually enclosed in a tough protective external coating, often pigmented black from the ink-sac secre ...
... When the female is ready to deposit the eggs in protected areas under rocks or in discarded shells, the female uses the arms to wipe the stored spermatophores onto each egg. Cuttlefish eggs are individually enclosed in a tough protective external coating, often pigmented black from the ink-sac secre ...
Human reproductive s.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... d. ovaries – produces egg and estrogen and progesterone e. oviduct – connects the ovaries and uterus, where fertilization takes place 3. What is the primary function(s) of the male reproductive system? (1) To make the sperm 4. What is the primary function(s) of the female reproductive system? (1) To ...
... d. ovaries – produces egg and estrogen and progesterone e. oviduct – connects the ovaries and uterus, where fertilization takes place 3. What is the primary function(s) of the male reproductive system? (1) To make the sperm 4. What is the primary function(s) of the female reproductive system? (1) To ...
Methods of Reproduction
... which females produce eggs that develop without fertilization. • Parthenogenesis is seen to occur naturally in some invertebrates, along with several fish, amphibians, and reptiles as well as in many plants. • There are no known cases of parthenogenesis in mammals. ...
... which females produce eggs that develop without fertilization. • Parthenogenesis is seen to occur naturally in some invertebrates, along with several fish, amphibians, and reptiles as well as in many plants. • There are no known cases of parthenogenesis in mammals. ...
Reproduction In Organism
... Diplontic life-cycle- zygote (2n) divides mitotically, develops into embryo (2n). Oviparous animals lay eggs out-side the female body. Eggs can be fertilized/ unfertilized. Fertilized eggs covered which hard calcareous shell, laid in safe place in the environment. Unfertilised eggs laid in water. Ex ...
... Diplontic life-cycle- zygote (2n) divides mitotically, develops into embryo (2n). Oviparous animals lay eggs out-side the female body. Eggs can be fertilized/ unfertilized. Fertilized eggs covered which hard calcareous shell, laid in safe place in the environment. Unfertilised eggs laid in water. Ex ...
Human Reproduction Notes
... epididymus, where they complete maturation. Passage takes about 20 days. ...
... epididymus, where they complete maturation. Passage takes about 20 days. ...
Reproduction - VCE
... • Produced by budding • When it lands in a suitable environment it germinates • Spores are asexual reproductive cells produced by mosses, ferns and fungi and other organisms. ...
... • Produced by budding • When it lands in a suitable environment it germinates • Spores are asexual reproductive cells produced by mosses, ferns and fungi and other organisms. ...
Worksheet for grade 12 biology REPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMS
... 1. Bulbils: These are small, fleshy buds which develop into new plants as in Agave. 2. Clone: A group of organism derived from a single individual and hence morphologically and genetically similar. 3. Embryogenesis: The process of development of embryo from zygote. 4. Gametogenesis: The process of f ...
... 1. Bulbils: These are small, fleshy buds which develop into new plants as in Agave. 2. Clone: A group of organism derived from a single individual and hence morphologically and genetically similar. 3. Embryogenesis: The process of development of embryo from zygote. 4. Gametogenesis: The process of f ...
KIC and IVF - Kiran Infertility Center
... from releasing eggs quickly. Doctors carefully monitor blood hormone levels and take ultrasound measurements of ovaries to find out if eggs are mature. Once eggs are mature, doctor removes the same from ovaries. Generally, a needle is inserted through vaginal wall and eggs are taken out. Ultrasound ...
... from releasing eggs quickly. Doctors carefully monitor blood hormone levels and take ultrasound measurements of ovaries to find out if eggs are mature. Once eggs are mature, doctor removes the same from ovaries. Generally, a needle is inserted through vaginal wall and eggs are taken out. Ultrasound ...
introduction to reproduction
... Sexual reproduction, which involves two parents, occurs in most living plants and animals. The offspring that result from sexual reproduction are similar to the parents, but not identical. Sexual reproduction always involves the joining of two sex cells called gametes in a process called fertilisati ...
... Sexual reproduction, which involves two parents, occurs in most living plants and animals. The offspring that result from sexual reproduction are similar to the parents, but not identical. Sexual reproduction always involves the joining of two sex cells called gametes in a process called fertilisati ...
To reproduce - SDSU Heart Institute
... • “The hen is the egg’ egg’s way of making more eggs” eggs” (Samuel Butler) • The vehicle carrying genetic information must successfully get the egg fertilized, hatched (born), and far along enough in development to ensure it will produce another egg • The egg also wants more eggs like itself - the ...
... • “The hen is the egg’ egg’s way of making more eggs” eggs” (Samuel Butler) • The vehicle carrying genetic information must successfully get the egg fertilized, hatched (born), and far along enough in development to ensure it will produce another egg • The egg also wants more eggs like itself - the ...
Endocrine System
... Responds to hypothalamus by releasing hormones Some hormones trigger other glands to produce hormones ...
... Responds to hypothalamus by releasing hormones Some hormones trigger other glands to produce hormones ...
Spawn (biology)

Spawn is the eggs and sperm released or deposited, usually into water, by aquatic animals. As a verb, spawn refers to the process of releasing the eggs and sperm, also called spawning. Most aquatic animals, apart from aquatic mammals, reproduce through a process of spawning.Spawn consists of the reproductive cells (gametes) of aquatic animals, some of which will become fertilized and produce offspring. The process of spawning typically involves females releasing ova (unfertilized eggs) into the water, often in large quantities, while males simultaneously or sequentially release spermatozoa (milt) to fertilize the eggs.Most fish reproduce by spawning, and so do most other aquatic animals, including crustaceans such as crabs and shrimps, molluscs such as oysters and squid, echinoderms such as sea urchins and sea cucumbers, amphibians such as frogs and newts, other amphibious animals such as turtles, aquatic insects such as mayflies and mosquitoes, and corals (which are small aquatic animals and not plants). Fungi, such as mushrooms, are also said to ""spawn"" a white fibrous matter that forms the matrix from which they grow.There are many variations in the way spawning occurs, depending on sexual differences in anatomy, on how the sexes relate to each other, on where and how the spawn is released, and on whether or how the spawn is subsequently guarded.