5. Reproduction and Recruitment
... Direct Development Brooding or egg masses No free larvae High parental care ...
... Direct Development Brooding or egg masses No free larvae High parental care ...
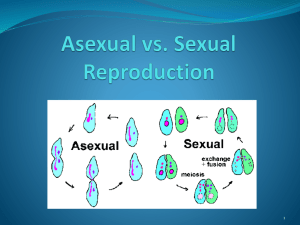
Asexual vs. Sexual Reproduction
... Lobsters Sharks Humans Butterflies Sunflowers Roses ...
... Lobsters Sharks Humans Butterflies Sunflowers Roses ...
Male reproductive investment and queen mating
... formation is irreversibly achieved during a single short mating flight. Males die almost immediately after mating (Hölldobler and Wilson, 1990; Starr, 1984) and only ‘‘survive’’ (sometimes for decades!) as sperm stored in a queen’s spermatheca (Hölldobler and Bartz, 1985; Pamilo, 1991). Even in so ...
... formation is irreversibly achieved during a single short mating flight. Males die almost immediately after mating (Hölldobler and Wilson, 1990; Starr, 1984) and only ‘‘survive’’ (sometimes for decades!) as sperm stored in a queen’s spermatheca (Hölldobler and Bartz, 1985; Pamilo, 1991). Even in so ...
Document
... This study provides evidence that fertilization of an egg clutch in sticklebacks is taking minutes rather than seconds (Fig. 1). This is exceptional if compared to fertilization durations of other teleost fishes [13,14] and contradicts the general assumption that fertilization is very fast in teleos ...
... This study provides evidence that fertilization of an egg clutch in sticklebacks is taking minutes rather than seconds (Fig. 1). This is exceptional if compared to fertilization durations of other teleost fishes [13,14] and contradicts the general assumption that fertilization is very fast in teleos ...
1 Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum Lesson title: In Vitro
... present in the woman's reproductive tract, the egg and the uterine lining are released as part of the menstrual cycle. But if fertilization does take place, the zygote, or fertilized egg, continues to move toward the uterus. There it may implant and develop into a fetus. In this case, menstruation ...
... present in the woman's reproductive tract, the egg and the uterine lining are released as part of the menstrual cycle. But if fertilization does take place, the zygote, or fertilized egg, continues to move toward the uterus. There it may implant and develop into a fetus. In this case, menstruation ...
1 Evolution of Viviparity in Salamanders
... distributed in Eurasia. Morphological patterns and life history traits are extremely variable in this species. The highest levels of variability are found in the Iberian Peninsula, where up to ten subspecies are currently recognized (Buckley and Alcobendas, 2002). Subspecies of S. salamandra have b ...
... distributed in Eurasia. Morphological patterns and life history traits are extremely variable in this species. The highest levels of variability are found in the Iberian Peninsula, where up to ten subspecies are currently recognized (Buckley and Alcobendas, 2002). Subspecies of S. salamandra have b ...
Treating Infertility
... called cysts on the ovaries, irregular menstrual periods, and an increase in the levels of certain hormones. Premature Ovarian Failure: A condition in which ovulation and the menstrual cycle stop before age 35 years. Progesterone: A female hormone that is produced in the ovaries and that prepares th ...
... called cysts on the ovaries, irregular menstrual periods, and an increase in the levels of certain hormones. Premature Ovarian Failure: A condition in which ovulation and the menstrual cycle stop before age 35 years. Progesterone: A female hormone that is produced in the ovaries and that prepares th ...
Amphibians!
... • Ovaries (in females) produce eggs • Testes (in males) produce sperm • The eggs are fertilized externally • From 19 to 30,000 eggs are laid by one female per breeding season ...
... • Ovaries (in females) produce eggs • Testes (in males) produce sperm • The eggs are fertilized externally • From 19 to 30,000 eggs are laid by one female per breeding season ...
Influence of Body Size and Population Density on
... in the laboratory for the presence of a fertilization membrane. The experiment was replicated ten times. In the second experiment, I investigated fertilization successof free-drifting eggs. Sperm and eggs were collected less than 1 h before experiments were conducted by injecting urchins with KC1 an ...
... in the laboratory for the presence of a fertilization membrane. The experiment was replicated ten times. In the second experiment, I investigated fertilization successof free-drifting eggs. Sperm and eggs were collected less than 1 h before experiments were conducted by injecting urchins with KC1 an ...
Answers Reproduction
... 1 Fertilisation in sexual reproduction happens when the the female sex cells (eggs or ova) are merges with the male sex cells (sperm). 2 Fertilisation may happen either externally or internally. With many acquatic animals, the sperm swims through the water to fertilise the egg (or ovum). This is c ...
... 1 Fertilisation in sexual reproduction happens when the the female sex cells (eggs or ova) are merges with the male sex cells (sperm). 2 Fertilisation may happen either externally or internally. With many acquatic animals, the sperm swims through the water to fertilise the egg (or ovum). This is c ...
Nat 4 Multicelular Organisms Homework
... 5. A female rabbit had 5 litters during one year; giving a total of 30 young. Of the young rabbits, 3 were still-born, 9 were eaten by predators and 6 died from disease. ...
... 5. A female rabbit had 5 litters during one year; giving a total of 30 young. Of the young rabbits, 3 were still-born, 9 were eaten by predators and 6 died from disease. ...
Mating behaviors of insects
... comparable for males and females (Jones 2006). Males and females have different strategies toward copulation and reproduction. Generally, males invest energy in locating mates and producing sperm; therefore they often search out and copulate with what appears to be any available and receptive female ...
... comparable for males and females (Jones 2006). Males and females have different strategies toward copulation and reproduction. Generally, males invest energy in locating mates and producing sperm; therefore they often search out and copulate with what appears to be any available and receptive female ...
Reproduction
... which the male then fertilizes. • Most things that produces eggs reproduce through sexual reproduction. ...
... which the male then fertilizes. • Most things that produces eggs reproduce through sexual reproduction. ...
Female modulation of reproductive rate and its role in postmating
... population origin of her mate (Fricke & Arnqvist 2004b). Here we ask whether the reproductive rate of females after mating is a decreasing function of decreased phylogenetic relatedness with their mates (Fricke & Arnqvist 2004a). One underlying assumption is that forms build co-adapted gene complexe ...
... population origin of her mate (Fricke & Arnqvist 2004b). Here we ask whether the reproductive rate of females after mating is a decreasing function of decreased phylogenetic relatedness with their mates (Fricke & Arnqvist 2004a). One underlying assumption is that forms build co-adapted gene complexe ...
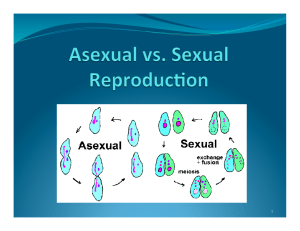
Asexual vs. Sexual Reproduction
... honeybees. In a hive, the sexually produced eggs become workers, while the asexually produced eggs become drones. Sexual Reproduction ...
... honeybees. In a hive, the sexually produced eggs become workers, while the asexually produced eggs become drones. Sexual Reproduction ...
Mating Systems in Sexual Animals | Learn Science at Scitable
... Although sperm competition is not a type of mating system per se, it is a form of male-male competition that plays an important role in mating systems. If more than one male mates with a female in a short time period, competition can occur after the males have released their sperm (Fisher & Hoekstra ...
... Although sperm competition is not a type of mating system per se, it is a form of male-male competition that plays an important role in mating systems. If more than one male mates with a female in a short time period, competition can occur after the males have released their sperm (Fisher & Hoekstra ...
Asexual vs. Sexual Reproduction
... gametes have one set of 23 chromosomes. Gametes are produced through a special type of cell division known as meiosis. 1. Fish and other aquatic animals release their gametes in the water, which is called external fertilization (Figure 1.3). These gametes will combine by chance. 2. Animals that live ...
... gametes have one set of 23 chromosomes. Gametes are produced through a special type of cell division known as meiosis. 1. Fish and other aquatic animals release their gametes in the water, which is called external fertilization (Figure 1.3). These gametes will combine by chance. 2. Animals that live ...
Asexual vs. Sexual Reproduction
... gametes have one set of 23 chromosomes. Gametes are produced through a special type of cell division known as meiosis. 1. Fish and other aquatic animals release their gametes in the water, which is called external fertilization (Figure 1.3). These gametes will combine by chance. 2. Animals that live ...
... gametes have one set of 23 chromosomes. Gametes are produced through a special type of cell division known as meiosis. 1. Fish and other aquatic animals release their gametes in the water, which is called external fertilization (Figure 1.3). These gametes will combine by chance. 2. Animals that live ...
Family Planning and Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART)
... • Frozen embryos that are left over after a couple using assisted reproduction has completed their family may be donated • In this case, the child will have no genetic link with either of its parents unless the embryos are donated by a relative ...
... • Frozen embryos that are left over after a couple using assisted reproduction has completed their family may be donated • In this case, the child will have no genetic link with either of its parents unless the embryos are donated by a relative ...
Trout Culture in the North Central Region
... used to estimate the average weight of the fish. In order for fish to survive and grow, water flow must be sufficient to keep oxygen levels high and to dilute and remove ammoWhen the yolk sac is almost entirely nia and other metabolic absorbed, the trout become swim-up products. The carrying cafry a ...
... used to estimate the average weight of the fish. In order for fish to survive and grow, water flow must be sufficient to keep oxygen levels high and to dilute and remove ammoWhen the yolk sac is almost entirely nia and other metabolic absorbed, the trout become swim-up products. The carrying cafry a ...
Plant Life Cycles
... Instead of producing sperm or egg directly, meiosis in plants in the diploid sporophyte stage produces spores. These are single cells which can be male or female and can divide. When these spores divide by mitosis, they make haploid gametophytes. It is the gametophytes that produce sperm or eggs. Sp ...
... Instead of producing sperm or egg directly, meiosis in plants in the diploid sporophyte stage produces spores. These are single cells which can be male or female and can divide. When these spores divide by mitosis, they make haploid gametophytes. It is the gametophytes that produce sperm or eggs. Sp ...
Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction
... The egg is fertilized by sperm outside the female The female lays the eggs and then the male fertilizes them. Fish and some amphibians Plants and fungi (pollen and spores) ...
... The egg is fertilized by sperm outside the female The female lays the eggs and then the male fertilizes them. Fish and some amphibians Plants and fungi (pollen and spores) ...
What is in vitro fertilisation (IVF) and how does it work?
... be fertilised. With more fertilised eggs, the clinic has a greater choice of embryos to use in your treatment. Step 3: checking on progress Throughout the drug treatment, the clinic will monitor your progress. This is done by vaginal ultrasound scans and, possibly, blood tests. 34–38 hours before yo ...
... be fertilised. With more fertilised eggs, the clinic has a greater choice of embryos to use in your treatment. Step 3: checking on progress Throughout the drug treatment, the clinic will monitor your progress. This is done by vaginal ultrasound scans and, possibly, blood tests. 34–38 hours before yo ...
117 Chicks come from eggs. What other things come
... in flowering and nonflowering plants. Students use terms such as gametophytes to describe ...
... in flowering and nonflowering plants. Students use terms such as gametophytes to describe ...
Spawn (biology)

Spawn is the eggs and sperm released or deposited, usually into water, by aquatic animals. As a verb, spawn refers to the process of releasing the eggs and sperm, also called spawning. Most aquatic animals, apart from aquatic mammals, reproduce through a process of spawning.Spawn consists of the reproductive cells (gametes) of aquatic animals, some of which will become fertilized and produce offspring. The process of spawning typically involves females releasing ova (unfertilized eggs) into the water, often in large quantities, while males simultaneously or sequentially release spermatozoa (milt) to fertilize the eggs.Most fish reproduce by spawning, and so do most other aquatic animals, including crustaceans such as crabs and shrimps, molluscs such as oysters and squid, echinoderms such as sea urchins and sea cucumbers, amphibians such as frogs and newts, other amphibious animals such as turtles, aquatic insects such as mayflies and mosquitoes, and corals (which are small aquatic animals and not plants). Fungi, such as mushrooms, are also said to ""spawn"" a white fibrous matter that forms the matrix from which they grow.There are many variations in the way spawning occurs, depending on sexual differences in anatomy, on how the sexes relate to each other, on where and how the spawn is released, and on whether or how the spawn is subsequently guarded.