15.1 Notes
... 2. Another type of body feature that suggests an evolutionary relationship is a vestigial structure—a body structure in a present-day organism that no longer serves its original purpose, but was probably useful to an ancestor. 3. A structure becomes vestigial when the species no longer needs the fe ...
... 2. Another type of body feature that suggests an evolutionary relationship is a vestigial structure—a body structure in a present-day organism that no longer serves its original purpose, but was probably useful to an ancestor. 3. A structure becomes vestigial when the species no longer needs the fe ...
Lecture 2 History and Evidence for Evolution
... process would necessarily improve the race, because in every generation the inferior would inevitably be killed off and the superior would remain – that is, the fittest would survive.” ...
... process would necessarily improve the race, because in every generation the inferior would inevitably be killed off and the superior would remain – that is, the fittest would survive.” ...
Historical Overview of Evolutionary Biology
... Founders of the Modern Synthesis Ronald A. Fisher: theoretical population geneticist; founder of modern statistics & experimental design J.B.S. Haldane: theoretical population geneticist; Haldane's rule of speciation Sewall Wright: theoretical population geneticist; believed that genetic drift was a ...
... Founders of the Modern Synthesis Ronald A. Fisher: theoretical population geneticist; founder of modern statistics & experimental design J.B.S. Haldane: theoretical population geneticist; Haldane's rule of speciation Sewall Wright: theoretical population geneticist; believed that genetic drift was a ...
Evolution by Natural Selection
... • He also noted that some of the differences were hereditary – passed on from one generation to the next. • Darwin had no knowledge, however, of the work of the Austrian monk Gregor Mendel that would become the foundation for modern genetics. • Darwin also realized the role of environmental pressure ...
... • He also noted that some of the differences were hereditary – passed on from one generation to the next. • Darwin had no knowledge, however, of the work of the Austrian monk Gregor Mendel that would become the foundation for modern genetics. • Darwin also realized the role of environmental pressure ...
What is Science?
... 1] Identify patterns in the diversity of life, especially puzzling ones, that appear to be problematic for the theory. 2] Hypothesize processes or forces that might be creating those patterns. They provide an explanation for the pattern in terms of one or more of the five evolutionary processes. 3] ...
... 1] Identify patterns in the diversity of life, especially puzzling ones, that appear to be problematic for the theory. 2] Hypothesize processes or forces that might be creating those patterns. They provide an explanation for the pattern in terms of one or more of the five evolutionary processes. 3] ...
Name Date Ch 19 reading guide – Biology in Focus (Adapted from
... organisms and the unity and diversity of life. 4. What are adaptations? Give two examples. ...
... organisms and the unity and diversity of life. 4. What are adaptations? Give two examples. ...
AP Biology 2011 Christmas Break Assignment
... prepared for a test over this material the first week we return to school. A. Reading Guide Questions: As you study this chapter, read several paragraphs at a time to catch the flow of ideas and understand the reasoning that is being described. In some places, the text describes a narrative or story ...
... prepared for a test over this material the first week we return to school. A. Reading Guide Questions: As you study this chapter, read several paragraphs at a time to catch the flow of ideas and understand the reasoning that is being described. In some places, the text describes a narrative or story ...
Natural Selection - SBI3U
... • Darwin observed that a key factor in the survival of an organism was how well it was suited for the environment. • The environment selected those individuals with variations that were best suited for that environment. • E.g. Darwin would’ve said that in a population, the environment favored the in ...
... • Darwin observed that a key factor in the survival of an organism was how well it was suited for the environment. • The environment selected those individuals with variations that were best suited for that environment. • E.g. Darwin would’ve said that in a population, the environment favored the in ...
Charles Darwin and Evolution
... • a. If Earth could change over time, couldn’t living things????? • b. IF Earth were old (like they are saying) it would give time for organisms to change!! ...
... • a. If Earth could change over time, couldn’t living things????? • b. IF Earth were old (like they are saying) it would give time for organisms to change!! ...
Mutation The primary source of variation for all life forms.
... 8. The approximate number of different species on our planet. 10. A structure that use to have a purpose in the past environment but doesn’t serve a purpose any longer. 13. The 2 processes stated above are always at work creating this in all life forms. 17. The number of genes that have been preserv ...
... 8. The approximate number of different species on our planet. 10. A structure that use to have a purpose in the past environment but doesn’t serve a purpose any longer. 13. The 2 processes stated above are always at work creating this in all life forms. 17. The number of genes that have been preserv ...
Name: Period: ______ Date: Natural Selection – Lab Replacement
... _____ 5. one of the first scientists to propose that species change over time _____ 6. ship on which Darwin served as naturalist _____ 7. his theory of evolution unifies all of biology _____ 8. the process by which evolution occurs _____ 9. argued that human populations grow faster than the resources ...
... _____ 5. one of the first scientists to propose that species change over time _____ 6. ship on which Darwin served as naturalist _____ 7. his theory of evolution unifies all of biology _____ 8. the process by which evolution occurs _____ 9. argued that human populations grow faster than the resources ...
Chapter 15 Darwin*s Theory of Evolution
... One of the first scientists to recognize that living things have changed over time Species were descended from other species Also realized that organisms had adapted to their environment By selective use or disuse of ...
... One of the first scientists to recognize that living things have changed over time Species were descended from other species Also realized that organisms had adapted to their environment By selective use or disuse of ...
INTRODUCTION - Penn State York
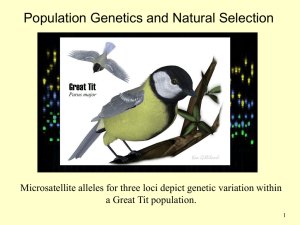
... Microsatellite alleles for three loci depict genetic variation within a Great Tit population. ...
... Microsatellite alleles for three loci depict genetic variation within a Great Tit population. ...
File
... *Describe the scientific explanations for the origin of life on Earth *Explain how the scientific theory of evolution is supported by fossil record, comparative anatomy, embryology, biogeography, molecular biology (changes in genetic make-up), and observed evolution (observations in nature) -Student ...
... *Describe the scientific explanations for the origin of life on Earth *Explain how the scientific theory of evolution is supported by fossil record, comparative anatomy, embryology, biogeography, molecular biology (changes in genetic make-up), and observed evolution (observations in nature) -Student ...
powerpoint here!
... ancestor and then, due to isolation and through chance, different climates and natural forces such as food availability and type, they evolved into thirteen different types of finches. The process of their evolution would probably have begun with immigrants from the mainland. As they dispersed to di ...
... ancestor and then, due to isolation and through chance, different climates and natural forces such as food availability and type, they evolved into thirteen different types of finches. The process of their evolution would probably have begun with immigrants from the mainland. As they dispersed to di ...
Synthesis
... paleontological evidence in this book (1944). • He used fossils to estimate the rate of evolutionary change, and compared these rates to those that had been observed in nature by people like Dobzhansky. • Change proceeded at varying rates in the fossil record, from quite quickly to very slowly. • Si ...
... paleontological evidence in this book (1944). • He used fossils to estimate the rate of evolutionary change, and compared these rates to those that had been observed in nature by people like Dobzhansky. • Change proceeded at varying rates in the fossil record, from quite quickly to very slowly. • Si ...
FJC Study Guide Quiz 2 Handout Page
... Who was Charles Darwin & what are his contributions to the study of evolution & natural selection? In 1831 Darwin sailed on the HMS Beagle. What was his job, what was the ship’s mission, what famous island did he visit & study? What are endemic species? Darwin noticed that plants/animals on the Gala ...
... Who was Charles Darwin & what are his contributions to the study of evolution & natural selection? In 1831 Darwin sailed on the HMS Beagle. What was his job, what was the ship’s mission, what famous island did he visit & study? What are endemic species? Darwin noticed that plants/animals on the Gala ...
Changes Over Time
... trip, Darwin continued to think about his trip and he continued to consult with other scientists about his ideas • Darwin thought the species gradually changed over many generations and became better adapted to the new conditions • He called this gradual change The Theory of Evolution • He knew that ...
... trip, Darwin continued to think about his trip and he continued to consult with other scientists about his ideas • Darwin thought the species gradually changed over many generations and became better adapted to the new conditions • He called this gradual change The Theory of Evolution • He knew that ...
Unit IV – Evolution, Change, and Diversity (15% of Public Exam)
... behavior (nocturnal, arboreal) that helps an organism survive and reproduce in a particular environment. ...
... behavior (nocturnal, arboreal) that helps an organism survive and reproduce in a particular environment. ...
The Struggle For Existence - in a secure place with other
... The Struggle For Existence The Revolutionary idea of Evolution in determining species diversification ...
... The Struggle For Existence The Revolutionary idea of Evolution in determining species diversification ...
Document
... - A mutation occurs when a DNA gene is damaged or changed in such a way as to alter the genetic message carried by that gene. ...
... - A mutation occurs when a DNA gene is damaged or changed in such a way as to alter the genetic message carried by that gene. ...
Evolution

Evolution is change in the heritable traits of biological populations over successive generations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including the levels of species, individual organisms, and molecules.All of life on earth shares a common ancestor known as the last universal ancestor, which lived approximately 3.5–3.8 billion years ago. Repeated formation of new species (speciation), change within species (anagenesis), and loss of species (extinction) throughout the evolutionary history of life on Earth are demonstrated by shared sets of morphological and biochemical traits, including shared DNA sequences. These shared traits are more similar among species that share a more recent common ancestor, and can be used to reconstruct a biological ""tree of life"" based on evolutionary relationships (phylogenetics), using both existing species and fossils. The fossil record includes a progression from early biogenic graphite, to microbial mat fossils, to fossilized multicellular organisms. Existing patterns of biodiversity have been shaped both by speciation and by extinction. More than 99 percent of all species that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates of Earth's current species range from 10 to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented.In the mid-19th century, Charles Darwin formulated the scientific theory of evolution by natural selection, published in his book On the Origin of Species (1859). Evolution by natural selection is a process demonstrated by the observation that more offspring are produced than can possibly survive, along with three facts about populations: 1) traits vary among individuals with respect to morphology, physiology, and behaviour (phenotypic variation), 2) different traits confer different rates of survival and reproduction (differential fitness), and 3) traits can be passed from generation to generation (heritability of fitness). Thus, in successive generations members of a population are replaced by progeny of parents better adapted to survive and reproduce in the biophysical environment in which natural selection takes place. This teleonomy is the quality whereby the process of natural selection creates and preserves traits that are seemingly fitted for the functional roles they perform. Natural selection is the only known cause of adaptation but not the only known cause of evolution. Other, nonadaptive causes of microevolution include mutation and genetic drift.In the early 20th century the modern evolutionary synthesis integrated classical genetics with Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection through the discipline of population genetics. The importance of natural selection as a cause of evolution was accepted into other branches of biology. Moreover, previously held notions about evolution, such as orthogenesis, evolutionism, and other beliefs about innate ""progress"" within the largest-scale trends in evolution, became obsolete scientific theories. Scientists continue to study various aspects of evolutionary biology by forming and testing hypotheses, constructing mathematical models of theoretical biology and biological theories, using observational data, and performing experiments in both the field and the laboratory. Evolution is a cornerstone of modern science, accepted as one of the most reliably established of all facts and theories of science, based on evidence not just from the biological sciences but also from anthropology, psychology, astrophysics, chemistry, geology, physics, mathematics, and other scientific disciplines, as well as behavioral and social sciences. Understanding of evolution has made significant contributions to humanity, including the prevention and treatment of human disease, new agricultural products, industrial innovations, a subfield of computer science, and rapid advances in life sciences. Discoveries in evolutionary biology have made a significant impact not just in the traditional branches of biology but also in other academic disciplines (e.g., biological anthropology and evolutionary psychology) and in society at large.