* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Polygons - My CCSD
Survey
Document related concepts
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Surface (topology) wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Steinitz's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Shapley–Folkman lemma wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Regular polytope wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
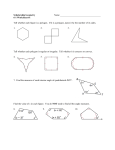
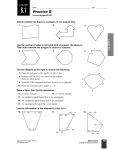
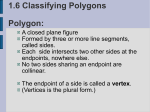
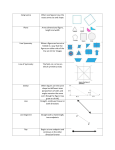
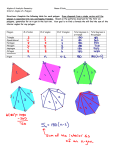
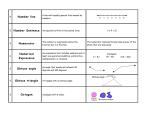
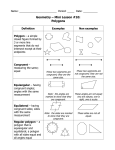
6.1 Polygons Objectives: (1) The student will be able to identify, name, and describe polygons. (2) The student will be able to find the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a quadrilateral. Toolbox: Summary: Polygon – is a plane figure that is formed By 3 or more segments (sides) such that No 2 sides with a common endpoint are Collinear and each side intersects exactly 2 other sides one at each endpoint (vertex) Naming Polygons – by their sides Number of Sides Type of Polygon 3 Triangle 4 Quadrilateral 5 Pentagon 6 Hexagon 7 Heptagon 8 Octagon 9 Nonagon 10 Decagon 12 Dodecagon n n-gon Convex – if no line that contains a side of the polygon contains a point in the interior of the polygon (diagonal cannot be in the exterior of the polygon) Concave – a polygon that is not convex Equilateral – all sides congruent Equiangular – all angles congruent Regular – if it is both equilateral & equiangular! Diagonal – of a polygon is a segment that joins 2 nonconsecutive vertices Interior Angles of a Quadrilateral The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a quadrilateral is 360°. Examples: ~ See extra examples notes #1-3 4. Find m<F, m<G, and m<H. 5. Find m<K, m<L, & m<M. Is quadrilateral JKLM regular? Q: What is true of all points except the endpoints on a diagonal of a convex polygon? Q: What word describes a regular polygon by its side lengths? By its angle measures? Q: Describe how the sides of a polygon intersect. Hmwk: #12-30(E) omit #22, 31-35, 37-47 omit #40 Something to think about: A polygon has at least a pair each of supplementary angles and complementary angles. Can it be a quadrilateral? Explain or give an example.