* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Math 2 Geometry Based on Elementary Geometry, 3rd ed, by
Rotation formalisms in three dimensions wikipedia , lookup
Surface (topology) wikipedia , lookup
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Steinitz's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Shapley–Folkman lemma wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Regular polytope wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Area of a circle wikipedia , lookup
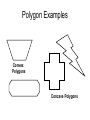
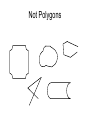
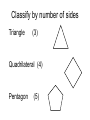
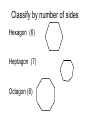
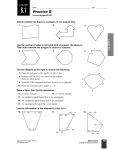
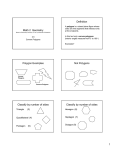
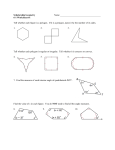
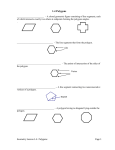
Math 2 Geometry Based on Elementary Geometry, 3rd ed, by Alexander & Koeberlein 2.5 Convex Polygons Definition A polygon is a closed plane figure whose sides are line segments that intersect only at the endpoints. In this text only: convex polygons (interior angles measure from 0 to 180) Examples? Polygon Examples Convex Polygons Concave Polygons Not Polygons Classify by number of sides Triangle (3) Quadrilateral (4) Pentagon (5) Classify by number of sides Hexagon (6) Heptagon (7) Octagon (8) Classify by number of sides Nonagon (9) Decagon (10) Informal Definition A diagonal of a polygon is a line segment that joins two nonconsecutive vertices. B A C E D Theorem 2.5.1 The total number of diagonals D in a polygon of n sides is given by the formula: n (n 3) D 2 Use the formula to find the number of diagonals of: • a triangle • a quadrilateral • a pentagon n (n 3) D 2 Theorem 2.5.2 The sum S of the measures of the interior angles of a polygon with n sides is given by: S = (n – 2) 180 • Informal Definitions • Equiangular polygon: All angles are congruent. • Equilateral polygon: The measure of all sides are equal. Definition A regular polygon is a polygon that is both equilateral and equiangular. Notice: A square is a regular quadrilateral. Not Regular Polygons Notice it is possible for Polygons to be either equilateral or equiangular but not both. Rhombus Rectangle Corollary 2.5.3 The measure I of each interior angle of a regular polygon of n sides is: (n 2) 180 I n Corollary 2.5.4 The sum of the four interior angles of a quadrilateral is 360 Corollary 2.5.5 The sum of the measures of the exterior angles of a polygon, one at each vertex, is 360. Corollary 2.5.6 The measure E of each exterior angle of a regular polygon of n sides is: 360 E n Informal Definition A polygram is the star-shaped figure that results when the sides of certain polygons are extended. Pentagram Hexagram