* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Black-Footed Ferret Bottleneck Scenario
Survey
Document related concepts
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
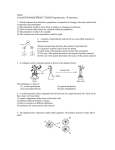
Black-Footed Ferret Bottleneck Scenario Names of Team Members: Hypothesis: If I observe the black-footed ferret population for one year, then they will adapt and survive. Materials: Buttons and M&M’s Procedures: 1. Received a few genes out of the gene pool. 2. Designated the genes received. 3. Data/Observations: Key to Genetic Characteristics Yellow Black Orange Pink Dark blue Green Purple Red White Camouflage Precise Vision Accurate sense of smell Strong claws and forearms Healthy jaw formation Agility Acute hearing Healthy rate of reproduction Immunity to canine distemper On your Key to Genetic Characteristics, Highlight the COLORS and GENES that your population received through the bottleneck. Analysis: 1. Calculate the percentage of genetic diversity (heterozygosity) of your population. Nine genes (colors) represent 100 percent genetic diversity in the original population. _4_ genes received / 9 original genes = __.4__(decimal) x 100= __40__% 2. List the genetic characteristics (colors) that your population received through the bottleneck. Red Black Yellow White 3. List the genetic characteristics that your population lost when it came through the bottleneck. (colors not received) 4. Using the five environmental situations, write a prediction about what will happen to your population during the coming year. 7. I believe that the population will die down to very few and slowly reproduce itself. The population is equipped to rebuild itself with a healthy rate of reproduction, good eyesight, and great at hiding. A low diversity level lowers the chances of reproduction. Changes such as weather can affect the population. 10. Our population is well equipped to be able to go out at night because we have a camouflage gene that makes it easier to hide from predators. A low diversity level lowers the chances of reproduction. If the moon was shining bright then predators can see them better. 2. Our population has the gene of great eyesight, which will help increase the chances of survival. A low diversity level lowers the chances of reproduction. Multiple hawks could affect the chances of survival. 11. Our population doesn’t have an acute hearing gene, which will increase the chance of being attacked. A low diversity level lowers the chances of reproduction. Multiple badgers can affect the chances of survival. 9. Our population doesn’t have the necessary gene to catch a prairie dog and take its home for shelter. A low diversity level lowers the chances of reproduction. If there aren’t enough homes to try and take. Is the population genetically equipped to survive in its environment? How well or how poorly? How does a high or low percentage of genetic diversity affect the population’s survival? How do random changes in the environment affect the population? Conclusion: The genes that we had such as camouflage, great eyesight, high health rate of reproduction, and immunities to canine dysfunction can overall help survival. But the canine dysfunction will definitely affect the chances of survival. Our hypothesis was true. Extension: Research a threatened species found in our area. You can determine whether genetic diversity within the species had an effect on its depletion. You should also examine whether the species was placed on the threatened list because of degradation or loss of habitat. Check your conclusions with the state’s natural resources agency or a local office of the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. Species: The Grizzly Bear Reason for decline in population: Hunting and Poaching Check your conclusion: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Grizzly_bear Honors Class: Discuss the impact of dominant versus recessive traits. Recessive traits have a much lower probability of becoming evident in the population unless the population becomes small enough to interbreed and bring forth those recessive traits, or unless that trait makes the animal better able to survive in its environment. Repeat the activity using two colors for each genetic characteristic (to represent dominant and recessive traits). For instance, dark blue beads could represent healthy jaw formation and light blue beads could represent a jaw malformation or deformity. Also use separate containers for each characteristic, and have students pick two beads form each of those containers. If the group receives only recessive color beads for a characteristic, then the recessive trait will be expressed. If the group receives only dominant color beads or if it receives a mix of dominant and recessive color beads for that characteristic, then the dominant trait will be expressed. (If the color selection of beads is limited, another token, such as colored paper squares, may be used.) Dark yellow Green Fire Orange Hot Pink Blue Lime Green Dark purple Light Red Gray 5. white patch color blind can only smell tree bark weak cavities hurt ankle deaf poor rate of reproduction canine distemper