* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
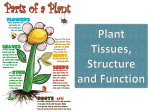
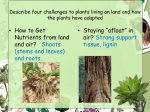
Name _______________________ due date _______ CHAPTER 3-2 TEST SHORT ANSWER 1. In what two ways is vascular tissue important to a plant? Vascular tissue enables a plant to efficiently transport water and food to all its cells and supports plants so they can grow large. (key words: structure/support- transportxylem/phloem- get more sunlight) 2. Explain how root like rhizoids differ from true roots. Root-like rhizoids are different from true roots because they lack vascular tissue. Although, both bring up water and nutrients and provide some support for the plant, vascular tissue allows roots to grow deeper and stronger thus obtaining more water and nutrients that in turn allow the plant grow much larger. 3. What are the five adaptations that plants need to survive on land? A. RHIZOIDS OR ROOTS TO ABSORB MOISTURE B. CUTICLES – HELP PREVENT DRYING OUT AND GUARD AGAINST WIDE AND ABRUPT TEMPERATURE CHANGES C. STOMATA - ALLOWS FOR GAS EXCHANGE AND REGULATES WATER LOSS D. STRUCTURES TO TRANSPORT SPERM, THROUGH AIR (WIND), OF BY ANIMALS- SPORES E. VASCULAR TISSUE – WHICH ALLOW PLANTS TO TRANSPORT MATERIAL OVER GREATER DISTANCES 4. What are the four differences between monocots and dicots. Monocotsa. 1 seed leaf or 1 cotyledon b. Parallel veins a. Scattered vascular tissue b. Parts in 3’s Dicotsa. 2 seed leaves or 2 cotyledons b. Branching veins c. Vascular tissue in bundles in a circular pattern d. Parts in 4’s and 5’s 5. What are the roles of phloem and xylem in the stem? Include a definition of each in your answer. The role of phloem and xylem is to transport food, water, and nutrients throughout the plant. Xylem- the vascular tissue that moves water and nutrients from the roots to the leaves Phloem- the vascular tissue that moves food moves throughout the plant from the leaves to the roots 6. What is a tropism? Name, define and give an example of the threes main types. Tropism- a plant’s growth in response toward or away from a stimulus Thigmotropism- Plants response to touch- vines, Venus fly trap Phototropism- Plants response to light, sunflowers, morning glories Gravitropism- Plants response to gravity- roots grow down, plant grows up 7. What are two main differences between angiosperms and gymnosperms? AngiospermsGymnospermsc. have flowers and fruit a. have cones d. seeds protected in fruit b. seeds not protected (naked seeds) 8. Draw and Label the parts of the flower.