* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name - dublin.k12.ca.us
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Indigenous horticulture wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Cultivated plant taxonomy wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Hydroponics wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Embryophyte wikipedia , lookup
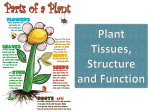
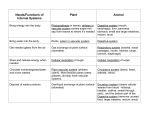
Name: Science Outline for Pages 190-199 Transporting Materials In Plants First we must revisit pages 184 and 185 to make sure we understand how plants rid themselves of waste, then, in the next lesson, we will see how this “waste” can move through certain plants. Recall what transpiration means, and define it here ________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________. Waste in plants is made from cellular activity (more on this in two lessons). In most plants, this waste is first stored in an organelle called the ________________________. It is then transported up a plant to the leaves, and released through tiny holes in the leaves called ______________________. Remember, a lot of the “waste” produced by plants is the goodies animals need to survive. What are these goodies? Okay, on to lesson 5 of this unit, and learning more about the amazing, miraculous plant world. First, use the space below to draw a picture of a plant. Make it a bush, tree, or flowering plant, and label the three main parts of all these types of (vascular) plants. Leave a bit of space to come back and add a few things after we finish this lesson. If you have time, make it pretty. BE SURE TO READ THESE TWO PAGES FIRST, THEN FILL IN BLANKS Nonvascular plants lack true ___________________, __________________, and ______________________. These types of plants, which include _______________, absorb water and nutrients from their surroundings. The water carries everything from cell to cell directly, and this limits how ___________ these types of plants can grow. Vascular plants, like trees, contain _________________ _____________________, which supports a plant and transports ________________ and __________________ throughout the plant. There are two types of vascular tissue. They are ____________ and ________________. ____________________ carries water and nutrients from the roots up to other parts of the plant. The “x” in xylem sounds like a “z” and so the word sounds like zylem. Using this, “zy-” rhymes with high, and the xylem brings goodies up or high in the plant. _________________________ carries food made in the leaves to other parts of the plant. The “ph-” in phloem makes the “f” sound and so the word sounds like “flowem”. Low rhymes with flow and these vascular tissue transport food down, or low, the plant. This is just a way to remember which way these vascular ___________ transport materials in a plant. All three main parts of a plant contain these tissues. True or False. Xylem and phloem tissue are found in nonvascular plants. Roots and root hairs __________________ water and nutrients from the _______. _______________ cells take these goodies up and into the stem. A _________________ pushes deep into the soil, and may store food for a plant. It also ________________ the plant to the ground to survive. ____________________ roots are more thin and spread out just below the surface of the soil. These roots form a mat which can ___________ soil in place and absorb water from a large area. The xylem and phloem tissues in roots ___________________ with these same tissue in the stems. This forms a sort of ___________________________ in the plant to allow the transport of needed materials. In trees, vascular tissue is gathered in ______________. You may have seen this pattern in a tree that has been cut. Stems also provide _________________________ for a plant, so it can grow high and bring the leaves closer to our energy source, the sun. Leaves of plant are the makers of food. They contain organelles called _________________________, which contain a green pigment that _________________ light energy. Leaves use __________________ _____________________, __________________, and _________________ to make sugar. _______________, like found in the human circulatory system, transports the sugar from the leaves to each cell in the plant. They then connect to the vascular tissue called phloem, and is now in the tree’s pipeline or transport system.




















![activity_19 (intro to the vascular plants) [Converted]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/004335628_1-4eb5ba8c060e49f205a91e995f3654d2-150x150.png)

