* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Module 2
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Child Lying wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
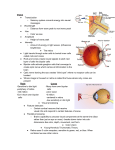
Normal Physiology Specialty 7.12010001 "General Medicine" 2 Year of study Module 4. Analyzers. Higher integrative functions 1. Where basically molecules of a pigment in cones contain? A. On bazilar membranes B. On mytochondria C. On mycrofilaments D. On sarcoplasmatic reticulum E. In membranes of disks ANSWER: E 2. Where basically molecules of a pigment in rodes contain? A. On mytochondria B. In membranes of disks C. On mycrofilaments D. On sarcoplasmatic reticulum E. On chromosoms ANSWER: B 3. What neurons of the retina give origin to the optic nerve? A. All listed B. Horizontal C. Bipolar D. Amacrinic E. Ganglose ANSWER: E 4. What connections take part in transfer of excitation in visual receptors? A. Calmoduline B. Retinal C. Opsin D. All listed E. Calcium ANSWER: D 5. How the amplitude of hyperpolarization in an eye changes at increase in its illumination? A. First decreases, and then is restored B. Does not change C. Decreases D. First decreases, and then increases E. Increases ANSWER: E 6. What color is jodopsin sensitive to? A. Red B. Green C. Blue D. Yellow E. White ANSWER: C 7. What color chlorolab is sensitive to? A. Blue B. Green C. Red D. Yellow E. White ANSWER: A 8. What color erhythrolab is sensitive to? A. Red B. Green C. Blue D. Yellow E. White ANSWER: A 9. What is the visual acuity? A. The maximal ability of an eye to perceive separate objects B. The maximal ability of an eye to perceive space C. The maximal ability of an eye to perceive depth of space D. The maximal ability of an eye to estimate distance E. The maximal ability of an eye to perceive color ANSWER: A 10. When the maximal visual acuity will be observed? A. At hit of light rays on the fovea centralis B. At hit of light rays on rods C. At hit of light rays on blind spot D. At hit of light rays in lateral pole E. At hit of light rays on cornea ANSWER: A 11. What provides binocular vision? A. Exact perception of depth of space B. Perception of colors C. Perception of light only D. Perception of separate objects E. Exact perception of infrared waves ANSWER: A 12. At what conditions expansion of a pupil is observed? A. A pain B. Strengthening of attention C. Fear D. A rage E. All listed ANSWER: E 13. What color for a field of vision the least? A. Yellow B. Blue C. White D. Green E. Red ANSWER: D 14. For what color the field of vision is the widest? A. Green B. Blue C. White D. Yellow E. Red ANSWER: C 15. Where photoreceptors are located? A. A cornea B. A retina C. Iris D. A crystalline lens E. Vitreous a body ANSWER: B 16. Electroretinogram is a total electric potential which is allocated from: A. Retina B. Rods C. Cones D. The Optic nerve E. Iris ANSWER: A 17. What types of neurons are there in a retina? A. Bipolar B. Horizontal C. All listed D. Amacrinic E. Ganglose ANSWER: C 18. What structures of a brain are the primary centers of spatial orientation? A. A cortex B. Apper hillocs of quadrigeminal body C. Cranked bodies D. Thalamus E. Lateral hillocs of quadrigeminal body ANSWER: B 19. What primary colours are according to the theory of oponent colors? A. Green, pink, black, white B. Green, red, yellow, white C. Green, red, violet, dark blue D. Green, red, yellow, dark blue E. Black, white, yellow, brown ANSWER: В 20. What primary colours according to theory by Helmholts? A. Green, red, violet B. Green, red, black C. Green, red, blue D. Green, red, yellow E. Green, red, white ANSWER: С 21. What colors are recognized by the international convention as the main things (primary)? A. Green, red, white B. Green, red, violet C. Green, red, black D. Green, red, yellow E. Green, red, blue ANSWER: E 22. How refer to a condition when the person does not perceive red color? A. Protanopy B. Dateranopy C. Tritanopy D. Prothanomalia E. Dischromatopsia ANSWER: A 23. How the condition when the person does not perceive green color refers to? A. Tritanopy B. Dateranopy C. Prothanopia D. Dateranomalia E. Dischromatopsia ANSWER: B 24. How refer to a condition when the person does not perceive dark blue color? A. Prothanopia B. Dateranopy C. Tritanopy D. Trichanomaliaa E. Dischromatopsia ANSWER: C 25. What importance has pupilary reflex? A. A. Raises an acuteness of peripheral sight B. B. Raises depth of the central sight C. Reduces astigmatism D. D. The field of vision expands E. Protective ANSWER: E 26. What functions are carried out with a aqueous humor in the eyeball? A. All listed B. Improvement of optical properties of a cornea C. Protection of a cornea and conjunctive from drying D. Condfuction of sound E. Removal of alien bodies ANSWER: B 27. What does not belong to the optical system of the eye? A. A cornea B. Pupil of the eye C. A crystalline lens D. Vitreous a body E. Aqueous fluid of the anterior chamber of an eye ANSWER: B 28. What is the reduced eye? A. All mediums have the same parameter of refraction and a uniform spherical surface B. Emetropic an eye of the person C. One of environments is under a corner to light which passes in other environment D. An eye of the person at a far-sightedness E. An eye of the person at short-sightedness ANSWER: A 29. What image is formed on a retina? A. Reduced, direct, present B. Reduced, turned, real C. Usual, turned, the present D. Reduced, turned, deformed E. Usual, direct, present ANSWER: B 30. What structures of an eye absorb infra-red light rays? A. Aqueous humor of the anterior chamber, a crystalline lens B. A cornea C. A crystalline lens D. Vitreous a body E. Vessels of the forward chamber of an eye ANSWER: A 31. Otholith membrane in utricle is located: A. In a face-to-face plane B. Horizontally C. Under a sharp corner D. Vertically E. In saggital plane ANSWER: D 32. Receptors of utricle perceive: A. The beginning and the terminations of horizontal movements B. The beginning and the terminations of vertical movements C. The beginning and the terminations of rotary movements D. Movement in a horizontal plane E. Movement in a vertical plane ANSWER: A 33. Receptors of saccule perceive: A. The beginning and the terminations of horizontal movements B. The beginning and the terminations of vertical movements C. The beginning and the terminations of rotary movements D. Movement in a horizontal plane E. Movement in a vertical plane ANSWER: B 34. Otholith membranes supervise change of position of a head: A. Any changes of position of a head B. Inclinations of a head forward C. Inclinations of a head back D. Inclinations of a head to the right E. Inclinations of a head to the left ANSWER: A 35. Adequate stimulus for receptors semicircular channels is: A. Changes of angular acceleration B. Changes of rectilinear acceleration C. Inclinations of a head "forward-back" D. Inclinations of a head "to the right-to the left" E. Rectilinear acceleration ANSWER: A 36. The centers of vestibular nerves are located: A. In the brain medulla B. In a spinal cord C. In a cerebellum D. In a cortex of a brain E. In an intermediate brain ANSWER: A 37. Quick reflexes at intensive irritation of receptors of the vestibular apparatus are caused by that nervous fibres, which send impulses to: A. alfa-and gama-motorneurons of muscles extensors B. Thalamus C. Hypothalamus D. Eyemotor nerves E. A temporal cortex of a brain ANSWER: A 38. Nystagmus of the eye is supported by that: A. Nervous fibres of the vestibular analyzer contact with thalamus B. Fibres of a vestibular nerve contact to kernels of a wandering nerve C. Nervous fibres of the vestibular analyzer contact with hypothalamus D. Nervous fibres of the vestibular analyzer contact to centers of oculomotor a nerve E. Nervous fibres of the vestibular analyzer contact with neurones of cortexs of a brain ANSWER: D 39. The quick reflexes directed on supporting of a pose, is supported with: A. Contact neurons a vestibular nerve with the impellent centers of a spinal cord and a cerebellum B. Contact neurons a vestibular nerve with the autonomic centers of a spinal cord and a trunk of a brain C. Contact a vestibular of neurons to the motor centers of brain stem and cerebellum D. Contact neurons a vestibular nerve with the impellent centers basal ganglia and a cortex of a brain; E. Contact neurons a vestibular nerve with the impellent centers of a cerebellum and basal ganglia ANSWER: C 40. The central division of the vestibular analyzer is: A. In occipital shares of a cortex of a brain B. In precentral gyrus C. In temporal shares of a cortex of a brain D. In postcentral gyrus E. In spinal ganglia ANSWER: D 41. Receptors of an acoustic analyzer belong to: A. Secondary sensory cells B. Primary sensory cells C. Proprioreceptors D. Interoreceptors E. Exteroreceptors ANSWER: A 42. Hair cells of an acoustic analyzer are contained in: A. Cochlea of an internal ear on the basic membrane B. To a cochlea of an internal ear of a vestibular membrane C. In saccule on otholith membrane D. In utricle shipped in cupul E. On the tympanic cavity ANSWER: A 43. Length of fibres of the basic membrane of a cochlea of an internal ear: A. Identical on all extent B. From a basis decreases to its top C. From a basis increases to its top D. From top increases to base A. Increases to the middle of distance, and later decreases ANSWER: C 44. Space of an middle scale is filled: A. With endolymph B. With perilymph C. Air D. Jell substance E. Bones ANSWER: A 45. The space of the apper and lower scale is filled with: A. With endolymph B. Perilymph C. Air D. Jell substance E. Bones ANSWER: B 46. System of ossicles in middle ear: A. Strengthens fluctuation of a sound wave, but reduces amplitude B. Reduces fluctuation of a wave length, but reduces amplitude C. Reduces fluctuation of a sound wave, but reduces amplitude A. Strengthens fluctuation of sound waves and strengthens amplitude B. Does not change parameters of fluctuations of a sound wave ANSWER: A 47. Fluctuation of a membrane of an oval aperture is transferred to: A. Perilymph vestibular scale and through vestibular a membrane - endolymph B. Endolymph vestibular scale and through vestibular a membrane - endolymph C. Endolymph vestibular scale and through the basic membrane - endolymph D. Endolymph vestibular scale and through an integumentary membrane endolymph E. Perilymph vestibular scale and through tectorial a membrane - endolymph ANSWER: A 48. Receptor hair cells in cochlea are placed A. On tectorial membrane B. On a vestibular membrane C. On the basilar membrane D. In saccule E. In utricle ANSWER: C 49. Excitation of hair cells in organ of Corti occurs due to: A. Movements epithelial the cells caused by movement endolymph B. Deformations of hair caused by fluctuation of an in tegumentary membrane C. Deformations of hair caused by fluctuation of the basilar membrane D. Movements of hair cells caused by movement perilymph E. Deformation fibrocytes caused by movement of a vestibular membrane ANSWER: C 50. Long action of a loud sound leads to protective reaction. Its mechanism: A. Contraction of m.tensor tympany and m.stapedius which change fluctuation auditory ossicles B. A relaxation m.tensor tympany and m.stapedius which change fluctuation auditory ossicles C. A relaxation m.tensor tympany and m.stapedius which cease to influence fluctuation auditory ossicles D. A pressure m.sphyncter tympany and m.stapedius which reduce the area of an eardrum E. Change of the order of connection auditory ossicles ANSWER: A 51. Fibers from ventral nucleus of cochlear nerve go: A. To olivar complexes B. To collateral complexes only C. To reticular complexes D. To medial complexes E. To dorsal nuclei ANSWER: A 52. The pain which arises in an organism of the person subordinates its consciousness, fills all ideas, lifts the important functions of an organism. It operates by a principle A. Dominants B. Temporary summation in CNS; C. From time excitation hypothalamo-hypophisial system D. Time excitation CNS and oppression sympathetic system E. Constant oppression hypothalamo-hypophisial system ANSWER: A 53. According to modern representations of sensation of a pain classify in a place of occurrence. What pain thus distinguish? A. Somatic and visceral, superficial and deep B. Somatic and visceral, skin and hypodermic C. Superficial and deep, cellular and tissue D. External and internal, ventral and dorsal; E. Distal and proximal, natural and artificial ANSWER: A 54. How to classify the pain which arises in a site of a leather? A. deep B. visceral C. superficial D. external E. distal ANSWER: C 55. What kind of a pain can be head and a toothache? A. proximal B. deep C. superficial D. external E. distal ANSWER: B 56. How to concern, to what kind of a pain which arise at disease of heart and are localized in the left hand? A. distal B. superficial C. early D. external E. reflex ANSWER: E 57. What name have a site of a leather especially sensitive to a pain which appear in parallel with disease of this or that body? A. Zones of the raised skin sensitivity B. . Zones hypoesthesia C. From a zone hypoalgesia D. Zones hypodinamia E. Zones hyperdinamia ANSWER: A 58. Original unpleasant sensation at irritation of the certain painful receptors is itch. Where placed such painful receptors? A. Under epidermis B. In a muscular fabric C. In a connecting fabric D. In muscular and connecting fabrics E. Near internal bodies ANSWER: A 59. At irritation of painful receptors which are placed under epidermis the certain chemical compounds, there are unpleasant sensations on a leather. What name these sensations have? A. The displayed pain B. Relax pain C. Itch D. Hyperalgesia E. An early pain ANSWER: C 60. What name the theory which proves existence in an organism of the person of independent painful receptors has. Specify its correct name. A. The theory of specificity B. The theory of sensitivity C. The theory unspecificity D. The theory of intensity E. The theory gait the control ANSWER: A 61. What name the theory which proves existence in an organism of the person of receptors which answer to both painful and not painful sensations, depending on force irritant has. Specify its correct name. A. The theory of sensitivity B. The theory of intensity C. The theory unspecificity D. The theory of specificity E. The theory gait the control ANSWER: B 62. According to representations about special pain receptors, what is their name? A. free nervous terminations B. body of Mercel C. body of Pacini D. flasks of Crause and of Pacini E. body of Crause ANSWER: A 63. In a medical practice apply local anesthetics is used. Which of the listed mechanisms possibly provides effect of anesthesia? A. Increase in a threshold of depolarizing B. Reduction of duration of potential of rest C. Reduction of duration of potential of action D. Decrease in a critical level depolarizing E. Increase excitility fabrics ANSWER: A 64. Patient 36 years old has disorder of blood supply of inner ear. What artery is injured? A. A. basilaris B. A. temporalis superficialis C. A. cerebri media D. A. cerebri anterior E. A. cerebri posterior ANSWER: A 65. Passenger in the sheep after long trip gets nystagmus. What is level of control of this reaction? A. Medulla oblongata B. Spinal cord C. Cerebellum D. Motor cortex E. Basal ganglia ANSWER: A 66. Passenger in the plane after long trip gets dizziness, pale skin, pulse slows down, nystagmus where revealed. What analyzer system is irritated? A. Vestibular B. Proprioceptive C. Visceral D. Auditory E. Visual ANSWER: A 67. At what level of central nervous system vestibulo-autonomic reactions are carried out? A. Medulla oblongata B. Hypothalamus C. Cerebellum D. Motor cortex E. Basal ganglia ANSWER: B 68. Examinee get application of novocaine to the tip of the tongue. How changes sensation of the tongue? A. Lac of sweet taste B. Lac of salty taste C. Lac of sour taste D. Lac of better taste E. All answers are proper ANSWER: A 69. Patient complains that bright light and loud sounds increase existing pain. What is mechanism? A. Formation of dominant centre in the brain B. Summation of excitation C. Transformation of excitation D. Occlusion in central pathways E. Radiation of excitation ANSWER: B 70. What natural neurotransmitter act like anesthetics? A. Beta-endorphin B. Oxitocine C. Vasopressin D. Calcitonine E. Somatoliberine ANSWER: A 71. Patient gets pain in place of cutting by insect. What is mechanism of pain? A. Revealing of histamine B. Injure of nerve fiber C. Injure of nerve centre D. Revealing of ATP E. Inhibition of pain receptors ANSWER: A 72. How changes taste sensation after blockade of glossopharyngeal nerve? A. Lac of sweet taste B. Lac of better taste C. Lac of sour taste D. Lac of salty taste E. All answers are proper ANSWER: B 73. What kind of sensation is projected to cerebral cortex round the thalamus? A. Vision B. Somatic C. Taste D. Smell E. Hearing ANSWER: D 74. What receptors detect loss of water in the body? A. Baroreceptors at carotid sinus B. Osmoreceptors at diencephalon C. Chemoreceptors at carotid sinus D. Mechanoreceptors in stomach E. Stretch receptors in chewing muscles ANSWER: B 75. What is true about taste receptors: A. Cause hyperpolarisation of neurons B. Located in tongue muscled C. Are nerve endings D. Located in salivatory glands E. Produce impulses to be spreading by trigeminal nerve ANSWER: E 76. What is true about smell receptors: A. Are important for tasting food B. Percept pain sensation C. Are epithelial cells D. Are projected to thalamus E. Belong to proprioreceptors ANSWER: A 77. What area of cerebral cortex in experimental animal was injured to cause smell disorder? A. Cingular gyrus B. Occipital ar C. Prefrontal cortex D. Precentral gyrus E. Temporal gyrus ANSWER: C 78. What analyzer system is not desturbed in patient with thalamic disorder? A. Smell B. Vision C. Hearing D. Proprioceptive E. Taste ANSWER: A 79. Doctor gives anesthesia for performing surgical operation at right arm of the patient. What nerve structure necessary to inhibit? A. Pain receptors B. Peripheral nerves C. Conductive fibers in spinal cord D. Basal ganglia E. Central nociceptive neurons ANSWER: B 80. Experimental animal removes extremity after irritation by high temperature stimulus. What effect this reflex directed to? A. Adaptation to high temperature B. Creation conditioned reflex C. Removing irritant D. Increase heat loss E. Keeping body posture ANSWER: C 81. Experimental animal lose stretch reflex in left lower extremity after giving novocaine subcutaneously around peripheral nerve. What link in reflex arc is disturbed? A. Receptors B. Afferent fibers C. Cortical center D. Spinal ganglion E. Effector organ ANSWER: B 82. Patient 82 years old loose taste sensation because some cortical disorder. What cortical area is desturbed? A. Lower frontal gyrus and corpus callosum B. Uncus and hyppocampus C. Uncus and lower postcentral gyrus D. Angular gyrus and hyppocampus E. Corpus callosum and cingular gyrus ANSWER: C 83. Patient gets application of anesthetic lidokaine to pharynx before undergoing fibrogastroscopy. What effect helps to performing this procedure? A. Inhibition of salivation B. Inhibition of taste sensati C. Inhibition of anti-peristalsis D. Stimulation of chewing reflex E. Anesthesia ANSWER: C 84. Sleeping dog wakes up, when owner closes to his nose piece of sausage. What condition triggers waking up of the dog? A. Chemical structure of substance B. Quantity of receptors in the nose C. Duration of irritation D. Concentration of odorous substance E. Functional condition of receptors ANSWER: D 85. Patient gets demyelinization of entire ascending conductive pathways in spinal cord. What analyzer system function is kept? A. Temperature sensation B. Vestibular analyzer C. Taste sensation D. Proprioceptive sensation E. Vision fuction ANSWER: E 86. Patient gets injure of glossopharingeal nerve. What taste can’t he fill? A. Bitter B. Salty C. Sweet D. Sour E. All kinds ANSWER: A 87. Sportsmen, who in playing chess at final competition, gets increase heartbeat rate till 100 per minute. What is the mechanism on increase heartbeat? A. Increase adrenalin production and decrease tone of n. vagus B. Decrease adrenalin production and increase tone of n. vagus C. Increase adrenalin production and increase tone of n. vagus D. Decrease adrenalin production and decrease tone of n. vagus E. Normal adrenalin production and Normal tone of n. vagus ANSWER: A 88. When performing training task student 18 years old gets increase heartbeat from75 till 95 per minute, arterial pressure rises from 120/80 till 160/95 mm Hg and sweating occurs. What psychical condition causes it possibly? A. Sthenic negative emotion B. First stage of stress C. Asthenic negative emotion D. Neurotic condition E. Positive emotion ANSWER: A 89. New computer program was introduced in office. Director note, that young office workers, who know PC well, master it quickly. But experienced office workers were not glad and told that previous order of work was more usable. What physiological mechanisms may explain such a reaction of office workers? A. Rate of creating new conditioned reflexes depends on age B. Rate of creating new conditioned reflexes depends on working analyzer system C. Rate of creating new unconditioned reflexes depends on age D. Rate of creating new conditioned reflexes depends on experience E. Rate of creating new unconditioned reflexes depends on social conditiones ANSWER: A 90. Mother taking care for her newborn child notes at age of 2-3 his lower interest to communication, but she spends more time with him. At age 4-5 child was asking her a lot about everything, but she was busier then before. A. Analytic activity of the brain rises after 4 year age B. Myelin develops after 3 year age C. Differentiation of nerve cells finish after 5 year age D. Analytic activity of the brain rises because of loss attention from parents E. Speech centers are not formed before 3 year age ANSWER: A 91. Women at age 48 complaints to increase of arterial pressure that occurs at the end of working day. She works as a controller through 12 years. What physiological processes may support this reaction? A. Sitting work B. Work without fresh air C. No communication D. Strained attention E. Work with computer ANSWER: D 92. Boy 11 years old travel to foreign country with his parents for 10-days rest. At forth day of excursions and amusements boy gets weak bewildered and does not like to go and see anything. What is reason of such a reaction of the boy? A. Child is not attentive B. Children have brighter image memory, then adults C. Adults have lower attention then children D. Analyzer systems are more active in children E. Analytic activity is developed better in young age ANSWER: B 93. Persons working at conveyor through 5 years perform their work easier then new workers performing similar operations. What functional peculiarity explains this? A. Automation of skilled movement B. Adapting to new situation C. Training of certain muscles D. Formation of acceptor of the action result E. Formation of social motivation ANSWER: A 94. After long lasting training sportsman get tired. He changes kind of training and his workability was restored. What link of reflex arc gets tired the first? A. Nerve centers B. Afferent link C. Receptors D. Efferent link E. Muscle fibers ANSWER: A 95. Patient 52 years old has headache, dizziness, heard breathing. Anemia was revealed. What plasma protein deficiency causes this? A. Transferin B. Ceruloplasmin C. Albumines D. Gama-globulines E. Fetoprotein ANSWER: A 96. Man after hard physical load gets increase of blood clotting speed. It is caused by increase of value in the blood of: A. Adrenalin B. Thyroid hormone C. Somatotropin D. Thrombomodulin E. Plasmins ANSWER: A 97. Sportsman hard athlete after long period of training gets capability to push load of rather grater mass, than before. What functional status provides such an effect? A. Loss of roof reflex B. Rising of functional reserves in the body C. Decrease of functional reserves in the body D. Development of differential inhibition E. Creation of conditioned reflex ANSWER: B 98. An alpinist is at getting up in mountains which are snow-capped, in sun weather lost the tinted glasses, that resulted in temporal blindness. What is it linked with? A. With disintegration of rodopsyn B. With disintegration of erhythrolab C. With disintegration of chlorolab D. With disintegration of cianolab E. With disintegration of melanin ANSWER: A 99. The patient of 50 years appealed to the doctor with complaints about difficulty of reading of shallow font of newspapers. What lenses did a doctor prescribe glasses with him after an inspection? A. Biconvex collecting lenses which multiply optical force B. Biconvex collecting lenses which diminish optical force C. Biconvex dispersive lenses which multiply optical force D. Biconvex dispersive lenses which diminish optical force E. Cylinder lenses ANSWER: A 100. Researches of mechanisms which provide the processes of memory conducted in experiments on lady-cats through the study of separate processes in neurons. What from these processes did provide memorizing? A. Circulation of excitation for a long time B. Depolarizing of neurons of memory C. Remaining changes of exchange D. Hiperpolarizingof neurons E. Increase of synthesis of nucleic acids ANSWER: A