* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download pharmalogical emergencies
Survey
Document related concepts
5-HT2C receptor agonist wikipedia , lookup
Adherence (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Chlorpromazine wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Atypical antipsychotic wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Antipsychotic wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
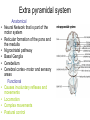
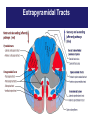
Pharmacological emergencies Jacob Alexander February 2016 TAPPP Range of side effects from commonly prescribed medication • • • • Medication Induced Movement Disorders Serotonergic Syndrome Drug Induced Weight Gain Drug induced dysphoria, negative syndrome like symptoms • Drug related anticholinergic side effects • Drug induced cardiac complication- QTc prolongation Medication Induced Movement Disorders Extra pyramidal system • • • • • • • • • • Anatomical Neural Network that is part of the motor system Reticular formation of the pons and the medulla Nigrostriatal pathway Basal Ganglia Cerebellum Cerebral cortex- motor and sensory areas Functional Causes involuntary reflexes and movements Locomotion Complex movements Postural control Extrapyramidal Tracts Extrapyramidal Tract Extrapyramidal Side Effects (EPSEs) • The first generation (conventional) antipsychotics may cause significant extrapyramidal side effects, more so than the second generation antipsychotic agents. • Risperidone and Ziprasidone more likely to cause EPSEs amongst second generation antipsychotic agents • EPSEs require careful assessment and management Objectives Objectives • Early Identification • Encourage and alleviate anxiety for patient and carers • Be able to explain causes • Be able to explain treatments • Be able to choose/ prescribe treatment options Types of EPSEs • • • • • Dystonia Parkinsonism Akathisia Tardive Dyskinesia Acetylcholine-Dopamine dysregulation syndromes EPSEs time to onset Immediately after use 48 hours from initiation of drug or increase in dose 3 weeks from initiation of drug or increase in dose 6 months or more of use Hypersensitivity reactions Dystonia Parkinsonian symptoms Tardive dyskinesia / dystonia/ akathisia Akathisia Dystonia • Occurs usually within 48 hours of initiation of the medication • Involves bizarre and severe muscle contractions • Can be painful and frightening • Characterized by odd posturing and strange facial expressions Drug-induced Parkinsonism • Usually occurs after 3 or more weeks of treatment • Characterized by: – Cogwheeling rigidity – Tremors – Rhythmic oscillations of the extremities – Pill rolling movement of the fingers Akathisia • Usually occurs after 3 or more weeks of treatment • Subjectively experienced as desire or need to move • Described as feeling like jumping out of the skin • Mild: a vague feeling of apprehension or irritability • Severe: an inability to sit still, resulting in rocking, running, or agitated dancing Tardive Dyskinesia Dyskinesia Tardive • Usually occurs late in the course of longterm treatment • Characterized by abnormal involuntary movements (lip smacking, tongue protrusion, foot tapping) • Often irreversible Complications of Tardive Complications of Tardive Dyskinesia Dyskinesia • • • • • Inability to wear dentures Impaired respirations Weight loss Impaired gait Impaired posture Dopamine-Acetylcholine Imbalance in the Extrapyramidal System • A rare side effect • Characterized by hallucinations, dry mouth, blurred vision, decreased absorption of antipsychotics, decreased gastric motility, tachycardia, and urinary retention • Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome Methods to Improve Assessment of EPSEs • Use rating scales. – AIMS – Simpson Neurological Rating Scale • Videotape the exam for comparison at a later date Treatment Treatment of EPSEs • Titrate dose • Switch to AP less likely to cause extrapyramidal side-effects • Evaluate need for EPSE causing other meds- metaclorpromide, amoxapine, SSRIs • Anticholinergic agents- benztropine, trihexyphenidyl, benadryl • Akathisia- benzodiazepines and beta blockers • • • • http://youtu.be/pSXzuCNlI6Q akathisia http://youtu.be/2krwEbm5hBo dystonia http://youtu.be/_s1lzxHRO4U catatonia http://youtu.be/FUr8ltXh1Pc tardive dyskinesia • http://youtu.be/j86omOwx0Hk parkinsonism Serotonergic Syndrome Drugs implicated in severe serotonin syndrome Drugs Mechanism 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. L-tryptophan SSRIs TCAs MOAIs Pethidine Tramadol LSD Buspirone Amphetamines and anorectics Atypical Antidepressant St John’s wort Lithium Serotonin precursor Inhibits serotonin reuptake Inhibits serotonin reuptake Inhibit Metabolism of 5-HT Serotonin agonist Inhibits serotonin reuptake Partial serotonin agonist Partial serotonin agonist Increased 5_HT release and decreased reuptake 10. Various 11. All of the above? 12. Unknown Clinical features of serotonin syndrome • Cognitive Confusion, agitation, hypomania, hyperactivity, restlessness • Autonomic Hyperthermia, sweating, tachycardia, hypertension, mydriasis, flushing, shivering • Neuromuscular Clonus(spontaneous/inducible/ocular), hyperreflexia, hypertonia, ataxia, tremor Hypertonia and clonus are always symmetrical and are often much more dramatic in the lower limbs Sternbach Criteria • • • • • • • • • • Mental state changes (confusion, hypomania) Agitation Myoclonus Hyperreflexia Diaphoresis Shivering Tremor Diarrhoea Inco-ordination Fever Hunter Serotonin Toxicity Criteria Treatment • Cessation of offending agent • Mild to moderate – resolves spontaneously in 24-72 hours • Supportive care , temperature management, benzodiazepines • In severe cases- cyproheptadine, propranolol, chlorpromazine Dealing with drug induced QTc prolongation QTc <400 ms (men) <470 ms (women) <400 ms (men) <400 ms (men) >500 ms (men or women) No action required, referral to cardiologist based on specific concerns Consider: Dose reduction Medication change Repeat ECG Cardiology referral? Stop suspected causative agent and switch to alternative that is less cardio offensive Refer to cardiologist as a matter of priority Abnormal T Wave Morphology- review treatment: reduce dose, switch to drug of lower effect, cardiologist referral